webpack是现代前端开发中最火的模块打包工具,只需要通过简单的配置,便可以完成模块的加载和打包。那它是怎么做到通过对一些插件的配置,便可以轻松实现对代码的构建呢?
webpack的配置
const path = require('path');
module.exports = {
entry: "./app/entry", // string | object | array
// Webpack打包的入口
output: { // 定义webpack如何输出的选项
path: path.resolve(__dirname, "dist"), // string
// 所有输出文件的目标路径
filename: "[chunkhash].js", // string
// 「入口(entry chunk)」文件命名模版
publicPath: "/assets/", // string
// 构建文件的输出目录
/* 其它高级配置 */
},
module: { // 模块相关配置
rules: [ // 配置模块loaders,解析规则
{
test: /\.jsx?$/, // RegExp | string
include: [ // 和test一样,必须匹配选项
path.resolve(__dirname, "app")
],
exclude: [ // 必不匹配选项(优先级高于test和include)
path.resolve(__dirname, "app/demo-files")
],
loader: "babel-loader", // 模块上下文解析
options: { // loader的可选项
presets: ["es2015"]
},
},
},
resolve: { // 解析模块的可选项
modules: [ // 模块的查找目录
"node_modules",
path.resolve(__dirname, "app")
],
extensions: [".js", ".json", ".jsx", ".css"], // 用到的文件的扩展
alias: { // 模块别名列表
"module": "new-module"
},
},
devtool: "source-map", // enum
// 为浏览器开发者工具添加元数据增强调试
plugins: [ // 附加插件列表
// ...
],
}从上面我们可以看到,webpack配置中需要理解几个核心的概念 Entry 、 Output、 Loaders、 Plugins、 Chunk:
Entry:指定webpack开始构建的入口模块,从该模块开始构建并计算出直接或间接依赖的模块或者库
Output:告诉webpack如何命名输出的文件以及输出的目录
Loaders:由于webpack只能处理javascript,所以我们需要对一些非js文件处理成webpack能够处理的模块,比如sass文件
Plugins:
Loaders将各类型的文件处理成webpack能够处理的模块,plugins有着很强的能力。插件的范围包括,从打包优化和压缩,一直到重新定义环境中的变量。但也是最复杂的一个。比如对js文件进行压缩优化的UglifyJsPlugin插件Chunk:coding split的产物,我们可以对一些代码打包成一个单独的chunk,比如某些公共模块,去重,更好的利用缓存。或者按需加载某些功能模块,优化加载时间。在webpack3及以前我们都利用
CommonsChunkPlugin将一些公共代码分割成一个chunk,实现单独加载。在webpack4 中CommonsChunkPlugin被废弃,使用SplitChunksPlugin
webpack详解
读到这里,或许你对webpack有一个大概的了解,那webpack 是怎么运行的呢?我们都知道,webpack是高度复杂抽象的插件集合,理解webpack的运行机制,对于我们日常定位构建错误以及写一些插件处理构建任务有很大的帮助。
不得不说的tapable
webpack本质上是一种事件流的机制,它的工作流程就是将各个插件串联起来,而实现这一切的核心就是Tapable,webpack中最核心的负责编译的 Compiler和负责创建bundles的 Compilation都是Tapable的实例。在Tapable1.0之前,也就是webpack3及其以前使用的Tapable,提供了包括:
plugin(name:string,handler:function)注册插件到Tapable对象中apply(…pluginInstances:(AnyPlugin|function)[])调用插件的定义,将事件监听器注册到Tapable实例注册表中applyPlugins*(name:string,…)多种策略细致地控制事件的触发,包括applyPluginsAsync、applyPluginsParallel等方法实现对事件触发的控制,实现
(1)多个事件连续顺序执行
(2)并行执行
(3)异步执行
(4)一个接一个地执行插件,前面的输出是后一个插件的输入的瀑布流执行顺序
(5)在允许时停止执行插件,即某个插件返回了一个 undefined的值,即退出执行
我们可以看到,Tapable就像nodejs中 EventEmitter,提供对事件的注册 on和触发 emit,理解它很重要,看个栗子:比如我们来写一个插件
function CustomPlugin() {}
CustomPlugin.prototype.apply = function(compiler) {
compiler.plugin('emit', pluginFunction);
}在webpack的生命周期中会适时的执行:
this.apply*("emit",options)当然上面提到的Tapable都是1.0版本之前的,如果想深入学习,可以查看Tapable和事件流(https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000008060440)。
那1.0的Tapable又是什么样的呢?1.0版本发生了巨大的改变,不再是此前的通过 plugin注册事件,通过 applyPlugins*触发事件调用,那1.0的Tapable是什么呢?
