查询
练习脚本
--建立价格区间表
create table t_pricetable
(
id number primary key,
price number(10,2),
ownertypeid number,
minnum number,
maxnum number
);
--业主类型
create table t_ownertype
(
id number primary key,
name varchar2(30)
);
--业主表
create table t_owners
(
id number primary key,
name varchar2(30),
addressid number,
housenumber varchar2(30),
watermeter varchar2(30),
adddate date,
ownertypeid number
);
--区域表
create table t_area
(
id number,
name varchar2(30)
);
--收费员表
create table t_operator
(
id number,
name varchar2(30)
);
--地址表
create table t_address
(
id number primary key,
name varchar2(100),
areaid number,
operatorid number
);
--账务表
create table t_account
(
id number primary key,
owneruuid number,
ownertype number,
areaid number,
year char(4),
month char(2),
num0 number,
num1 number,
usenum number,
meteruser number,
meterdate date,
money number(10,2),
isfee char(1),
feedate date,
feeuser number
);
create sequence seq_account;
--业主类型
insert into t_ownertype values(1,'居民');
insert into t_ownertype values(2,'行政事业单位');
insert into t_ownertype values(3,'商业');
--地址信息--
insert into t_address values( 1,'明兴花园',1,1);
insert into t_address values( 2,'鑫源秋墅',1,1);
insert into t_address values( 3,'华龙苑南里小区',2,2);
insert into t_address values( 4,'河畔花园',2,2);
insert into t_address values( 5,'霍营',2,2);
insert into t_address values( 6,'回龙观东大街',3,2);
insert into t_address values( 7,'西二旗',3,2);
--业主信息
insert into t_owners values(1,'范冰',1,'1-1','30406',to_date('2015-04-12','yyyy-MM-dd'),1 );
insert into t_owners values(2,'王强',1,'1-2','30407',to_date('2015-02-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),1 );
insert into t_owners values(3,'马腾',1,'1-3','30408',to_date('2015-03-18','yyyy-MM-dd'),1 );
insert into t_owners values(4,'林小玲',2,'2-4','30409',to_date('2015-06-15','yyyy-MM-dd'),1 );
insert into t_owners values(5,'刘华',2,'2-5','30410',to_date('2013-09-11','yyyy-MM-dd'),1 );
insert into t_owners values(6,'刘东',2,'2-2','30411',to_date('2014-09-11','yyyy-MM-dd'),1 );
insert into t_owners values(7,'周健',3,'2-5','30433',to_date('2016-09-11','yyyy-MM-dd'),1 );
insert into t_owners values(8,'张哲',4,'2-2','30455',to_date('2016-09-11','yyyy-MM-dd'),1 );
insert into t_owners values(9,'昌平区中西医结合医院',5,'2-2','30422',to_date('2016-10-11','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_owners values(10,'美廉美超市',5,'4-2','30423',to_date('2016-10-12','yyyy-MM-dd'),3 );
--操作员
insert into t_operator values(1,'马小云');
insert into t_operator values(2,'李翠花');
--地区--
insert into t_area values(1,'海淀');
insert into t_area values(2,'昌平');
insert into t_area values(3,'西城');
insert into t_area values(4,'东城');
insert into t_area values(5,'朝阳');
insert into t_area values(6,'玄武');
--价格表--
insert into t_pricetable values(1,2.45,1,0,5);
insert into t_pricetable values(2,3.45,1,5,10);
insert into t_pricetable values(3,4.45,1,10,null);
insert into t_pricetable values(4,3.87,2,0,5);
insert into t_pricetable values(5,4.87,2,5,10);
insert into t_pricetable values(6,5.87,2,10,null);
insert into t_pricetable values(7,4.36,3,0,5);
insert into t_pricetable values(8,5.36,3,5,10);
insert into t_pricetable values(9,6.36,3,10,null);
--账务表--
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,1,1,1,'2012','01',30203,50123,0,1,sysdate,34.51,'1',to_date('2012-02-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,1,1,1,'2012','02',50123,60303,0,1,sysdate,23.43,'1',to_date('2012-03-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,1,1,1,'2012','03',60303,74111,0,1,sysdate,45.34,'1',to_date('2012-04-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,1,1,1,'2012','04',74111,77012,0,1,sysdate,52.54,'1',to_date('2012-05-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,1,1,1,'2012','05',77012,79031,0,1,sysdate,54.66,'1',to_date('2012-06-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,1,1,1,'2012','06',79031,80201,0,1,sysdate,76.45,'1',to_date('2012-07-