Spring-session is a very cool new project that aims to provide a simpler way of managing sessions in Java based web applications. One of the features that I explored with spring-session recently was the way it supports externalizing session state without needing to fiddle with the internals of specific web containers like Tomcat or Jetty.
To test spring-session I have used a shopping cart type application(available here) which makes heavy use of session by keeping the items added to the cart as a session attribute, as can be seen from these screenshots:
Consider first a scenario without Spring session. So this is how I have exposed my application:
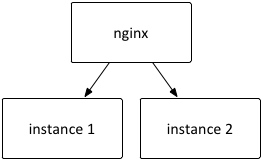
I am using nginx to load balance across two instances of this application. This set-up is very easy to run using Spring boot, I brought up two instances of the app up using two different server ports, this way:
mvn spring-boot:run -Dserver.port=8080
mvn spring-boot:run -Dserver.port=8082
and this is my nginx.conf to load balance across these two instances:
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
upstream sessionApp {
server localhost:8080;
server localhost:8082;
}
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://sessionApp;
}
}
}
I display the port number of the application in the footer just to show which instance is handling the request.
If I were to do nothing to move the state of the session out the application then the behavior of the application would be erratic as the session established on one instance of the application would not be recognized by the other instance - specifically if Tomcat receives a session id it does not recognize then the behavior is to create a new session.
Introducing Spring session into the application
There are container specific ways to introduce a external session stores - One example is here, where Redis is configured as a store for Tomcat. Pivotal Gemfire provides a module to externalize Tomcat's session state.
The advantage of using Spring-session is that there is no dependence on the container at all - maintaining session state becomes an application concern. The instructions on configuring an application to use Spring session is detailed very well at the Spring-session site, just to quickly summarize how I have configured my Spring Boot application, these are first the dependencies that I have pulled in:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.session</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-session</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.session</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-session-data-redis</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId>
<version>1.4.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>2.4.1</version>
</dependency>
and my configuration to use Spring-session for session support, note the Spring Boot specific FilterRegistrationBean which is used to register the session repository filter:
import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.FilterRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.session.data.redis.config.annotation.web.http.EnableRedisHttpSession;
import org.springframework.session.web.http.SessionRepositoryFilter;
import org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Configuration
@EnableRedisHttpSession
public class SessionRepositoryConfig {
@Bean
@Order(value = 0)
public FilterRegistrationBean sessionRepositoryFilterRegistration(SessionRepositoryFilter springSessionRepositoryFilter) {
FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
filterRegistrationBean.setFilter(new DelegatingFilterProxy(springSessionRepositoryFilter));
filterRegistrationBean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/*"));
return filterRegistrationBean;
}
@Bean
public JedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory() {
return new JedisConnectionFactory();
}
}
And that is it! magically now all session is handled by Spring-session, and neatly externalized to Redis.
If I were to retry my previous configuration of using nginx to load balance two different Spring-Boot applications using the common Redis store, the application just works irrespective of the instance handling the request. I look forward to further enhancements to this excellent new project.
The sample application which makes use of Spring-session is available here: https://github.com/bijukunjummen/shopping-cart-cf-app.git。
Reference:
-
Externalizing Session State for a Spring Boot Application Using Spring-Session:https://dzone.com/articles/externalizing-session-state;
-
Spring Session - Spring Boot:http://docs.spring.io/spring-session/docs/current/reference/html5/guides/boot.html;
-
Scaling out with Spring Session:https://blog.jayway.com/2015/05/31/scaling-out-with-spring-session/;
-
利用spring session解决共享Session问题:http://blog.youkuaiyun.com/patrickyoung6625/article/details/45694157;
-
SpringSession原理解析:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000004369392;
-
通过Spring Session实现新一代的Session管理:http://www.infoq.com/cn/articles/Next-Generation-Session-Management-with-Spring-Session.




 本文介绍如何使用Spring Session简化Java Web应用中的会话管理,并通过Redis实现会话状态的外部化,确保负载均衡环境下的一致性。
本文介绍如何使用Spring Session简化Java Web应用中的会话管理,并通过Redis实现会话状态的外部化,确保负载均衡环境下的一致性。

















 6985
6985

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