暴露出很多的钩子,可以使用它们为插件创建钩子函数
const {
SyncHook,
SyncBailHook,
SyncWaterfallHook,
SyncLoopHook,
AsyncParallelHook,
AsyncParallelBailHook,
AsyncSeriesHook,
AsyncSeriesBailHook,
AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook
} = require("tapable");我们来看看怎么使用。
class Order {
constructor() {
this.hooks = { //hooks
goods: new SyncHook(['goodsId', 'number']),
consumer: new AsyncParallelHook(['userId', 'orderId'])
}
}
queryGoods(goodsId, number) {
this.hooks.goods.call(goodsId, number);
}
consumerInfoPromise(userId, orderId) {
this.hooks.consumer.promise(userId, orderId).then(() => {
//TODO
})
}
consumerInfoAsync(userId, orderId) {
this.hooks.consumer.callAsync(userId, orderId, (err, data) => {
//TODO
})
}
}对于所有的hook的构造函数均接受一个可选的string类型的数组。
const hook = new SyncHook(["arg1", "arg2", "arg3"]);// 调用tap方法注册一个consument
order.hooks.goods.tap('QueryPlugin', (goodsId, number) => {
return fetchGoods(goodsId, number);
})
// 再添加一个
order.hooks.goods.tap('LoggerPlugin', (goodsId, number) => {
logger(goodsId, number);
})
// 调用
order.queryGoods('10000000', 1)对于一个 SyncHook,我们通过 tap来添加消费者,通过 call来触发钩子的顺序执行。
对于一个非 sync*类型的钩子,即 async*类型的钩子,我们还可以通过其它方式注册消费者和调用
// 注册一个sync 钩子
order.hooks.consumer.tap('LoggerPlugin', (userId, orderId) => {
logger(userId, orderId);
})
order.hooks.consumer.tapAsync('LoginCheckPlugin', (userId, orderId, callback) => {
LoginCheck(userId, callback);
})
order.hooks.consumer.tapPromise('PayPlugin', (userId, orderId) => {
return Promise.resolve();
})
// 调用
// 返回Promise
order.consumerInfoPromise('user007', '1024');
//回调函数
order.consumerInfoAsync('user007', '1024')通过上面的栗子,你可能已经大致了解了 Tapable的用法,它的用法:
插件注册数量
插件注册的类型(sync, async, promise)
调用的方式(sync, async, promise)
实例钩子的时候参数数量
是否使用了
interception
Tapable详解
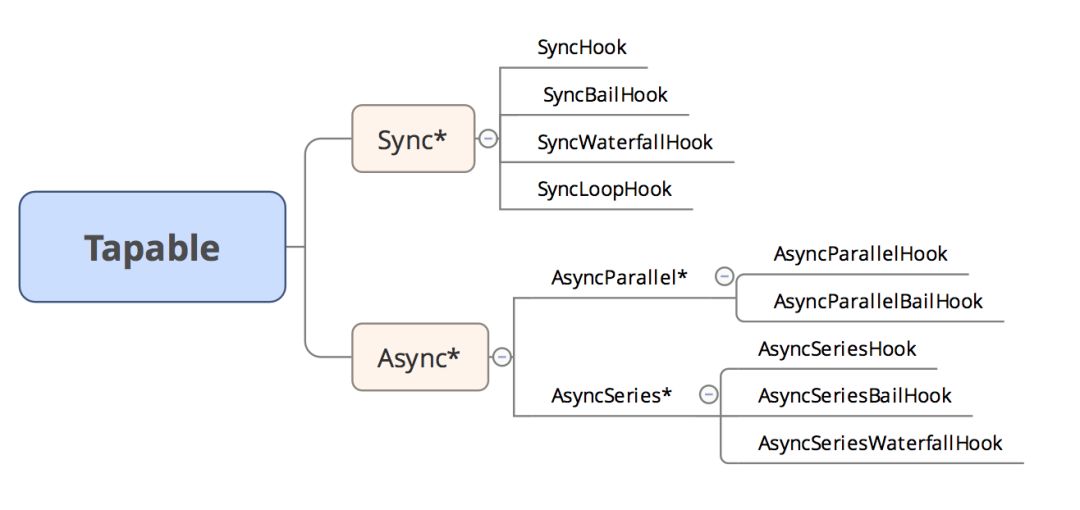
对于 Sync*类型的钩子来说:
注册在该钩子下面的插件的执行顺序都是顺序执行。
只能使用
tap注册,不能使用tapPromise和tapAsync注册
// 所有的钩子都继承于Hook
class Sync* extends Hook {
tapAsync() { // Sync*类型的钩子不支持tapAsync
throw new Error("tapAsync is not supported on a Sync*");
}
tapPromise() {// Sync*类型的钩子不支持tapPromise
throw new Error("tapPromise is not supported on a Sync*");
}
compile(options) { // 编译代码来按照一定的策略执行Plugin
factory.setup(this, options);
return factory.create(options);
}
}对于 Async*类型钩子:支持 tap、 tapPromise、 tapAsync注册。
class AsyncParallelHook extends Hook {
constructor(args) {
