目录
一、核心代码部分
首先上代码,如下代码是测试成环的case(切记,需要JDK配置为1.7,我用到的是jdk-7u80-windows-x64.exe版本)
package com.mfanw;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
public class MainMap {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
final Map<MyString, String> map = new HashMap<>(8);
final int count = 6;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
map.put(new MyString("" + i), "" + i);
}
Thread[] ts = new Thread[2];
for (int c = 0; c < 2; c++) {
final int fc = c;
ts[c] = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
String key = (fc + count) + "";
map.put(new MyString(key), key); // 此处为断点A
System.out.println(map);
}
});
ts[c].start();
}
System.out.println("haha");
Thread.sleep(1000 * 60 * 60 * 24);
}
}
class MyString {
public String text;
public MyString(String text) {
this.text = text;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
MyString myString = (MyString) o;
return Objects.equals(text, myString.text);
}
/**
* 确保全部元素都落在HashMap的第0个table内
*
* @return 0
*/
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return text;
}
}
二、核心代码的两个断点
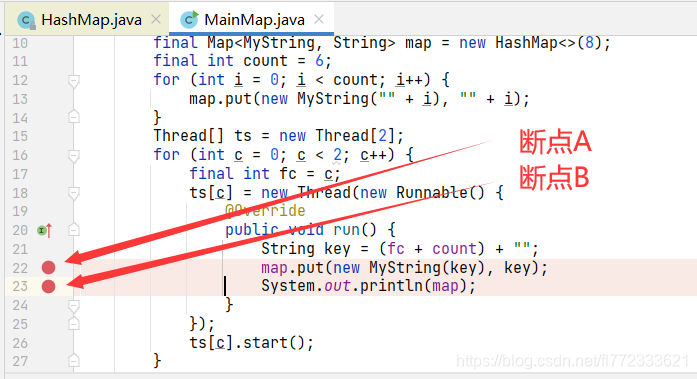
断点A和断点B:如下图所示
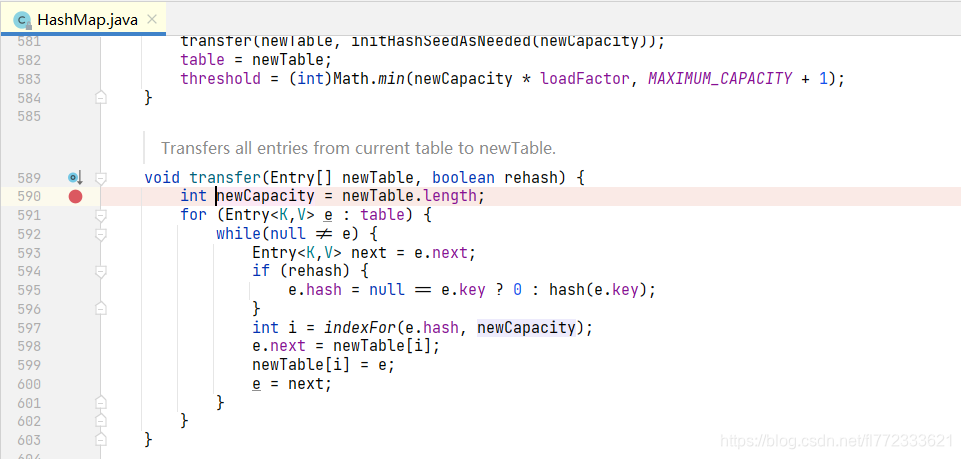
断点C:如下图所示
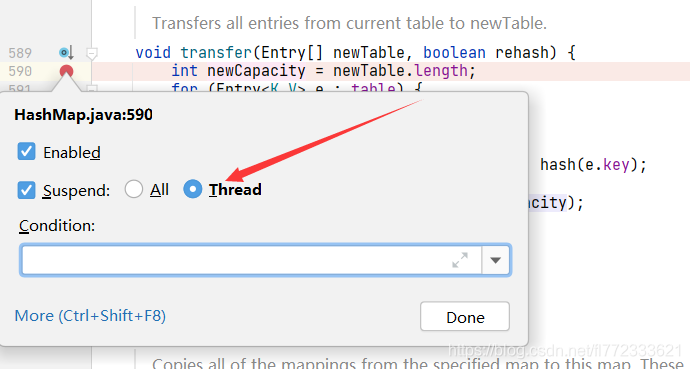
注意:如下图,确保全部的断点,都是Thread级别(在断点上右击,该配置仅idea需要操作,eclipse默认完美支持Thread断点)
三、Debug运行
3.1 运行Thread-0部分
Debug运行main方法,可能会首先在断点C内停止,可以跳过。
当运行到断点A停止后,应该可以看到是两个线程被中断。
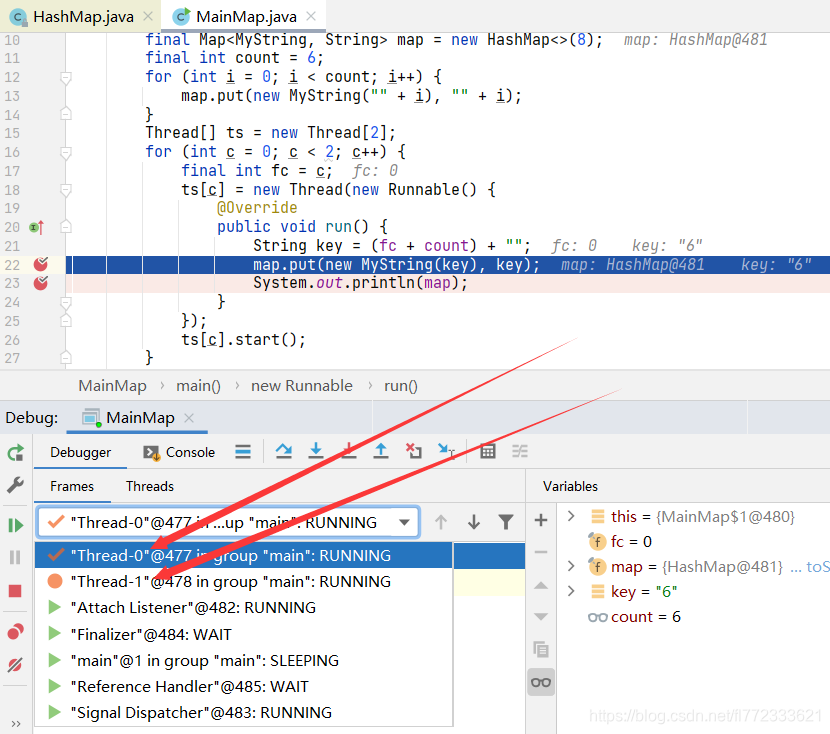
切换到 Thread-0 并点击运行,会马上在断点C处中断,手工执行到594行。
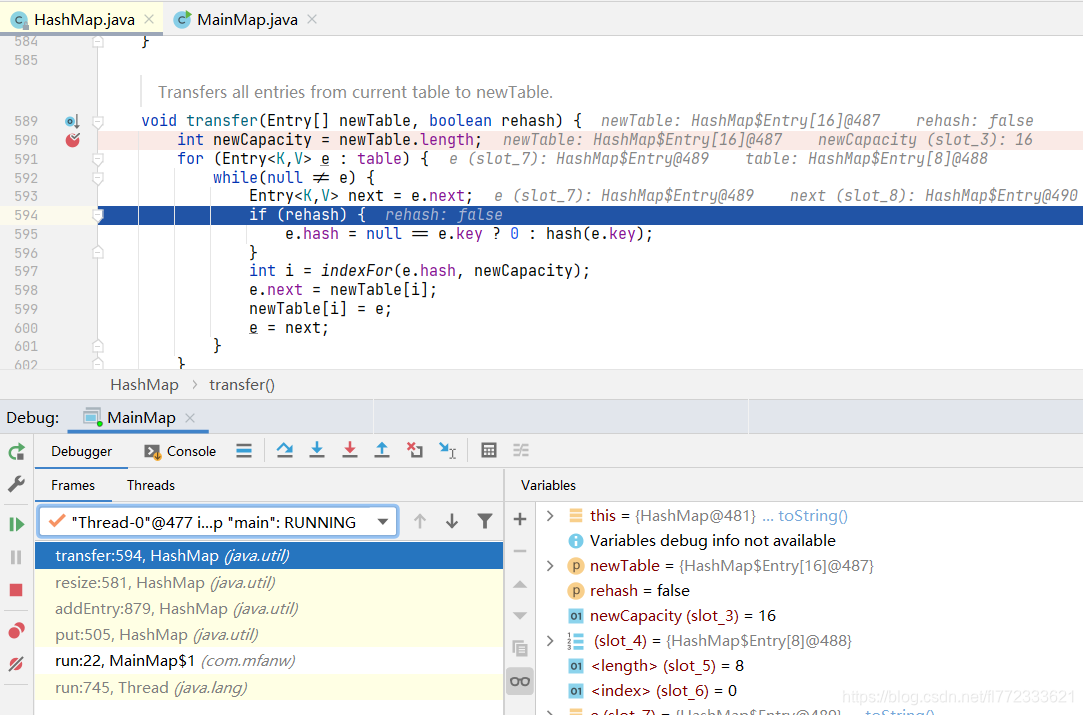
注意:目前的table是 5 → 4 → 3 → 2 → 1 → 0
e=5(因为它也要尝试头插法转移元素到newTable)
next=e.next=4
3.2 运行Thread-1部分(第一种测试)
承接3.1的操作后进行该步骤
切换到Thread-1,一路F8执行过去,会直接抛出 Exception in thread "Thread-0" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space,原因是已经成环。

3.3 运行Thread-1部分(第二种测试)
承接3.1的操作后进行该步骤
切换到Thread-1,一直点击运行,直到断点B处
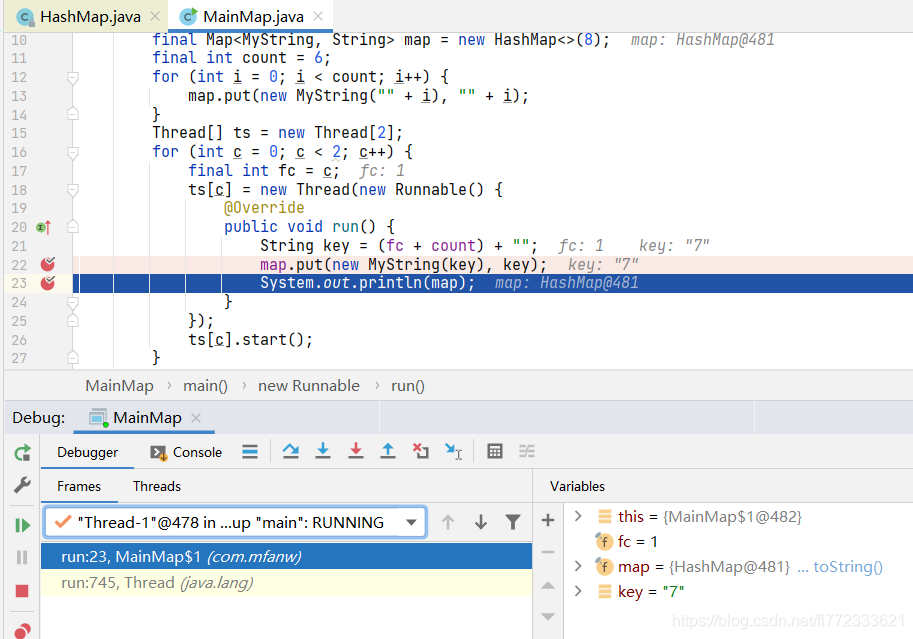
Thread-1的 transfer方法会将 table=5 → 4 → 3 → 2 → 1 → 0 转移到 newTable内,且顺序颠倒过来,因为它是头插法转移,
先转移5,再转移4,再转移3...... 也就是最终 newTable = 0 → 1 → 2 → 3 → 4 → 5
然后Thread-1再头插法插入新元素,最终 newTable = 7 → 0 → 1 → 2 → 3 → 4 → 5