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,1,1,1,'2012','07',80201,88331,0,1,sysdate,65.65,'1',to_date('2012-08-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,1,1,1,'2012','08',88331,89123,0,1,sysdate,55.67,'1',to_date('2012-09-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,1,1,1,'2012','09',89123,90122,0,1,sysdate,112.54,'1',to_date('2012-10-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,1,1,1,'2012','10',90122,93911,0,1,sysdate,76.21,'1',to_date('2012-11-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,1,1,1,'2012','11',93911,95012,0,1,sysdate,76.25,'1',to_date('2012-12-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,1,1,1,'2012','12',95012,99081,0,1,sysdate,44.51,'1',to_date('2013-01-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,2,1,3,'2012','01',30334,50433,0,1,sysdate,34.51,'1',to_date('2013-02-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,2,1,3,'2012','02',50433,60765,0,1,sysdate,23.43,'1',to_date('2013-03-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,2,1,3,'2012','03',60765,74155,0,1,sysdate,45.34,'1',to_date('2013-04-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,2,1,3,'2012','04',74155,77099,0,1,sysdate,52.54,'1',to_date('2013-05-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,2,1,3,'2012','05',77099,79076,0,1,sysdate,54.66,'1',to_date('2013-06-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,2,1,3,'2012','06',79076,80287,0,1,sysdate,76.45,'1',to_date('2013-07-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,2,1,3,'2012','07',80287,88432,0,1,sysdate,65.65,'1',to_date('2013-08-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,2,1,3,'2012','08',88432,89765,0,1,sysdate,55.67,'1',to_date('2013-09-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,2,1,3,'2012','09',89765,90567,0,1,sysdate,112.54,'1',to_date('2013-10-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,2,1,3,'2012','10',90567,93932,0,1,sysdate,76.21,'1',to_date('2013-11-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,2,1,3,'2012','11',93932,95076,0,1,sysdate,76.25,'1',to_date('2013-12-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,2,1,3,'2012','12',95076,99324,0,1,sysdate,44.51,'1',to_date('2014-01-14','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,100,1,3,'2012','12',95076,99324,0,1,sysdate,44.51,'1',to_date('2014-01-01','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
insert into t_account values( seq_account.nextval,101,1,3,'2012','12',95076,99324,0,1,sysdate,44.51,'1',to_date('2015-01-01','yyyy-MM-dd'),2 );
update t_account set usenum=num1-num0;
update t_account set money=usenum*2.45;
commit;
一、单表查询
(一)简单条件查询
1、精确查询
需求:查询水表编号为 30408 的业主记录
select
*
from
T_OWNERS
where
watermeter='30408'
2、模糊查询
需求:查询业主名称包含“刘”的业主记录
select
*
from
t_owners
where
name like '%刘%'
3、and 运算符
需求:查询业主名称包含“刘”的并且门牌号包含 5 的业主记录
select
*
from
t_owners
where
name like '%刘%'
and housenumber like '%5%'
4、or 运算符
需求:查询业主名称包含“刘”的或者门牌号包含 5 的业主记录
select
*
from
t_owners
where
name like '%刘%'
or housenumber like '%5%'
5、and 与 or 运算符混合使用
需求:查询业主名称包含“刘”的或者门牌号包含 5 的业主记录,并且地址编号 为 3 的记录。
select
*
from
t_owners
where
(name like '%刘%' or housenumber like '%5%')
and addressid=3
因为 and 的优先级比 or 大,所以我们需要用 ( ) 来改变优先级。
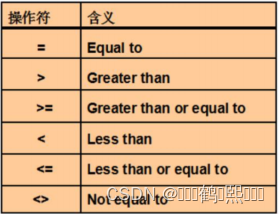
6、 范围查询
需求:查询台账记录中用水字数大于等于 10000,并且小于等于 20000 的记录 我们可以用>= 和<=来实现,语句
select
*
from
T_ACCOUNT
where
usenum>=10000
and usenum<=20000
select
*
from
T_ACCOUNT
where
usenum between 10000 and 20000
7、空值查询
需求:查询 T_PRICETABLE 表中 MAXNUM 为空的记录
select
*
from
T_PRICETABLE
where
maxnum is null
需求:查询 T_PRICETABLE 表中 MAXNUM 不为空的记录
select
*
from
T_PRICETABLE
where
maxnum is not null
(二)去掉重复记录
需求:查询业主表中的地址 ID,不重复显示
select
distinct addressid
from T_OWNERS
(三)排序查询
1、升序排序
需求:对 T_ACCOUNT 表按使用量进行升序排序
select
*
from
T_ACCOUNT
order by usenum
2、降序排序
select
*
from
T_ACCOUNT
order by usenum desc
(四)基于伪列的查询(ROWID、ROWNUM)
在 Oracle 的表的使用过程中,实际表中还有一些附加的列,称为伪列。