super(args);
this.call = this._call = undefined;
}
compile(options) {
factory.setup(this, options);
return factory.create(options);
}
}class Hook {
constructor(args) {
if(!Array.isArray(args)) args = [];
this._args = args; // 实例钩子的时候的string类型的数组
this.taps = []; // 消费者
this.interceptors = []; // interceptors
this.call = this._call = // 以sync类型方式来调用钩子
this._createCompileDelegate("call", "sync");
this.promise =
this._promise = // 以promise方式
this._createCompileDelegate("promise", "promise");
this.callAsync =
this._callAsync = // 以async类型方式来调用
this._createCompileDelegate("callAsync", "async");
this._x = undefined; //
}
_createCall(type) {
return this.compile({
taps: this.taps,
interceptors: this.interceptors,
args: this._args,
type: type
});
}
_createCompileDelegate(name, type) {
const lazyCompileHook = (...args) => {
this[name] = this._createCall(type);
return this[name](...args);
};
return lazyCompileHook;
}
// 调用tap 类型注册
tap(options, fn) {
// ...
options = Object.assign({ type: "sync", fn: fn }, options);
// ...
this._insert(options); // 添加到 this.taps中
}
// 注册 async类型的钩子
tapAsync(options, fn) {
// ...
options = Object.assign({ type: "async", fn: fn }, options);
// ...
this._insert(options); // 添加到 this.taps中
}
注册 promise类型钩子
tapPromise(options, fn) {
// ...
options = Object.assign({ type: "promise", fn: fn }, options);
// ...
this._insert(options); // 添加到 this.taps中
}
}每次都是调用 tap、 tapSync、 tapPromise注册不同类型的插件钩子,通过调用 call、 callAsync 、 promise方式调用。其实调用的时候为了按照一定的执行策略执行,调用 compile方法快速编译出一个方法来执行这些插件。
const factory = new Sync*CodeFactory();
class Sync* extends Hook {
// ...
compile(options) { // 编译代码来按照一定的策略执行Plugin
factory.setup(this, options);
return factory.create(options);
}
}
class Sync*CodeFactory extends HookCodeFactory {
content({ onError, onResult, onDone, rethrowIfPossible }) {
return this.callTapsSeries({
onError: (i, err) => onError(err),
onDone,
rethrowIfPossible
});
}
}compile中调用 HookCodeFactory#create方法编译生成执行代码。
class HookCodeFactory {
constructor(config) {
this.config = config;
this.options = undefined;
}
create(options) {
this.init(options);
switch(this.options.type) {
case "sync": // 编译生成sync, 结果直接返回
return new Function(this.args(),
"\"use strict\";\n" + this.header() + this.content({
// ...
onResult: result => `return ${result};\n`,
// ...