切换到Thread-0, 引用3.1章节末尾的注意内容可知 e=5 , next=4
目前的 table是 7 → 0 → 1 → 2 → 3 → 4 → 5 (7是Thread-1刚刚给加进去的)
注意:此处的 newTable 是上层方法 resize内new出来的,所以此处newTable是empty
第一次循环
e.next = newTable[i]; // 5.next = null
newTable[i] = e; // newTable头结点设置为5
e = next; // 设置e=4进入下一次循环第二次循环
Entry<K,V> next = e.next; // e=4, next = 4.next=5
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i]; // 4.next = newTable的头结点 = 5
newTable[i] = e; // newTable头结点设置为4
e = next; // 设置e=5进入下一次循环第三次循环
Entry<K,V> next = e.next; // e=5, next=5.next=null
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i]; // 5.next=newTable的头结点=4,HashMap终于成环了
newTable[i] = e; // newTable头结点设置为5
e = next; // 设置e=null也就无法进入下一次循环了








 本文详细解析了Java HashMap在并发环境下插入新元素可能导致环形结构的问题,通过关键代码分析和debug过程展示了成环的条件,并提供了两种测试方法。重点讲解了如何通过Thread级别断点调试和理解线程间的交互。
本文详细解析了Java HashMap在并发环境下插入新元素可能导致环形结构的问题,通过关键代码分析和debug过程展示了成环的条件,并提供了两种测试方法。重点讲解了如何通过Thread级别断点调试和理解线程间的交互。
















 1143
1143

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