伪列就 像表中的列一样,但是在表中并不存储。
伪列只能查询,不能进行增删改操作。 接下来学习两个伪列:ROWID 和 ROWNUM。
1、ROWID
表中的每一行在数据文件中都有一个物理地址,ROWID 伪列返回的就是该行的 物理地址。使用 ROWID 可以快速的定位表中的某一行。ROWID 值可以唯一的 标识表中的一行。由于 ROWID 返回的是该行的物理地址,因此使用 ROWID 可 以显示行是如何存储的。
select
rowID,t.*
from
T_AREA t
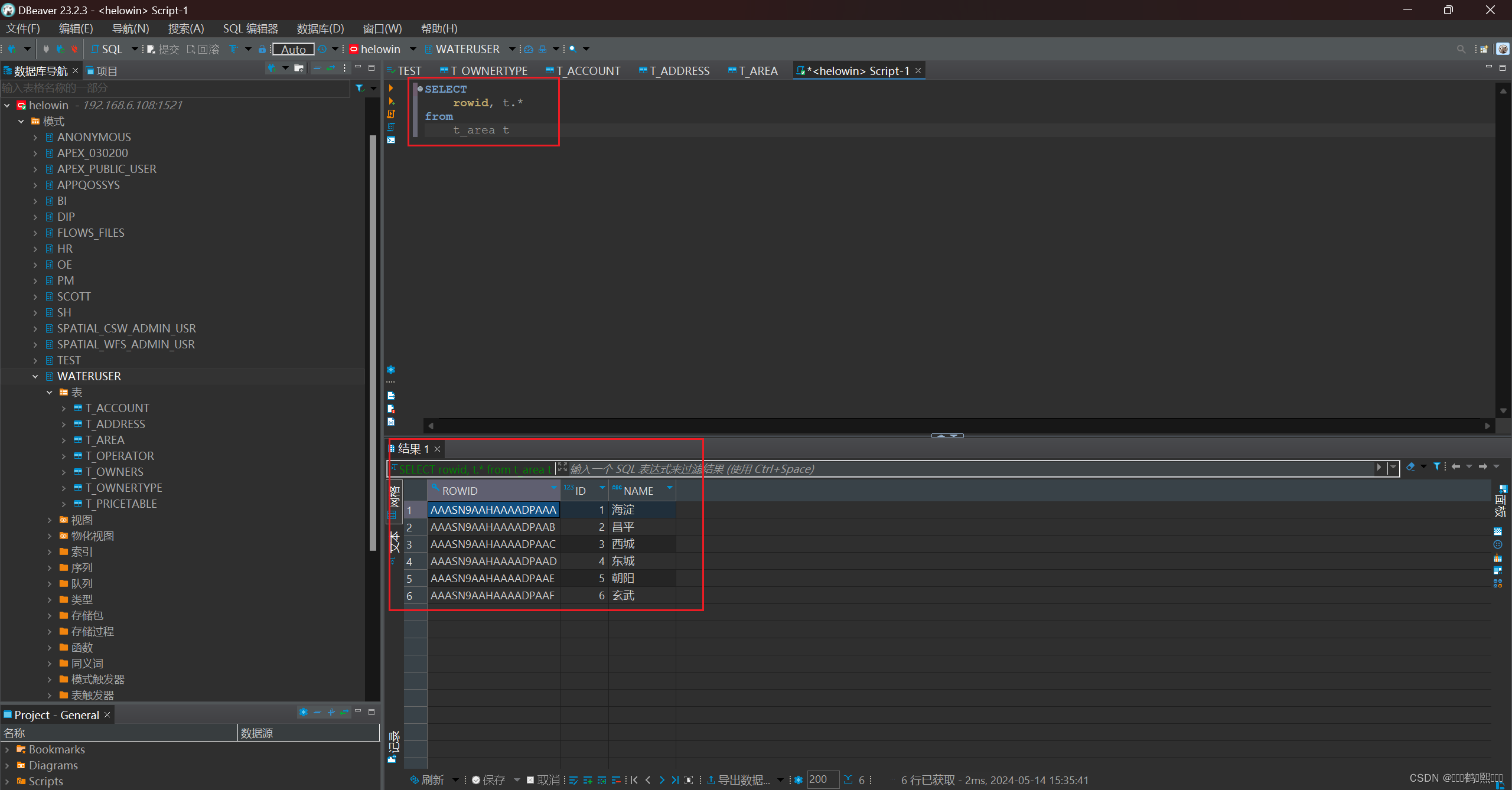
可以通过指定 ROWID 来查询记录
select
rowID,t.*
from
T_AREA t
where
ROWID='AAAM1uAAGAAAAD8AAC';
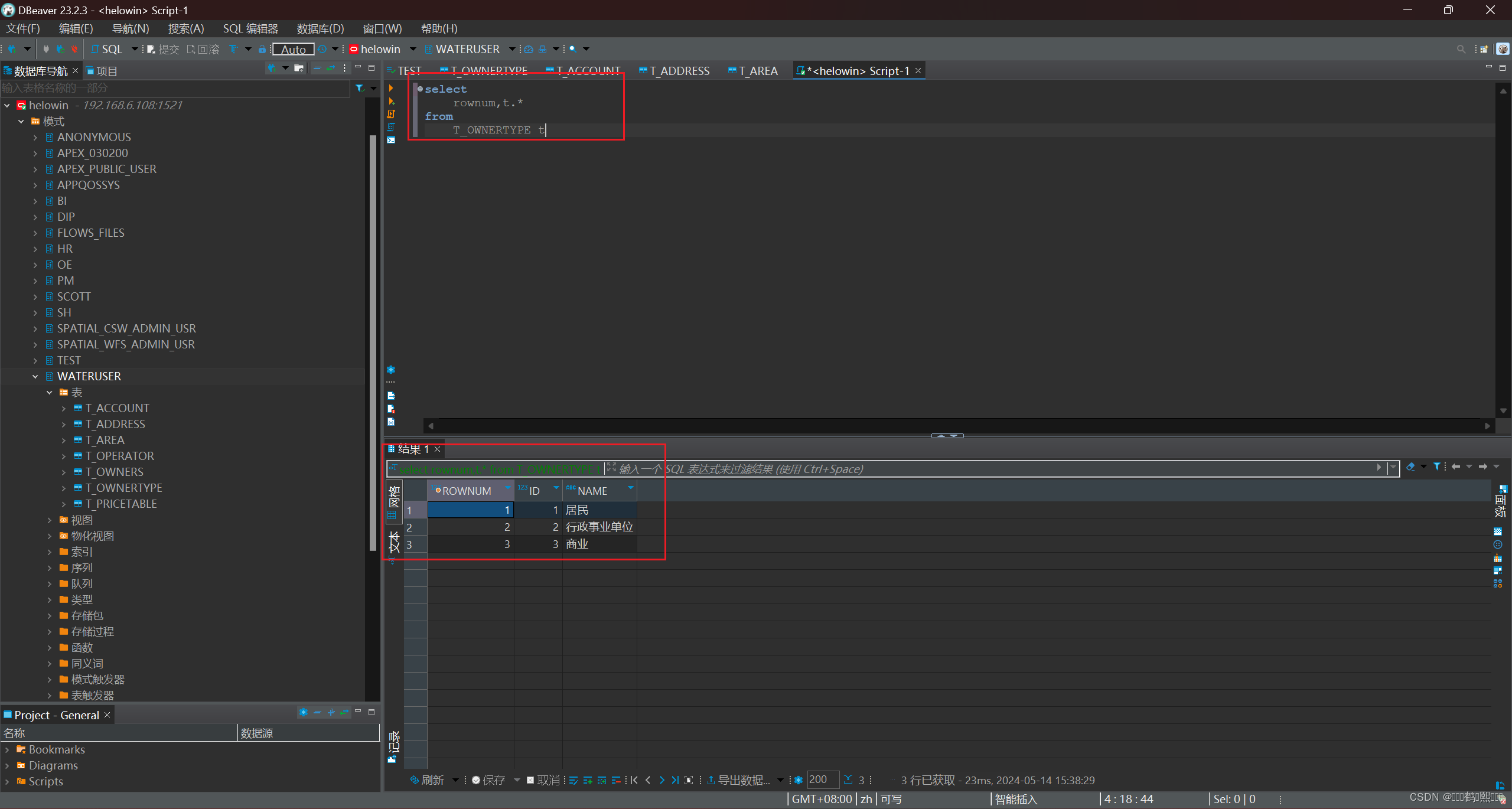
2、ROWNUM
在查询的结果集中,ROWNUM 为结果集中每一行标识一个行号,第一行返回 1, 第二行返回 2,以此类推。通过 ROWNUM 伪列可以限制查询结果集中返回的行数。
select
rownum,t.*
from
T_OWNERTYPE t
(五)聚合统计
ORACLE 的聚合统计是通过分组函数来实现的,与 MYSQL 一致。
1、聚合函数
(1)求和 sum
需求:统计 2012 年所有用户的用水量总和
select
sum(usenum)
from
t_account
where
year='2012'
(2)求平均 avg
需求:统计 2012 年所有用水量(字数)的平均值
select
avg(usenum)
from
T_ACCOUNT
where
year='2012'
(3)求最大值 max
需求:统计 2012 年最高用水量(字数)
select
max(usenum)
from
T_ACCOUNT
where
year='2012'
(4)求最小值 min
需求:统计 2012 年最低用水量(字数)
select
min(usenum)
from
T_ACCOUNT
where
year='2012'
(5)统计记录个数 count
需求:统计业主类型 ID 为 1 的业主数量
select
count(*)
from
T_OWNERS
where ownertypeid=1
2、分组聚合 group by
需求:按区域分组统计水费合计数
select
areaid,sum(money)
from
t_account
group by areaid
3、分组后条件查询 having
需求:查询水费合计大于 16900 的区域及水费合计
select
areaid,sum(money)
from
t_account
group by
areaid
having
sum(money)>169000
二、连表查询
(一)多表内连接查询
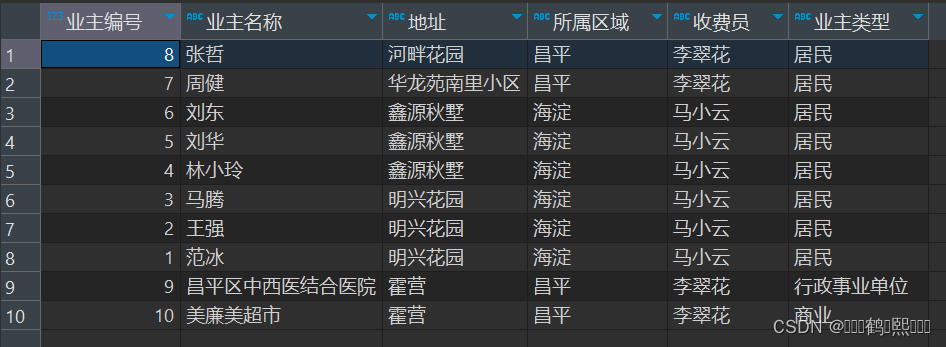
(1)需求:查询显示业主编号,业主名称,业主类型名称,如下图:
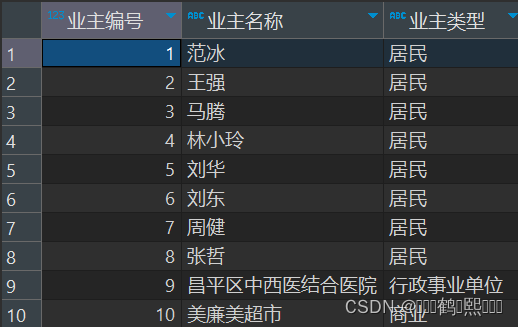
select
o.id 业主编号,
o.name 业主名称,
ot.name 业主类型
from
T_OWNERS o,
T_OWNERTYPE ot
where o.ownertypeid=ot.id
(2)需求:查询显示业主编号,业主名称、地址和业主类型,如下图
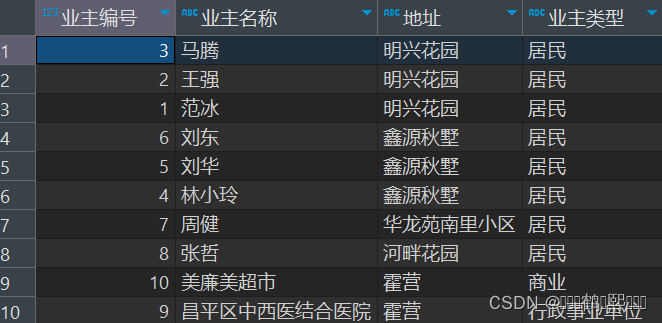
select
o.id 业主编号,
o.name 业主名称,
ad.name 地址,
ot.name 业主类型
from
T_OWNERS o,
T_OWNERTYPE ot,
T_ADDRESS ad
where o.ownertypeid=ot.id and o.addressid=ad.id
(3)需求:查询显示业主编号、业主名称、地址、所属区域、业主分类,如下 图:
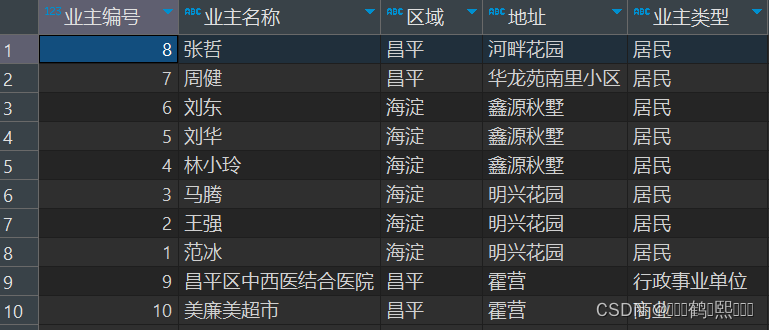
SELECT
o.ID 业主编号,
o.NAME 业主名称,
ar.NAME 区域,
ad.NAME 地址,
ot.NAME 业主类型
FROM
T_OWNERS o,
T_OWNERTYPE ot,
T_ADDRESS ad,
T_AREA ar
WHERE
o.OWNERTYPEID = ot.ID
AND o.ADDRESSID = ad.ID
AND ad.AREAID = ar.ID
(4)需求:查询显示业主编号、业主名称、地址、所属区域、收费员、业主分 类,如下图:
select
ow.id 业主编号,
ow.name 业主名称,
ad.name 地址,
ar.name 所属区域,
op.name 收费员,
ot.name 业主类型
from
T_OWNERS ow,
T_OWNERTYPE ot,
T_ADDRESS ad,
T_AREA ar,
T_OPERATOR op
where
ow.ownertypeid = ot.id
and ow.addressid = ad.id
and ad.areaid = ar.id
and ad.operatorid = op.id
(二)左外连接查询
需求:查询业主的账务记录,显示业主编号、名称、年、月、金额。如果此业主 没有账务记录也要列出姓名。
SELECT
ow.id,
ow.name,
ac.year,
ac.month,
ac.money
FROM
T_OWNERS ow
left join T_ACCOUNT ac on ow.id=ac.owneruuid
或
SELECT
ow.id,
ow.name,
ac.year,
ac.month,
ac.money
FROM
T_OWNERS ow,
T_ACCOUNT ac
WHERE ow.id=ac.owneruuid(+)
(三)右外连接查询
跟左外连接查询相反
三、子查询
(一)where子句中的子查询
1、单行子查询
1、只返回一条记录
2、单行操作符
需求:查询 2012 年 1 月用水量大于平均值的台账记录
select
*
from
T_ACCOUNT
where
year='2012'
and month='01'
and usenum > (
select avg(usenum) from T_ACCOUNT where year='2012' and month='01'
)
2、多行子查询
1、返回了多条记录
2、多行操作符
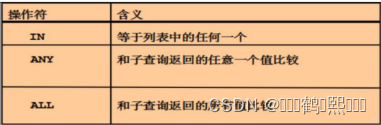
使用in运算符
(1)需求:查询地址编号为 1 、3、4 的业主记录
select
*
from
T_OWNERS
where
addressid in ( 1,3,4 )
(2)需求:查询地址含有“花园”的业主的信息
select
*
from
T_OWNERS
where
addressid in (
select id from t_address where name like '%花园%'
)
(二)from子句中的子查询
from 子句的子查询为多行子查询
需求:查询显示业主编号,业主名称,业主类型名称,条件为业主类型为”居民”, 使用子查询实现。
select
*
from
(
select
o.id 业主编号,
o.name 业主名称,
ot.name 业主类型
from
T_OWNERS o,
T_OWNERTYPE ot
where
o.ownertypeid=ot.id
)
where
业主类型='居民'
(三)select 子句中的子查询
select 子句的子查询必须为单行子查询
(1)需求:列出业主信息,包括 ID,名称,所属地址。
select
id,
name,
(select name from t_address where id=addressid) addressname
from
t_owners
(2)需求:列出业主信息,包括 ID,名称,所属地址,所属区域。
select
id,
name,
( select name from t_address where id=addressid ) addressname,
( select (select name from t_area where id=areaid ) from t_address where id=addressid ) adrename
from
t_owners;
四、分页查询
(一)简单分页
需求:分页查询台账表 T_ACCOUNT,每页 10 条记录
select
rownum,
t.*
from
T_ACCOUNT t
where
rownum<=10
显示第 11 条到第 20 条的记录
因为where执行>10的时候,rownum还没到10,所以要先把20条以内的数据查找出来,再截取10~20条的数据
select
*
from
(
select