}));
case "async": // async类型, 异步执行,最后将调用插件执行结果来调用callback,
return new Function(this.args({
after: "_callback"
}), "\"use strict\";\n" + this.header() + this.content({
// ...
onResult: result => `_callback(null, ${result});\n`,
onDone: () => "_callback();\n"
}));
case "promise": // 返回promise类型,将结果放在resolve中
// ...
code += "return new Promise((_resolve, _reject) => {\n";
code += "var _sync = true;\n";
code += this.header();
code += this.content({
// ...
onResult: result => `_resolve(${result});\n`,
onDone: () => "_resolve();\n"
});
// ...
return new Function(this.args(), code);
}
}
// callTap 就是执行一些插件,并将结果返回
callTap(tapIndex, { onError, onResult, onDone, rethrowIfPossible }) {
let code = "";
let hasTapCached = false;
// ...
code += `var _fn${tapIndex} = ${this.getTapFn(tapIndex)};\n`;
const tap = this.options.taps[tapIndex];
switch(tap.type) {
case "sync":
// ...
if(onResult) {
code += `var _result${tapIndex} = _fn${tapIndex}(${this.args({
before: tap.context ? "_context" : undefined
})});\n`;
} else {
code += `_fn${tapIndex}(${this.args({
before: tap.context ? "_context" : undefined
})});\n`;
}
if(onResult) { // 结果透传
code += onResult(`_result${tapIndex}`);
}
if(onDone) { // 通知插件执行完毕,可以执行下一个插件
code += onDone();
}
break;
case "async": //异步执行,插件运行完后再将结果通过执行callback透传
let cbCode = "";
if(onResult)
cbCode += `(_err${tapIndex}, _result${tapIndex}) => {\n`;
else
cbCode += `_err${tapIndex} => {\n`;
cbCode += `if(_err${tapIndex}) {\n`;
cbCode += onError(`_err${tapIndex}`);
cbCode += "} else {\n";
if(onResult) {
cbCode += onResult(`_result${tapIndex}`);
}
cbCode += "}\n";
cbCode += "}";
code += `_fn${tapIndex}(${this.args({
before: tap.context ? "_context" : undefined,
after: cbCode //cbCode将结果透传
})});\n`;
break;
case "promise": // _fn${tapIndex} 就是第tapIndex 个插件,它必须是个Promise类型的插件
code += `var _hasResult${tapIndex} = false;\n`;
code += `_fn${tapIndex}(${this.args({
before: tap.context ? "_context" : undefined
})}).then(_result${tapIndex} => {\n`;
code += `_hasResult${tapIndex} = true;\n`;
if(onResult) {
code += onResult(`_result${tapIndex}`);
}
// ...
break;
}
return code;
}
// 按照插件的注册顺序,按照顺序递归调用执行插件
callTapsSeries({ onError, onResult, onDone, rethrowIfPossible }) {
// ...
const firstAsync = this.options.taps.findIndex(t => t.type !== "sync");
const next = i => {
// ...
const done = () => next(i + 1);
// ...
return this.callTap(i, {
// ...
onResult: onResult && ((result) => {
return onResult(i, result, done, doneBreak);
}),
// ...
