迪杰斯特拉算法
不能将迪杰斯特拉算法用于包含负权边的图。可以用贝尔曼-福德算法。
# coding=UTF-8
graph = {}#路径及权重
graph["start"] = {}
graph["start"]["a"] = 6
graph["start"]["b"] = 2
graph["a"] = {}
graph["a"]["fin"] = 1
graph["b"] = {}
graph["b"]["a"] = 3
graph["b"]["fin"] = 5
graph["fin"] = {}
infinity = float("inf") #定义无群大
costs = {}#开销
costs["a"] = 6
costs["b"] = 2
costs["fin"] = infinity
parents = {}#父节点
parents["a"] = "start"
parents["b"] = "start"
parents["fin"] = None
#处理过的节点
processed = []
def find_lowest_cost_node(costs):
lowest_cost = float("inf")
lowest_cost_node = None
for node in costs:
cost = costs[node]
if cost<lowest_cost and node not in processed:
lowest_cost = cost
lowest_cost_node = node
return lowest_cost_node
node = find_lowest_cost_node(costs) #在未处理的节点中找出开销最小的节点
while node is not None:
cost = costs[node]
neighbors = graph[node]
for n in neighbors.keys(): #遍历当前节点的所有邻居
new_cost = cost +neighbors[n]
if costs[n] >new_cost: #如果通过前往该邻居更近
costs[n] = new_cost #更新当前节点的开销
parents[n] = node #将该邻居的父亲节点设置为当前节点
processed.append(node) #将当前节点标记为已经处理过
node = find_lowest_cost_node(costs) #找出接下来要处理的节点
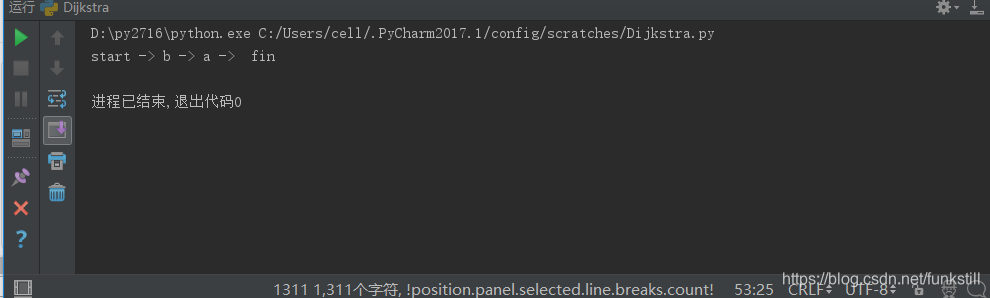
#输出最短路径
temp = "fin"
path = " fin"
while parents[temp]!="start":
path = parents[temp]+" -> "+path
temp = parents[temp]
print "start -> "+path
贪婪算法(近似算法)
简单易行,每步都选择最优解。
# coding=UTF-8
#找出可以覆盖所有州的最少的广播台集合
states_need = set(["mt","wa","or","id","nv","ut","ca","az"])#要覆盖的州
stations = {} #广播电台
stations["kone"] = set(["id","nv","ut"])
stations["ktwo"] = set(["wa","id","mt"])
stations["kthree"] = set(["or","nv","ca"])
stations["kfour"] = set(["nv","ut"])
stations["kfive"] = set(["ca","az"])
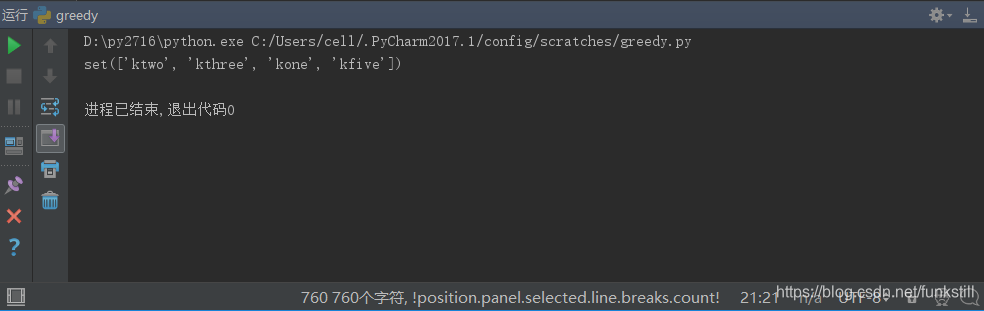
final_stations = set()
while states_need:
best_station = None
states_coverd = set() # 该广播台覆盖的所有未覆盖的州
for station, states_for_station in stations.items():
coverd = states_need & states_for_station # 当前广播站能覆盖的需要覆盖的州
if len(coverd) > len(states_coverd):
best_station = station
states_coverd = coverd
final_stations.add(best_station)
states_need-=states_coverd
print final_stations
NP问题特征
- 元素较少时算法的运行速度非常快,但随着元素数量的增加,速度会变得非常慢。
- 涉及“所有组合”的问题通常是NP完全问题
- 不能将问题分成小问题,必须考虑各种可能的情况。这可能是NP完全问题。
- 如果问题涉及序列(如旅行商问题中的城市序列)且难以解决,它可能就是NP完全问题。
- 如果问题涉及集合(如广播台集合)且难以解决,它可能就是NP完全问题。
- 如果问题可转换为集合覆盖问题或旅行商问题,那它肯定是NP完全问题。





 本文介绍了迪杰斯特拉算法和贝尔曼-福德算法等图算法的应用场景,对比了它们处理带负权边图的能力,并探讨了贪婪算法及NP问题的特点。此外,还通过实例展示了动态规划解决问题的过程。
本文介绍了迪杰斯特拉算法和贝尔曼-福德算法等图算法的应用场景,对比了它们处理带负权边图的能力,并探讨了贪婪算法及NP问题的特点。此外,还通过实例展示了动态规划解决问题的过程。
















 414
414

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