rownum r,
t.*
from
T_ACCOUNT t
where
rownum<=20
)
where r>10
(二)基于排序的分页
需求:分页查询台账表 T_ACCOUNT,每页 10 条记录,按使用字数降序排序。
select
*
from
(
select
rownum r,
t.*
from '
(select * from T_ACCOUNT order by usenum desc) t
where
rownum <= 20
)
where
r>10
五、单行函数
六、行列转换
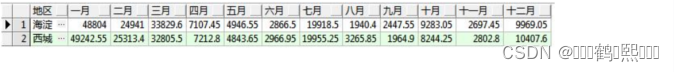
需求:按月份统计 2012 年各个地区的水费,如下图
select
(select name from T_AREA where id= areaid ) 区域,
sum( case when month='01' then money else 0 end) 一月,
sum( case when month='02' then money else 0 end) 二月,
sum( case when month='03' then money else 0 end) 三月,
sum( case when month='04' then money else 0 end) 四月,
sum( case when month='05' then money else 0 end) 五月,
sum( case when month='06' then money else 0 end) 六月,
sum( case when month='07' then money else 0 end) 七月,
sum( case when month='08' then money else 0 end) 八月,
sum( case when month='09' then money else 0 end) 九月,
sum( case when month='10' then money else 0 end) 十月,
sum( case when month='11' then money else 0 end) 十一月,
sum( case when month='12' then money else 0 end) 十二月
from
T_ACCOUNT
where
year='2012'
group by areaid
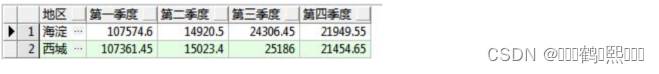
需求:按季度统计 2012 年各个地区的水费,如下图
select
(select name from T_AREA where id= areaid ) 区域,
sum( case when month>='01' and month<='03' then money else 0 end) 第一季度,
sum( case when month>='04' and month<='06' then money else 0 end) 第二季度,
sum( case when month>='07' and month<='09' then money else 0 end) 第三季度,
sum( case when month>='10' and month<='12' then money else 0 end) 第四季度
from
T_ACCOUNT
where
year='2012'
group by areaid
七、分析函数
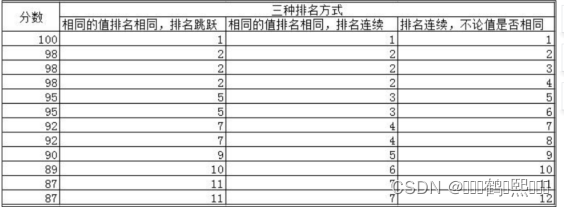
以下三个分析函数可以用于排名使用。
下图为三种排名方式的举例
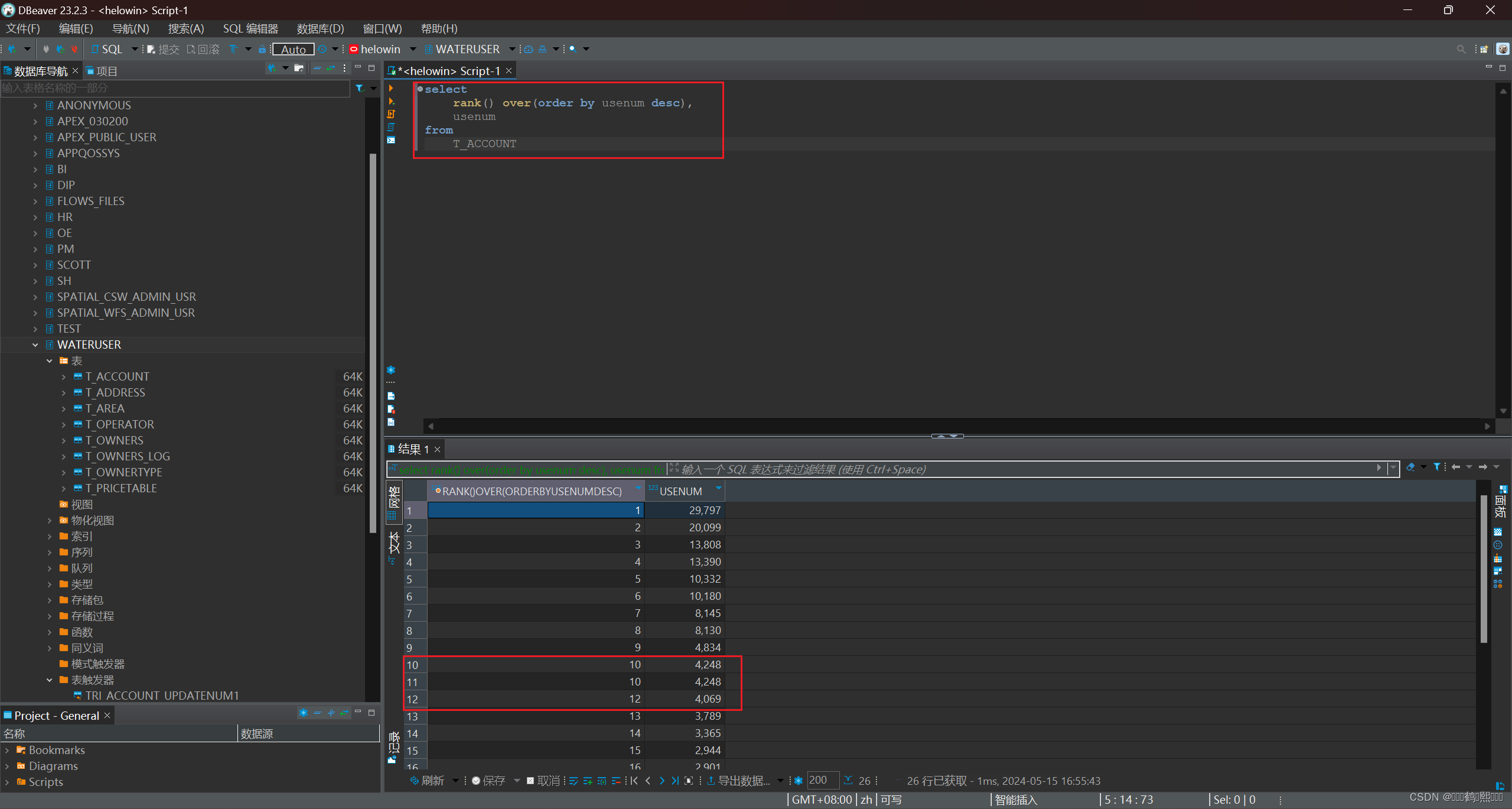
(1)RANK 相同的值排名相同,排名跳跃
需求:对 T_ACCOUNT 表的 usenum 字段进行排序,相同的值排名相同,排名跳跃
select
rank() over(order by usenum desc),
usenum
from
T_ACCOUNT
(2)DENSE_RANK 相同的值排名相同,排名连续
需求:对 T_ACCOUNT 表的 usenum 字段进行排序,相同的值排名相同,排名连续
select
dense_rank() over(order by usenum desc),
usenum
from
T_ACCOUNT
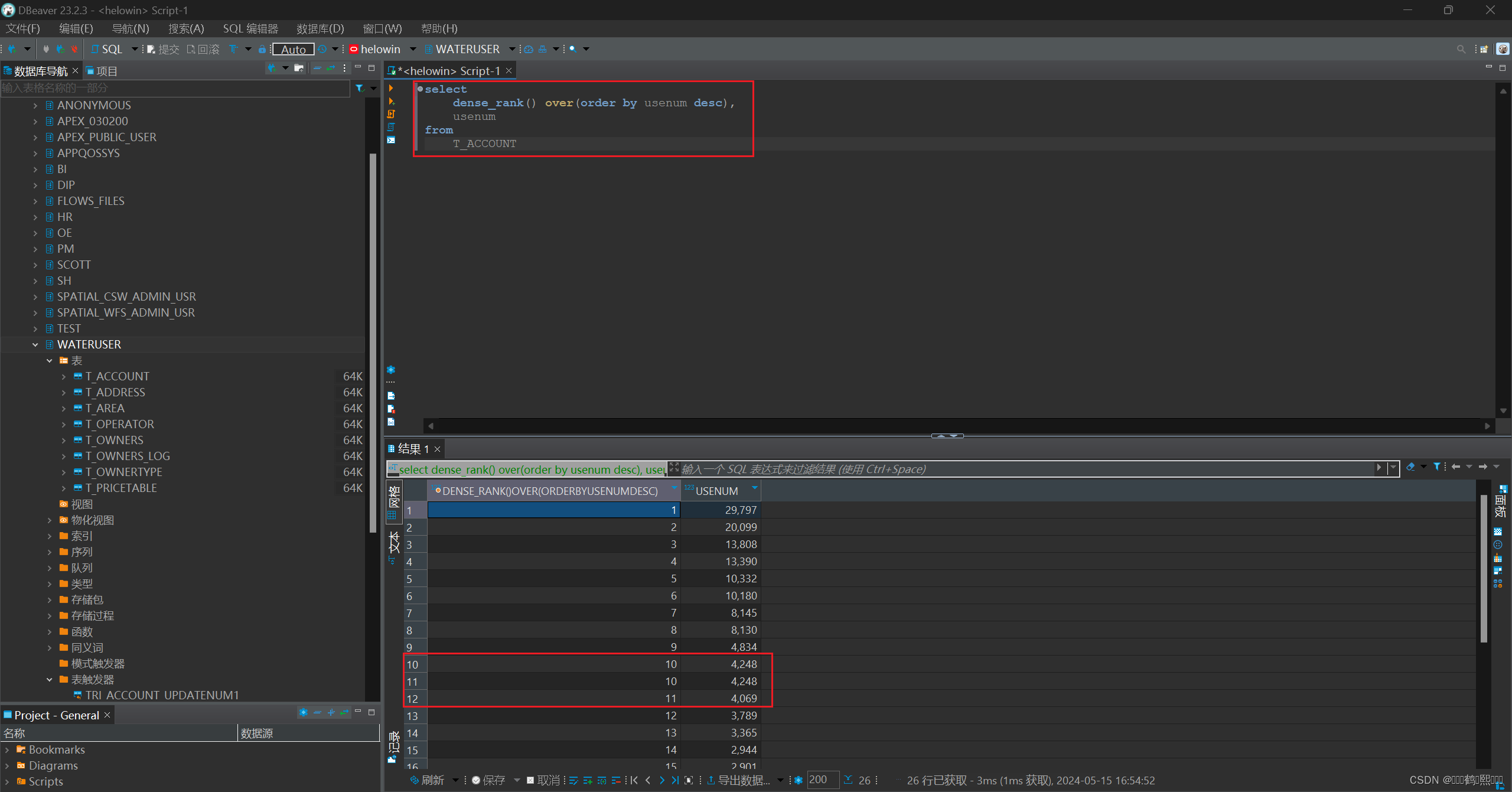
(3)ROW_NUMBER 返回连续的排名,无论值是否相等
需求:对 T_ACCOUNT 表的 usenum 字段进行排序,返回连续的排名,无论值是 否相等
select
row_number() over(order by usenum desc),
usenum
from
T_ACCOUNT
用 row_number()分析函数实现的分页查询相对三层嵌套子查询要简单的多:
select
*
from
(
select
row_number() over(order by usenum desc) rownumber,
usenum
from
T_ACCOUNT
)
where
rownumber>10
and rownumber<=20
八、集合运算
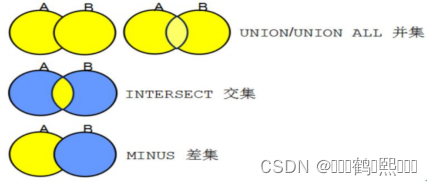
(一)什么是集合运算
集合运算,集合运算就是将两个或者多个结果集组合成为一个结果集。集合运算 包括:
1、UNION ALL(并集),返回各个查询的所有记录,包括重复记录。
2、UNION(并集),返回各个查询的所有记录,不包括重复记录。
3、INTERSECT(交集),返回两个查询共有的记录。
4、MINUS(差集),返回第一个查询检索出的记录减去第二个查询检索出的记录之 后剩余的记录。
(二)并集运算
UNION ALL 不去掉重复记录
select * from t_owners where id<=7
union all
select * from t_owners where id>=5
UNION 去掉重复记录
select * from t_owners where id<=7
union
select * from t_owners where id>=5
(三)交集运算
select * from t_owners where id<=7
intersect
select * from t_owners where id>=5
(四)差集运算
select * from t_owners where id<=7
minus
select * from t_owners where id>=5
可以用minus 运算符来实现分页
select rownum,t.* from T_ACCOUNT t where rownum<=20
minus
select rownum,t.* from T_ACCOUNT t where rownum<=10
PLSQL
一、PL/SQL
(一)什么是PL/SQL
PL/SQL(Procedure Language/SQL) 是 Oracle对SQL语言的过程化扩展,指在SQL命令语言中增加了过程处理语句(如分支、循环等),使SQL语言具有过程处理能力。把SQL语言的数据操纵能力与过程语言的数据处理能力结合起来,使得PLSQL面向过程但比过程语言简单、高效、灵活和实用。
基本语法
[declare
-- 声明变量
]
begin
-- 逻辑代码
[exception
-- 异常处理
]
end;
(二)变量
声明变量的语法:
变量名 类型(长度)
变量赋值的语法:
变量名:=变量值
变量的声明
需求:
声明变量水费单价、水费字数、吨数、金额。
对水费单价、字数进行赋值。吨数根据水费字数换算,规则为水费字数除以1000,并且四舍五入,保留两位小数。计算金额,金额=单价*吨数。
输出单价、数量和金额。
declare
v_price number(10, 2); --单价
v_usenum number; --水费字数
v_usenum2 number(10, 2); --吨数
v_money number(10, 2); --金额
begin
v_price:=2.45; --单价赋值
v_usenum:=9213; --水费字数
v_usenum2:=round(v_usenum/1000, 2); --吨数
v_money:=v_price*v_usenum2; --金额
DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line('金额'||v_money);
end;
select into 方式 赋值
注意:结果必须是一条记录,有多条记录和没有记录都会报错。
select 列名 into 变量名 from 表名 where 条件
declare
v_price number(10, 2); --单价
v_usenum number; --水费字数