});
};
return next(0);
}
callTapsLooping({ onError, onDone, rethrowIfPossible }) {
const syncOnly = this.options.taps.every(t => t.type === "sync");
let code = "";
if(!syncOnly) {
code += "var _looper = () => {\n";
code += "var _loopAsync = false;\n";
}
code += "var _loop;\n";
code += "do {\n";
code += "_loop = false;\n";
// ...
code += this.callTapsSeries({
// ...
onResult: (i, result, next, doneBreak) => { // 一旦某个插件返回不为undefined, 即一只调用某个插件执行,如果为undefined,开始调用下一个
let code = "";
code += `if(${result} !== undefined) {\n`;
code += "_loop = true;\n";
if(!syncOnly)
code += "if(_loopAsync) _looper();\n";
code += doneBreak(true);
code += `} else {\n`;
code += next();
code += `}\n`;
return code;
},
// ...
})
code += "} while(_loop);\n";
// ...
return code;
}
// 并行调用插件执行
callTapsParallel({ onError, onResult, onDone, rethrowIfPossible, onTap = (i, run) => run() }) {
// ...
// 遍历注册都所有插件,并调用
for(let i = 0; i < this.options.taps.length; i++) {
// ...
code += "if(_counter <= 0) break;\n";
code += onTap(i, () => this.callTap(i, {
// ...
onResult: onResult && ((result) => {
let code = "";
code += "if(_counter > 0) {\n";
code += onResult(i, result, done, doneBreak);
code += "}\n";
return code;
}),
// ...
}), done, doneBreak);
}
// ...
return code;
}
}在 HookCodeFactory#create中调用到 content方法,此方法将按照此钩子的执行策略,调用不同的方法来执行编译 生成最终的代码。
SyncHook中调用 callTapsSeries编译生成最终执行插件的函数, callTapsSeries做的就是将插件列表中插件按照注册顺序遍历执行。
class SyncHookCodeFactory extends HookCodeFactory {
content({ onError, onResult, onDone, rethrowIfPossible }) {
return this.callTapsSeries({
onError: (i, err) => onError(err),
onDone,
rethrowIfPossible
});
}
}SyncBailHook中当一旦某个返回值结果不为 undefined便结束执行列表中的插件。
class SyncBailHookCodeFactory extends HookCodeFactory {
content({ onError, onResult, onDone, rethrowIfPossible }) {
return this.callTapsSeries({
// ...
onResult: (i, result, next) => `if(${result} !== undefined) {\n${onResult(result)};\n} else {\n${next()}}\n`,
// ...
});
}
}SyncWaterfallHook中上一个插件执行结果当作下一个插件的入参。
class SyncWaterfallHookCodeFactory extends HookCodeFactory {
content({ onError, onResult, onDone, rethrowIfPossible }) {
return this.callTapsSeries({
// ...
onResult: (i, result, next) => {
let code = "";
code += `if(${result} !== undefined) {\n`;
code += `${this._args[0]} = ${result};\n`;
code += `}\n`;
code += next();
return code;
},
onDone: () => onResult(this._args[0]),
});
}
}AsyncParallelHook调用
callTapsParallel并行执行插件
class AsyncParallelHookCodeFactory extends HookCodeFactory {
content({ onError, onDone }) {
return this.callTapsParallel({
onError: (i, err, done, doneBreak) => onError(err) + doneBreak(true),
onDone
});
}
}webpack流程篇
本文关于webpack 的流程讲解是基于webpack4的。
webpack 入口文件
从webpack项目的package.json文件中我们找到了入口执行函数,在函数中引入webpack,那么入口将会是 lib/webpack.js,而如果在shell中执行,那么将会走到 ./bin/webpack.js,我们就以 lib/webpack.js为入口开始吧!
{
"name": "webpack",
"version": "4.1.1",
...
"main": "lib/webpack.js",
"web": "lib/webpack.web.js",
"bin": "./bin/webpack.js",
...
}webpack入口
const webpack = (options, callback) => {
// ...
// 验证options正确性
// 预处理options
options = new WebpackOptionsDefaulter().process(options); // webpack4的默认配置
compiler = new Compiler(options.context); // 实例Compiler
// ...
