A service engineer gets a list of jobs Ji with a serving time
si and a deadline
di. A job Ji needs time
si, and if it is completed at time
Ci, then the penalty of Ji is defined to be
max{0, Ci - di}. For convenience, we assume that the time
t when a job can be served is
0![]() t <
t <
![]() and
si and di are given positive integers such that
0 < si
and
si and di are given positive integers such that
0 < si![]() di. The goal is to find a schedule of jobs minimizing
the sum of the penalties of the jobs with the two largest penalties.
di. The goal is to find a schedule of jobs minimizing
the sum of the penalties of the jobs with the two largest penalties.
For example, there are six jobs Ji with the pair (si, di) of the serving time si and the deadline di, i = 1,..., 6, where (s1, d1) = (1, 7), (s2, d2) = (4, 7), (s3, d3) = (2, 4), (s4, d4) = (2, 15), (s5, d5) = (3, 5), (s6, d6) = (3, 8). Then Figure 1 represents a schedule which minimizes the sum of the penalties of the jobs with the two largest penalties. The sum of the two largest penalties of an optimal schedule is that of the penalties of J2 and J6, namely 6 and 1, respectively, which is equal to 7 in this example.

Input
Your program is to read from standard input. The input consists of
T test cases. The number of test cases T is given on the first line of the input. The first line of each test case contains an integer
n ( 1![]() n
n![]() 500),
the number of the given jobs. In the next n lines of each test case, the
i-th line contains two integer numbers
si and di, representing the serving time and the deadline of the job
Ji, respectively, where
1
500),
the number of the given jobs. In the next n lines of each test case, the
i-th line contains two integer numbers
si and di, representing the serving time and the deadline of the job
Ji, respectively, where
1![]() si
si![]() di
di![]() 10,
000.
10,
000.
Output
Your program is to write to standard output. Print exactly one line for each test case. The line contains the sum of the penalties of the jobs with the two largest penalties.
The following shows sample input and ouput for three test cases.
Sample Input
3 6 1 7 4 7 2 4 2 15 3 5 3 8 7 2 17 2 11 3 4 3 20 1 20 4 7 5 14 10 2 5 2 9 5 10 3 11 3 4 4 21 1 7 2 9 2 11 2 23
Sample Output
7 014
只想到最大惩罚值用贪心,不知道两个怎么搞,也是看了别人的题解,分析问题的思维好欠缺啊。
首先还是贪心,然后分三种情况讨论分析
1.所有惩罚值为0.答案就是0
2.有一个有惩罚值,答案就是该惩罚值。
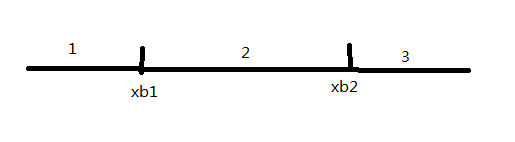
3有两个以上的惩罚值,我们假设最大为max1,次大为max2,就会有两个下标为xb1,xb2.
会把任务划分成三段
我们试着移动任务:
(1)从1找一个任务移动到2执行,则xb2所对应的惩罚值不变,xb1所对应的惩罚值增加。
(2)从2找一个任务移动到3执行,则xb1所对应的惩罚值不变,xb2所对应的惩罚值增加。
(3)从1找一个任务移动到3执行,虽然最大惩罚值会增大,但是则xb2所对应的惩罚值和xb1所对应的惩罚值减小。也就说最大惩罚值增大,次大惩罚值有可能减小。总和也就有可能减小。分析可以发现,最好也就是移动任务到xb2后面第一个。
所以我们只要枚举(3)情况就可以了。#include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <map> #include <cmath> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int MAXN = 510; int n; struct node { int s, d; }g[MAXN]; bool cmp(node a, node b) { return a.d<b.d; } int work() { int ans; sort(g,g+n,cmp); int i, j, xb1=-1, xb2=-1, sum = 0, max1=0, max2=0; /*for(i=0; i<n; i++) { printf("%d %d\n",g[i].s,g[i].d); }*/ for(i=0; i<n; i++) { sum += g[i].s; int temp = max(sum - g[i].d,0); if(temp>max1) { max2 = max1; max1 = temp; xb1 = xb2; xb2 = i; }else if(temp>max2) { max2 = temp; xb1 = xb2; xb2 = i; } } ans = max1 + max2; for(i=0; i<=xb1; i++) // 枚举移动的工作 { //每次都要初始化 sum = max1 = max2 = 0; for(j=0; j<n; j++) { if(j==i)continue;//跳过所选的工作 sum += g[j].s; int temp = max(sum - g[j].d,0); if(temp>max1) { max2 = max1; max1 = temp; }else if(temp>max2) { max2 = temp; } if(j==xb2) //把移动的工作放入xb2后面 { sum += g[i].s; int temp = max(sum - g[i].d,0); if(temp>max1) { max2 = max1; max1 = temp; }else if(temp>max2) { max2 = temp; } } } //cout<<i<<" "<<max1+max2<<endl; ans = min(ans, max1 + max2); //选择最优解 } return ans; } int main() { int t; scanf("%d",&t); while(t--) { scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=0; i<n; i++) { scanf("%d%d",&g[i].s,&g[i].d); } printf("%d\n",work()); } return 0; }





 本文探讨了电信服务工程师的任务调度问题,通过定义任务的完成时间和截止期限之间的惩罚值来衡量任务超时的程度,并提出了一种算法来最小化两个最大惩罚值之和。
本文探讨了电信服务工程师的任务调度问题,通过定义任务的完成时间和截止期限之间的惩罚值来衡量任务超时的程度,并提出了一种算法来最小化两个最大惩罚值之和。
















 3424
3424

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