v_usenum2 number(10, 2); --吨数
v_money number(10, 2); --金额
v_num0 number; --上月水表数
v_num1 number; --本月水表数
begin
v_price:=2.45; --单价赋值
--v_usenum:=9213; --水费字数
select usenum,num0,num1 into v_usenum,v_num0,v_num1 from t_account where year='2012' and month='01' and owneruuid=1;
v_usenum2:=round(v_usenum/1000, 2); --吨数
v_money:=v_price*v_usenum2; --金额
DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line('水费字数:'||v_usenum'金额:' ||v_money);
end;
(三)属性类型
引用型(不确定数据类型,但是知道一定是从表中的列提取出来的)
表名.列名%type
declare
v_price number(10, 2); --单价
v_usenum t_account.usenum%type; --水费字数
v_usenum2 number(10, 2); --吨数
v_money number(10, 2); --金额
v_num0 t_account.num0%type; --上月水表数
v_num1 t_account.num1%type; --本月水表数
begin
v_price:=2.45; --单价赋值
-- 从数据库中提取
select usenum,num0,num1 into v_usenum,v_num0,v_num1 from t_account where year='2012' and month='01' and owneruuid=1;
v_usenum2:=round(v_usenum/1000, 2); --吨数
v_money:=v_price*v_usenum2; --金额
DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line('水费字数:'||v_usenum'金额:'||v_money);
end;
记录型实用(类似于JAVA里的实体类)
表名%rowtype
declare
v_price number(10, 2); --单价
v_usenum2 number(10, 2); --吨数
v_money number(10, 2); --金额
v_account t_account&rowtype; --台账行记录类型
begin
v_price:=2.45; --单价赋值
-- 从数据库中提取
select * into v_account from t_account where year='2012' and month='01' and owneruuid=1;
v_usenum2:=round(v_account.usenum/1000, 2); --吨数
v_money:=v_price*v_usenum2; --金额
DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line('水费字数:'||t_account.usenum'金额:'||v_money);
end;
(四)异常
| 命令的与系统异常 | 产生原因 |
|---|---|
| NO_DATA_FOUND | 使用 select into 未返回行 |
| TOO_MANY_ROWS | 执行 select into 时,结果集超过一行 |
exception
when 异常类型 then
异常处理逻辑
(五)条件循环
if 条件 then
业务逻辑
end if;
if 条件 then
业务逻辑
else
业务逻辑
end if;
if 条件 then
业务逻辑
elseif 条件 then
业务逻辑
else
业务逻辑
end if;
(六)循环
1、无条件循环
loop
--循环语句
end loop;
范例:输出从1开始的100个数
declare
v_num number:=1;
begin
loop
dbms_output.put_line(v_num);
v_num:=v_num + 1;
exit when v_num > 100;
end loop;
end;
2、条件循环
while 条件
loop
--操作
end loop;
范例:输出从1开始的100个数
declare
v_num number:=1;
begin
while v_num <= 100
loop
dbms_output.put_line(v_num);
v_num:=v_num + 1;
end loop;
end;
3、for循环
for 变量 in 起始值..终止值
loop
--操作
end loop;
范例:输出从1开始的100个数
v_num不需要声明,但是只是局部变量
declare
begin
for v_num in 1..100
loop
dbms_output.put_line(v_num);
end loop;
end;
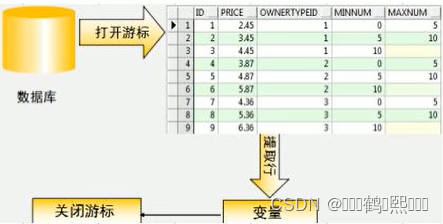
(七)游标
1、什么是游标
游标是系统为用户开设的一个数据缓冲区,存放SQL语句的执行结果。我们可以把游标理解为PL/SQL中的结果集。
2、语法结构及示例
声明游标
cursor 游标名称 is SQL语句;
使用游标语法
open 游标名称
loop
fetch 游标名称 into 变量
exit when 游标名称¬found
end loop;
close 游标名称
需求:打印业主类型为1的价格表
declare
v_pricetable t_pricetable%rowtype; --价格行对象
cursor cur_pricetable is select * from t_pricetable where ownertypeid=1; --定义游标
begin
open cur_pricetable; --打开游标
loop
fetch cur_pricetable into v_pricetable
exit when cur_pricetable%notfound; -- 退出
DBMS_OUTPUT.print_line('价格:'||v_pricetable.price||
'吨位:'||v_pricetable.minnum||
'-'||v_pricetable.maxnum);
end loop;
close cur_pricetable; --关闭游标
end;
带参数的游标
declare
v_pricetable t_pricetable%rowtype; --价格行对象
cursor cur_pricetable(v_ownertype number) is select * from t_pricetable where ownertypeid=v_ownertype; --定义游标
begin
open cur_pricetable(1); --打开游标
loop
fetch cur_pricetable into v_pricetable
exit when cur_pricetable%notfound; -- 退出
DBMS_OUTPUT.print_line('价格:'||v_pricetable.price||
'吨位:'||v_pricetable.minnum||
'-'||v_pricetable.maxnum);
end loop;
close cur_pricetable; --关闭游标
end;
for循环游标最简便方法
declare
--定义游标
cursor cur_pricetable(v_ownertype number) is select * from t_pricetable where ownertypeid=v_ownertype;
begin
for v_pricetable in cur_pricetable(1)
loop
exit when cur_pricetable%notfound; -- 退出
DBMS_OUTPUT.print_line('价格:'||v_pricetable.price||
'吨位:'||v_pricetable.minnum||
'-'||v_pricetable.maxnum);
end loop;
end;
二、存储函数
(一)什么是存储函数
存储函数又称为自定义函数。可以接收一个或者多个参数,返回一个结果。在函数中我们可以使用PL/SQL进行逻辑的处理。
(二)存储函数语法结构
CREATE[OR REPLACE] FUNCTION 函数名称
(参数名称 参数类型, 参数名称 参数类型, ...)