// 若options.watch === true && callback 则开启watch线程
compiler.watch(watchOptions, callback);
compiler.run(callback);
return compiler;
};webpack 的入口文件其实就实例了 Compiler并调用了 run方法开启了编译,webpack的编译都按照下面的钩子调用顺序执行:
before-run 清除缓存
run 注册缓存数据钩子
before-compile
compile 开始编译
make 从入口分析依赖以及间接依赖模块,创建模块对象
build-module 模块构建
seal 构建结果封装, 不可再更改
after-compile 完成构建,缓存数据
emit 输出到dist目录
编译&构建流程
webpack中负责构建和编译都是 Compilation。
class Compilation extends Tapable {
constructor(compiler) {
super();
this.hooks = {
// hooks
};
// ...
this.compiler = compiler;
// ...
// template
this.mainTemplate = new MainTemplate(this.outputOptions);
this.chunkTemplate = new ChunkTemplate(this.outputOptions);
this.hotUpdateChunkTemplate = new HotUpdateChunkTemplate(
this.outputOptions
);
this.runtimeTemplate = new RuntimeTemplate(
this.outputOptions,
this.requestShortener
);
this.moduleTemplates = {
javascript: new ModuleTemplate(this.runtimeTemplate),
webassembly: new ModuleTemplate(this.runtimeTemplate)
};
// 构建生成的资源
this.chunks = [];
this.chunkGroups = [];
this.modules = [];
this.additionalChunkAssets = [];
this.assets = {};
this.children = [];
// ...
}
//
buildModule(module, optional, origin, dependencies, thisCallback) {
// ...
// 调用module.build方法进行编译代码,build中 其实是利用acorn编译生成AST
this.hooks.buildModule.call(module);
module.build(/**param*/);
}
// 将模块添加到列表中,并编译模块
_addModuleChain(context, dependency, onModule, callback) {
// ...
// moduleFactory.create创建模块,这里会先利用loader处理文件,然后生成模块对象
moduleFactory.create(
{
contextInfo: {
issuer: "",
compiler: this.compiler.name
},
context: context,
dependencies: [dependency]
},
(err, module) => {
const addModuleResult = this.addModule(module);
module = addModuleResult.module;
onModule(module);
dependency.module = module;
// ...
// 调用buildModule编译模块
this.buildModule(module, false, null, null, err => {});
}
});
}
// 添加入口模块,开始编译&构建
addEntry(context, entry, name, callback) {
// ...
this._addModuleChain( // 调用_addModuleChain添加模块
context,
entry,
module => {
this.entries.push(module);
},
// ...
);
}
seal(callback) {
this.hooks.seal.call();
// ...
const chunk = this.addChunk(name);
const entrypoint = new Entrypoint(name);
entrypoint.setRuntimeChunk(chunk);
entrypoint.addOrigin(null, name, preparedEntrypoint.request);
this.namedChunkGroups.set(name, entrypoint);
this.entrypoints.set(name, entrypoint);
this.chunkGroups.push(entrypoint);
GraphHelpers.connectChunkGroupAndChunk(entrypoint, chunk);
GraphHelpers.connectChunkAndModule(chunk, module);
chunk.entryModule = module;
chunk.name = name;
// ...
this.hooks.beforeHash.call();
this.createHash();
this.hooks.afterHash.call();
this.hooks.beforeModuleAssets.call();
this.createModuleAssets();
if (this.hooks.shouldGenerateChunkAssets.call() !== false) {
this.hooks.beforeChunkAssets.call();
this.createChunkAssets();
}
// ...
}
createHash() {
// ...
}
// 生成 assets 资源并 保存到 Compilation.assets 中 给webpack写插件的时候会用到
createModuleAssets() {
for (let i = 0; i < this.modules.length; i++) {
const module = this.modules[i];
if (module.buildInfo.assets) {
for (const assetName of Object.keys(module.buildInfo.assets)) {
const fileName = this.getPath(assetName);
this.assets[fileName] = module.buildInfo.assets[assetName];
this.hooks.moduleAsset.call(module, fileName);
}
}
}
}
createChunkAssets() {
// ...