RETURN 结果变量数据类型
IS
变量声明部分;
BEGIN
逻辑部分;
RETURN 结果变量;
[EXCEPTION
异常处理部分]
END;
(三)案例
需求:创建存储函数,根据地址ID查询地址名称
create function fn_getaddress(v_id number)
return varchar2
is
v_name varchar2(30);
begin
select name into v_name from t_address where id=v_id;
return v_name;
end;
使用
select
fn_getaddress(3)
from
dual
需求:查询业主ID、业主名称、业主地址,业主地址使用刚才创建的函数来实现
select
id 编号,
name 业主名称,
fn_getaddress(addressid) 地址
from
t_owners
(三)存储过程
(一)什么是存储过程
存储过程是被命名的PL/SQL块,存储于数据库中,是数据库对象的一种。应用程序可以调用存储过程,执行相应的逻辑。
存储过程与存储函数都可以封装一定的业务逻辑并返回结果,存在区别如下:
1、存储函数中有返回值,且必须返回;而存储过程没有返回值,可以通过传出参数返回多个值。
2、存储函数可以在select语句中直接使用,而存储过程不能。过程多数是被应用程序所调用。
3、存储函数一般都是封装一个查询结果,而存储过程一般都封装一段事务代码。
(二)存储过程语法结构
参数只指定类型,不指定长度
过程参数的三种模式:
IN 传入参数(默认)
OUT 传出参数,主要用于返回程序运行结果
IN OUT 传入传出参数
CREATE [OR REPLACE] PROCEDURE 存储过程名称
(参数名 类型, 参数名 类型, ...)
IS|AS
变量声明部分;
BEGIN
逻辑部分
[EXCEPTION
异常处理部分]
END;
(三)案例
1、创建不带传出参数的存储过程:添加业务信息
-- 增加业主信息(从第11行开始添加)
create sequence seq_owners start with 11;
-- 增加业主信息过程存储
create or replace procedure pro_owners_add
(
v_name varchar2,
v_addressid number,
v_housenumber varchar2,
v_watermeter varchar2,
v_ownertypeid number
)
is
begin
INSERT INTO T_OWNERS values(seq_owners.nextval,v_name,v_addressid,v_housenumber,v_watermeter,sysdate,v_ownertypeid);
commit;
end;
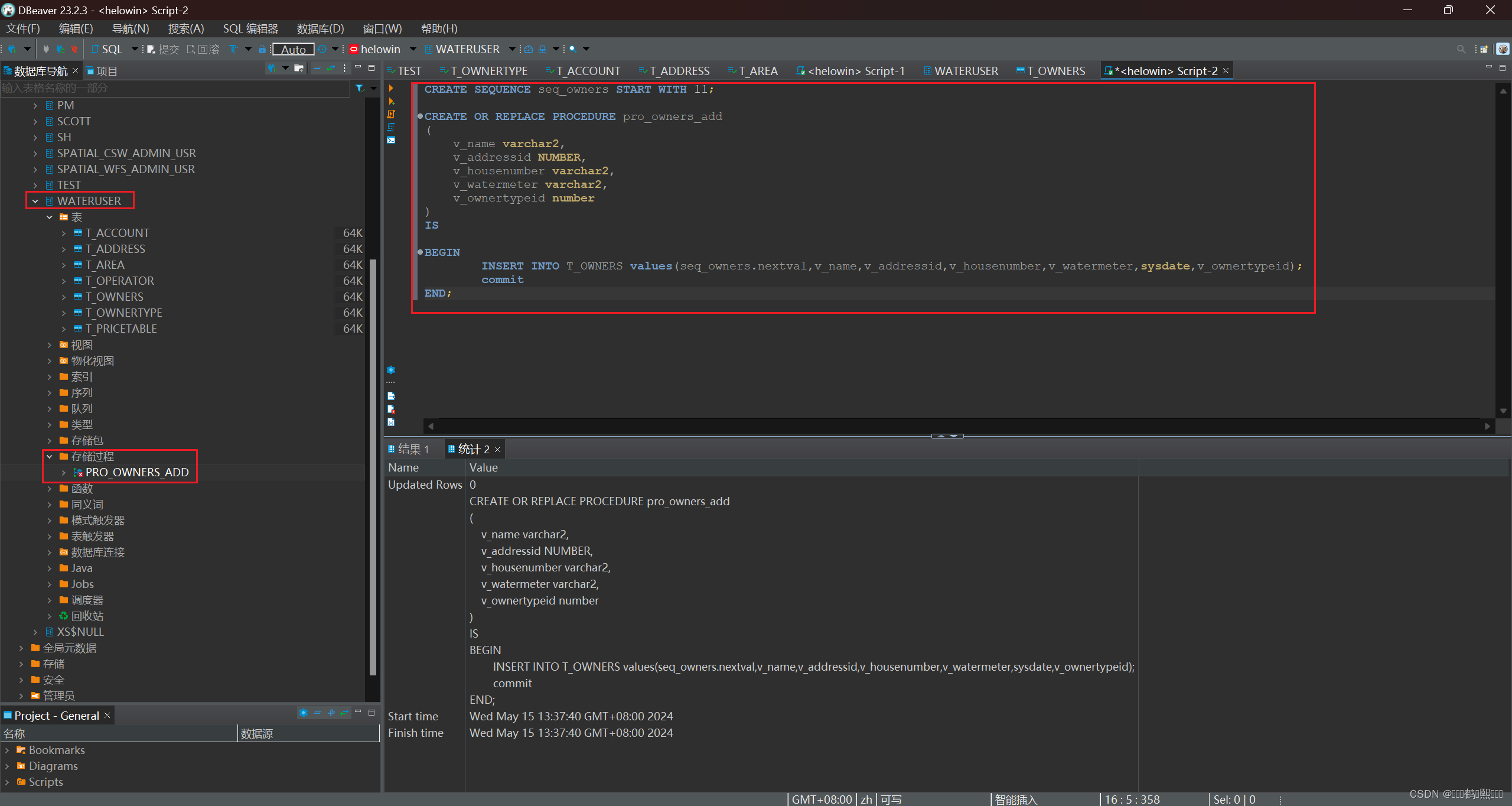
调用
call pro_owners_add('李逵', 520, '1314', '1521', 2);
或者
begin
pro_owners_add('李逵', 520, '1314', '1521', 2);
end;
2、创建传出参数的存储过程
需求:添加业主信息,传出参数为新增业主的ID
create or replace procedure pro_owners_add(
v_name varchar2,
v_addressid number,
v_housenumber varchar2,
v_watermeter varchar2,
v_ownertypeid number,
v_id out number
)
is
begin
select seq_owners.nextval into v_id from dual;
INSERT INTO T_OWNERS values(v_id,v_name,v_addressid,v_housenumber,v_watermeter,sysdate,v_ownertypeid);
commit;
end;
调用
declare
v_id number;
begin
pro_owners_add('费可', 2, '100', '200', 1, v_id);
dbms_output.put_line(v_id);
end;
(四)触发器
(一)什么是触发器
数据库触发器是一个与表相关联的、存储的PL/SQL程序。每当一个特定的数据操作语句(insert,update,delete)在指定的表上发出时,Oracle自动地执行触发器中定义的语句序列。
触发器可用于:
1、数据确认
2、实施复杂的安全性检查
3、做审计,跟踪表上所做的数据操作等
4、数据的备份和同步
触发器分类:
1、前置触发器(BEFORE)
2、后置触发器(AFTER)
(二)创建触发器的语法
FOR EACH ROW作用是标注此触发器是行级触发器 语句级触发器
CREATE [OR REPLACE] TRIGGER 触发器名
BEFORE | AFTER
[DELETE ] [[or] INSERT] [[or] UPDATE [OF 列名]]
ON 表名
[FOR EACH ROW] [WHEN(条件)]
declare
...
begin
PLSQL块
end;
在触发器中触发语句与伪记录的值
| 触发语句 | :old | :new |
|---|---|---|
| insert | 所有字段都是空(null) | 将要插入的数据 |
| update | 更新以前该行的值 | 更新后的值 |
| delete | 删除以前该行的值 | 所有字段都是空(null) |
(三)案例
1、前置触发器
需求:当用户输入本月累计表数后,自动计算出本月使用数
create or replace trigger tri_account_updatenum1
before
update of num1
on t_account
for each row
declare
begin
:new.usenum:=:new.num1-:new.num0;
end;
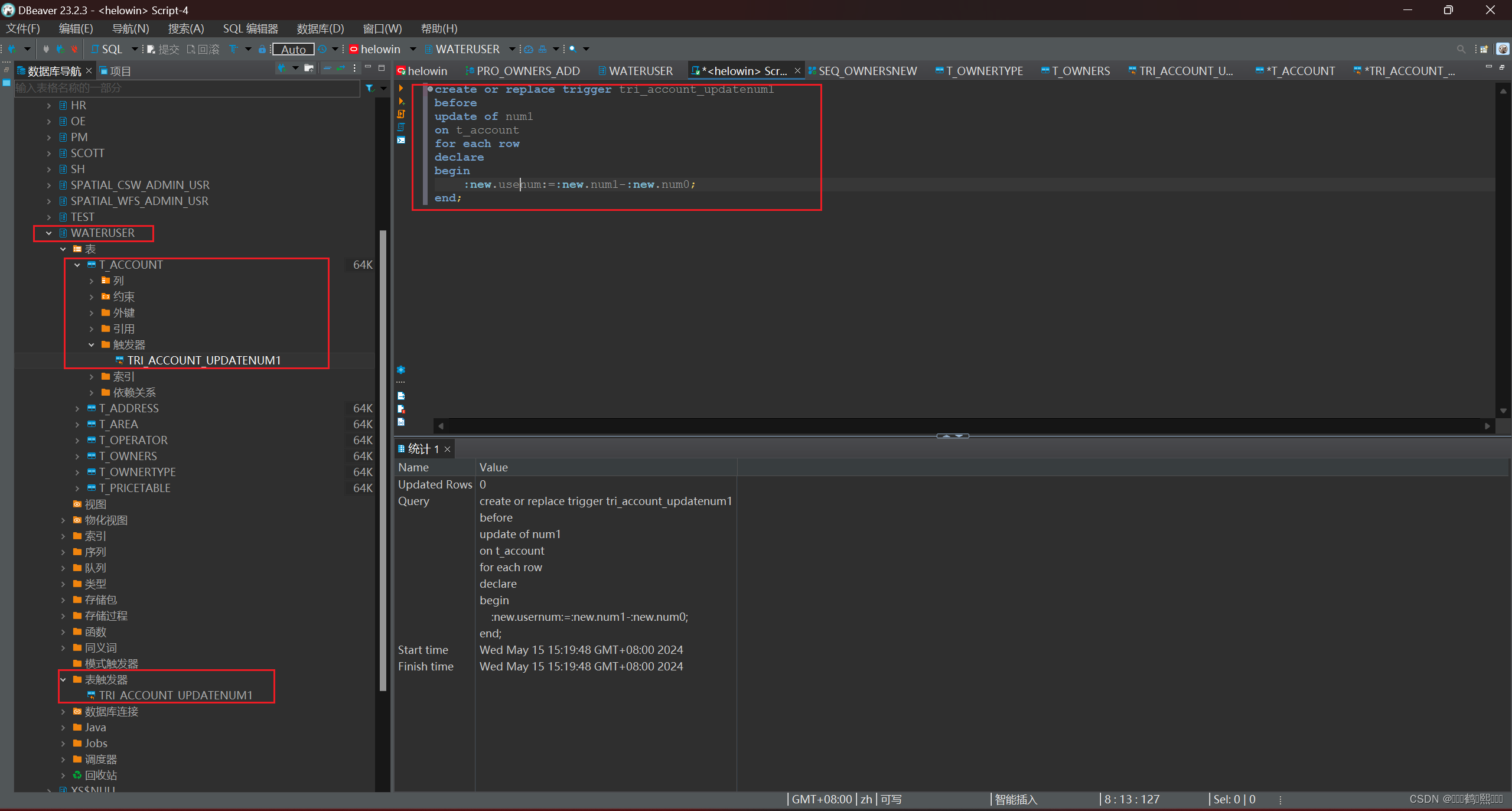
操作
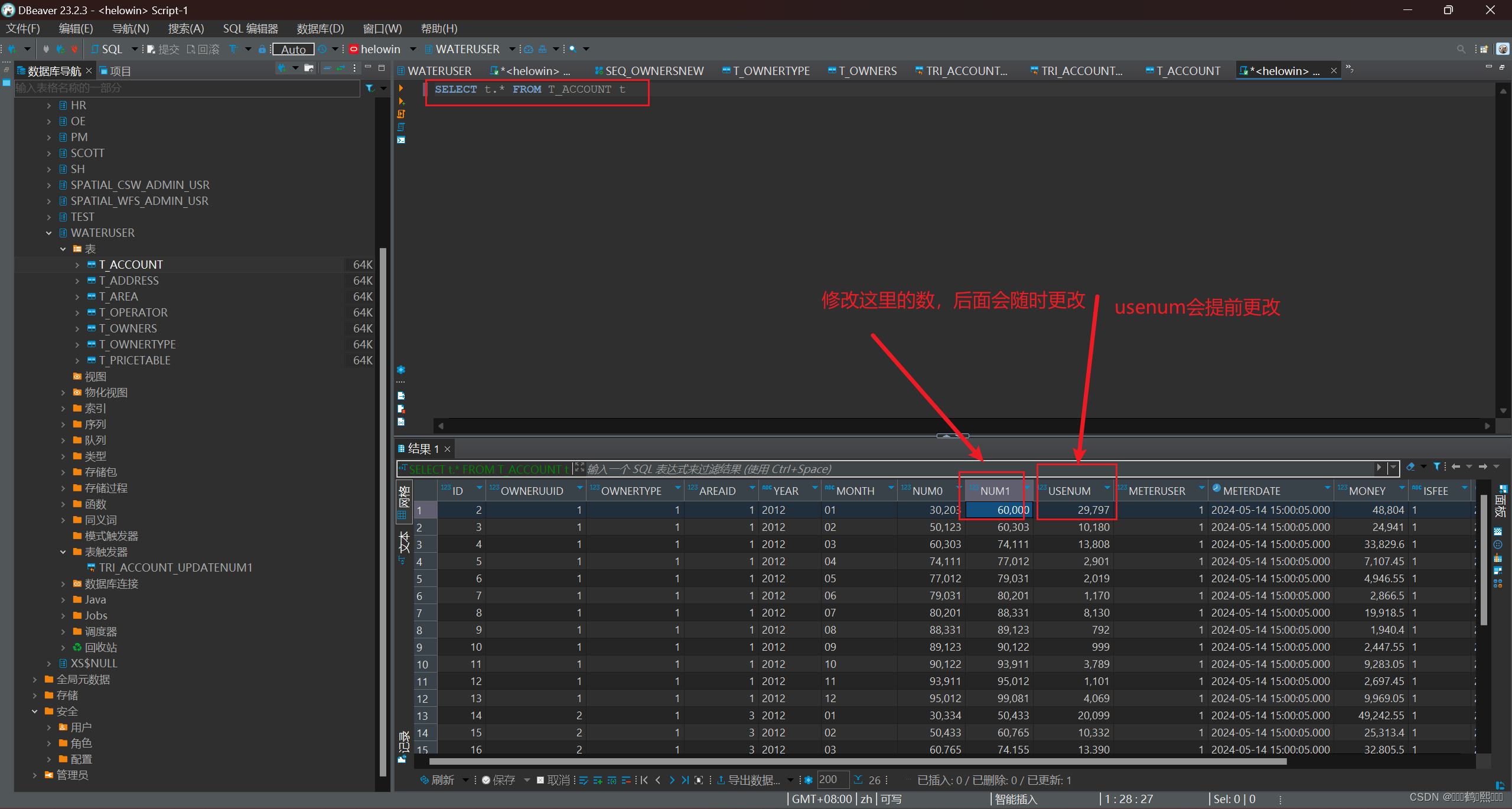
2、后置触发器