}
}在webpack make钩子中, tapAsync注册了一个 DllEntryPlugin, 就是将入口模块通过调用 compilation.addEntry方法将所有的入口模块添加到编译构建队列中,开启编译流程。
compiler.hooks.make.tapAsync("DllEntryPlugin", (compilation, callback) => {
compilation.addEntry(
this.context,
new DllEntryDependency(
this.entries.map((e, idx) => {
const dep = new SingleEntryDependency(e);
dep.loc = `${this.name}:${idx}`;
return dep;
}),
this.name
),
// ...
);
});随后在 addEntry 中调用 _addModuleChain开始编译。在 _addModuleChain首先会生成模块,最后构建。
class NormalModuleFactory extends Tapable {
// ...
create(data, callback) {
// ...
this.hooks.beforeResolve.callAsync(
{
contextInfo,
resolveOptions,
context,
request,
dependencies
},
(err, result) => {
if (err) return callback(err);
// Ignored
if (!result) return callback();
// factory 钩子会触发 resolver 钩子执行,而resolver钩子中会利用acorn 处理js生成AST,再利用acorn处理前,会使用loader加载文件
const factory = this.hooks.factory.call(null);
factory(result, (err, module) => {
if (err) return callback(err);
if (module && this.cachePredicate(module)) {
for (const d of dependencies) {
d.__NormalModuleFactoryCache = module;
}
}
callback(null, module);
});
}
);
}
}在编译完成后,调用 compilation.seal方法封闭,生成资源,这些资源保存在 compilation.assets, compilation.chunk, 在给webpack写插件的时候会用到。
class Compiler extends Tapable {
constructor(context) {
super();
this.hooks = {
beforeRun: new AsyncSeriesHook(["compilation"]),
run: new AsyncSeriesHook(["compilation"]),
emit: new AsyncSeriesHook(["compilation"]),
afterEmit: new AsyncSeriesHook(["compilation"]),
compilation: new SyncHook(["compilation", "params"]),
beforeCompile: new AsyncSeriesHook(["params"]),
compile: new SyncHook(["params"]),
make: new AsyncParallelHook(["compilation"]),
afterCompile: new AsyncSeriesHook(["compilation"]),
// other hooks
};
// ...
}
run(callback) {
const startTime = Date.now();
const onCompiled = (err, compilation) => {
// ...
this.emitAssets(compilation, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
if (compilation.hooks.needAdditionalPass.call()) {
compilation.needAdditionalPass = true;
const stats = new Stats(compilation);
stats.startTime = startTime;
stats.endTime = Date.now();
this.hooks.done.callAsync(stats, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
this.hooks.additionalPass.callAsync(err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
this.compile(onCompiled);
});
});
return;
}
// ...
});
};
this.hooks.beforeRun.callAsync(this, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
this.hooks.run.callAsync(this, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
this.readRecords(err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
this.compile(onCompiled);
});
});
});
}
// 输出文件到构建目录
emitAssets(compilation, callback) {
// ...
this.hooks.emit.callAsync(compilation, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
outputPath = compilation.getPath(this.outputPath);
this.outputFileSystem.mkdirp(outputPath, emitFiles);
});
}
newCompilationParams() {
const params = {
normalModuleFactory: this.createNormalModuleFactory(),
contextModuleFactory: this.createContextModuleFactory(),
compilationDependencies: new Set()
};
return params;
}
compile(callback) {
const params = this.newCompilationParams();
this.hooks.beforeCompile.callAsync(params, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
this.hooks.compile.call(params);
const compilation = this.newCompilation(params);
this.hooks.make.callAsync(compilation, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
compilation.finish();
// make 钩子执行后,调用seal生成资源
compilation.seal(err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
this.hooks.afterCompile.callAsync(compilation, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
// emit, 生成最终文件
return callback(null, compilation);
});
});
});
});
}
}最后输出
在 seal执行后,便会调用 emit钩子,根据webpack config文件的output配置的path属性,将文件输出到指定的path.





















 5627
5627

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