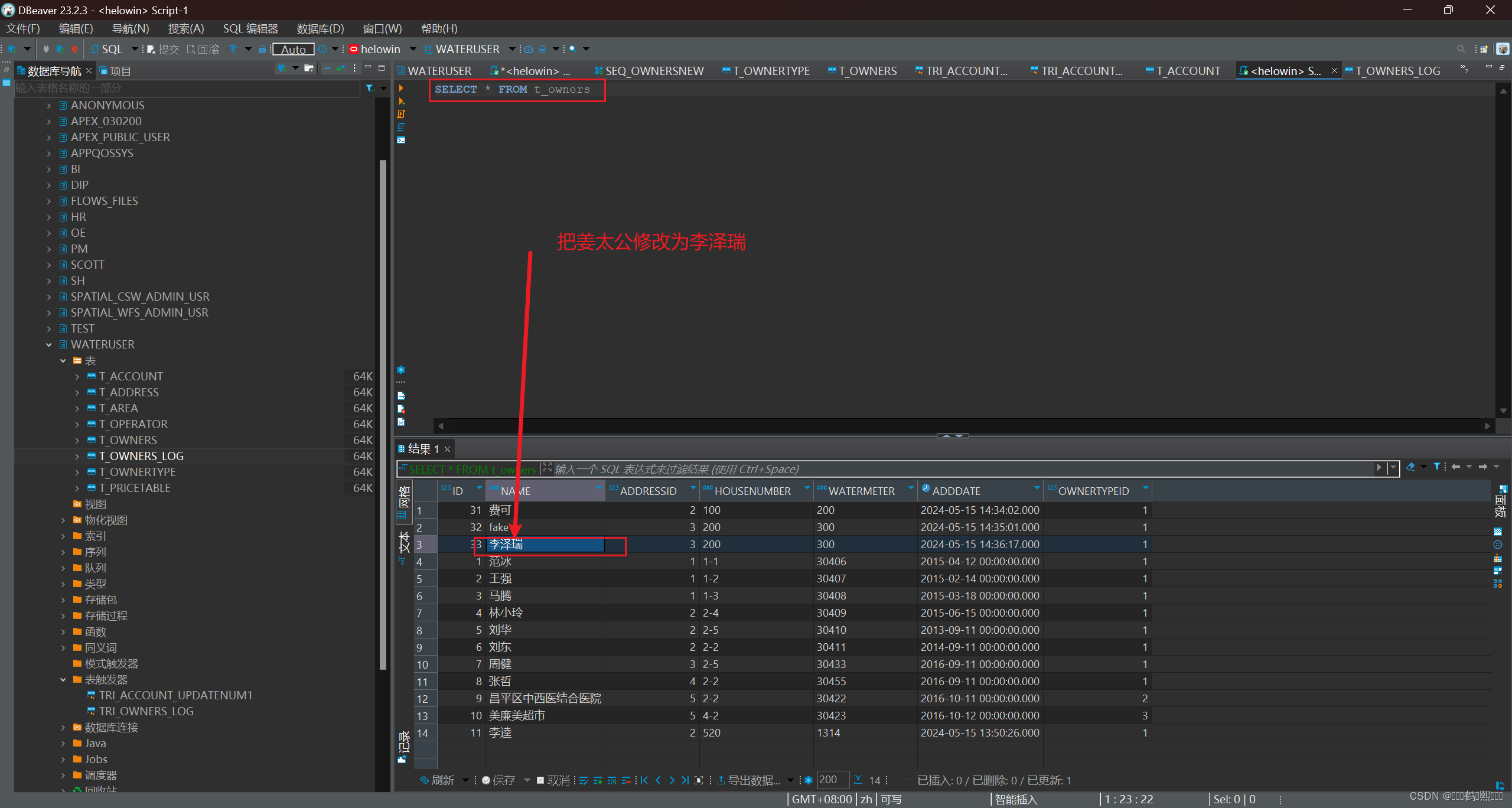
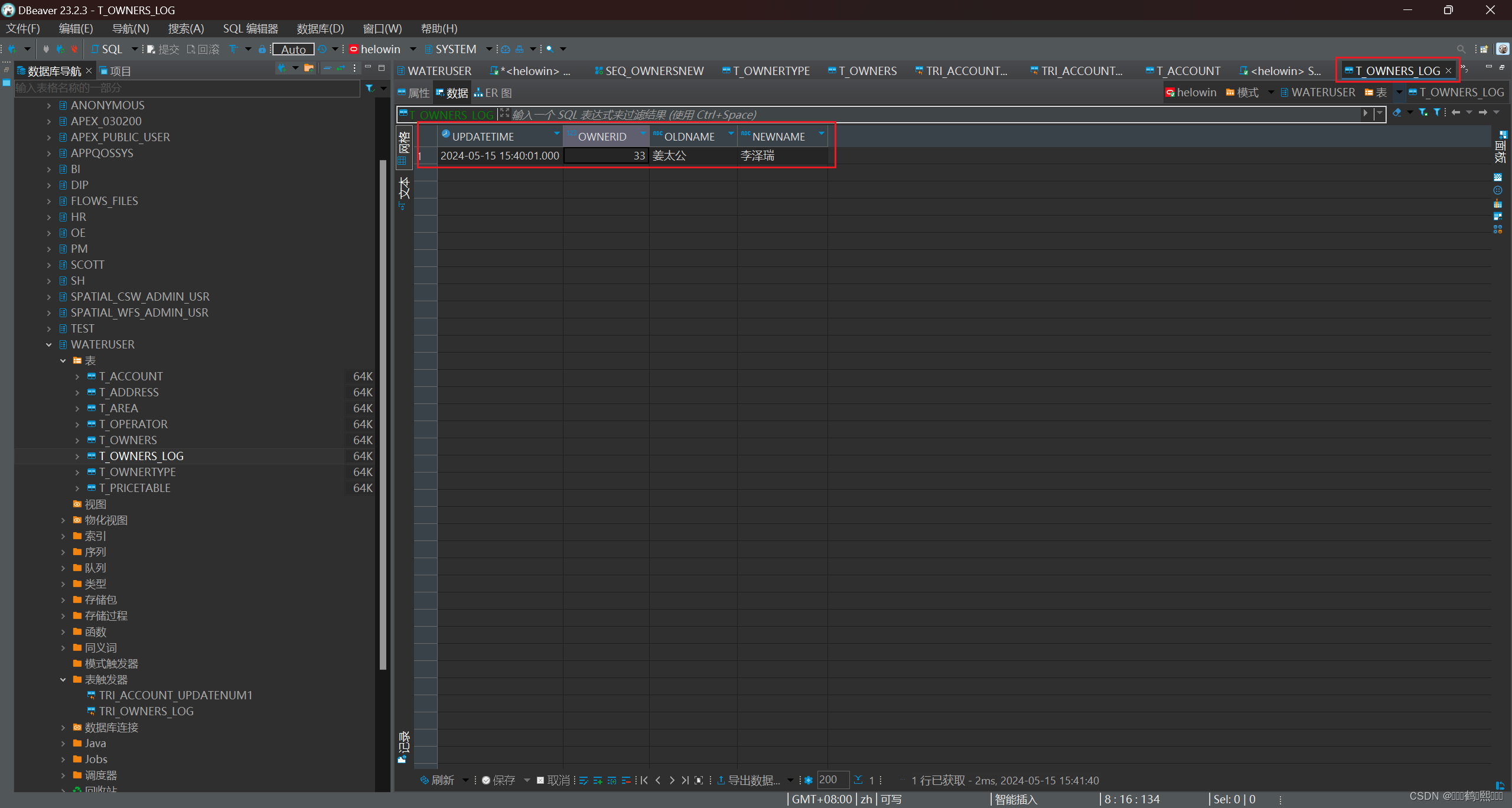
需求:当用户修改了业主信息表的数据时记录修改前与修改后的值
--创建日志表,记录业主名称修改前和修改后的名称
create table t_owners_log(
updatetime date,
ownerid number,
oldname varchar2(30),
newname varchar2(30)
);
-- 新建后置触发器
CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER tri_owners_log
AFTER
UPDATE OF NAME
ON t_owners
FOR EACH ROW
DECLARE
BEGIN
-- 向日志表插入记录
INSERT INTO t_owners_log values(sysdate, :NEW.id, :OLD.id, :NEW.name);
END;
操作