CNN模型
在传统的CNN网络中,在最后的卷积层之后会连接上若干个全连接层,将卷积层产生的特征图(feature map)映射成为一个固定长度的特征向量。一般的CNN结构适用于图像级别的分类和回归任务,因为它们最后都期望得到输入图像的分类的概率,如ALexNet网络最后输出一个1000维的向量表示输入图像属于每一类的概率。如下图所示:
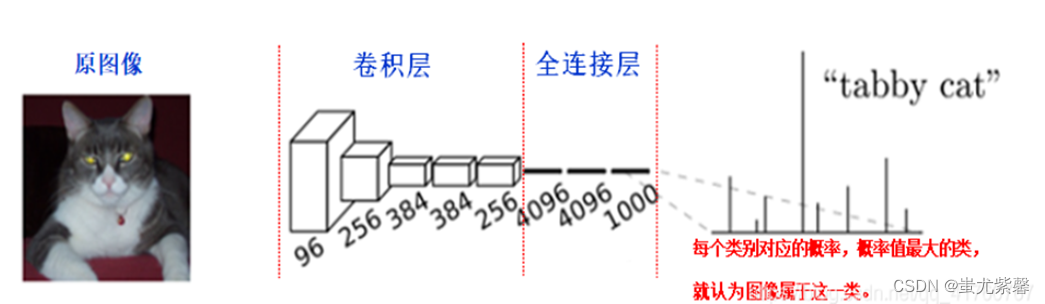
在CNN中, 猫的图片输入到AlexNet, 得到一个长为1000的输出向量, 表示输入图像属于每一类的概率, 其中在“tabby cat”这一类统计概率最高, 用来做分类任务。
FCN模型
FCN是对图像进行像素级的分类(也就是每个像素点都进行分类),从而解决了语义级别的图像分割问题。与前面介绍的经典CNN在卷积层使用全连接层得到固定长度的特征向量进行分类不同,FCN可以接受任意尺寸的输入图像,采用反卷积层对最后一个卷基层的特征图(feature map)进行上采样,使它恢复到输入图像相同的尺寸,从而可以对每一个像素都产生一个预测,同时保留了原始输入图像中的空间信息,最后奇偶在上采样的特征图进行像素的分类。如下图所示:
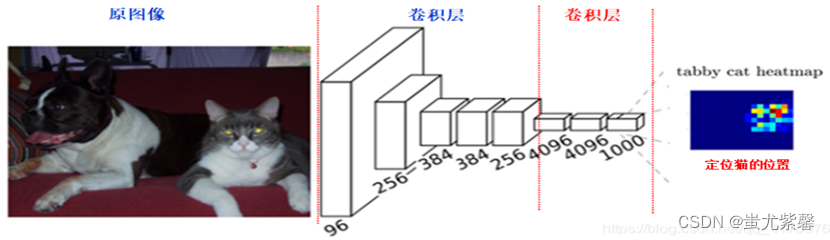
FCN具体实现过程
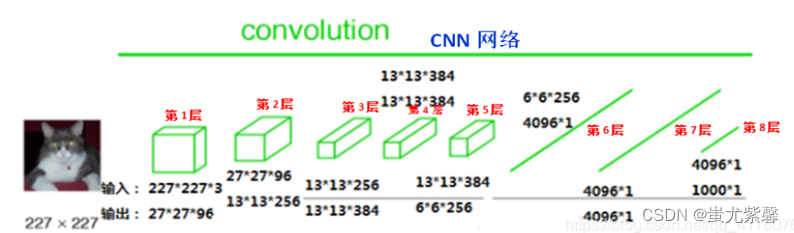
FCN与CNN的核心区别就是FCN将CNN末尾的全连接层转化成了卷积层:以Alexnet为例,输入是2272273的图像,前5层是卷积层,第5层的输出是256个特征图,大小是66,即25666,第6、7、8层分别是长度是4096、4096、1000的一维向量。如下图所示:
MobileNet模型
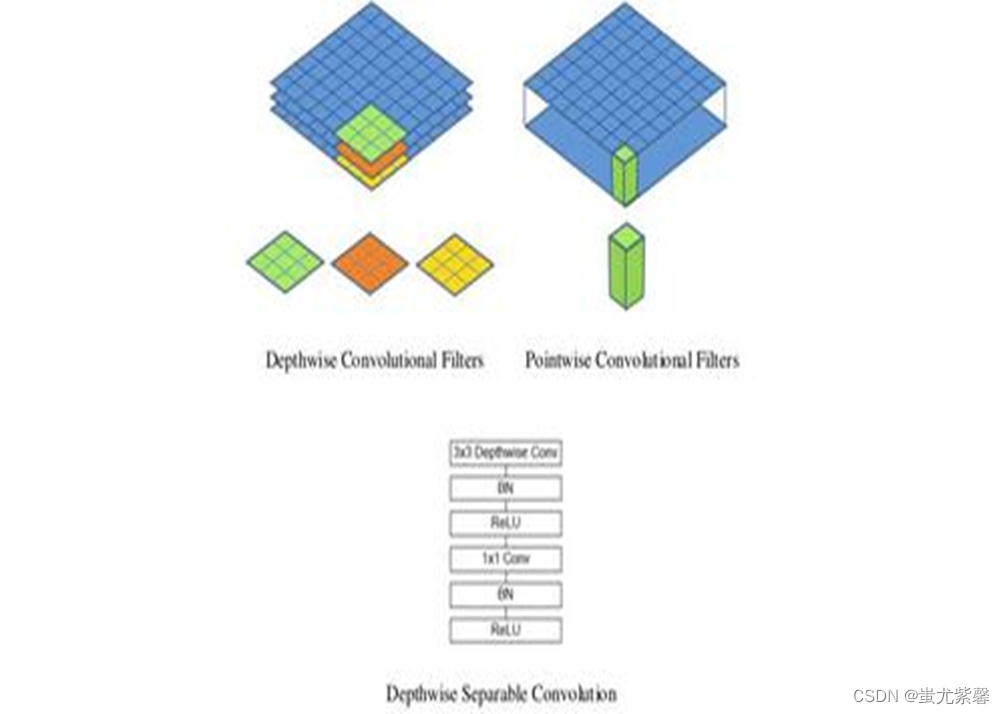
MobileNet模型是Google针对手机等嵌入式设备提出的一种轻量级的深层神经网络,其使用的核心思想是深度可分离卷积deepthwise separable convolution,深度可分离卷积由:DW(deepth wise)和PW(pointwise)两个部分结合起来,用来提取特征feature map,相比常规的卷积操作,其参数数量和运算成本低,其轻量表现在使用深度可分离卷积的方式大量减少了模型的参数。
实验环境
- 镜像:TensorFlow 2.5.0,Python 3.8,Cuda 11.2
- GPU:RTX 3090(24GB) * 1
- CPU:15 vCPU AMD EPYC 7543 32-Core Processor
- 内存:80GB
主要代码:
def crop(o1, o2, i):
o_shape2 = Model(i, o2).output_shape
output_height2 = o_shape2[1]
output_width2 = o_shape2[2]
o_shape1 = Model(i, o1).output_shape
output_height1 = o_shape1[1]
output_width1 = o_shape1[2]
cx = abs(output_width1 - output_width2)
cy = abs(output_height2 - output_height1)
if output_width1 > output_width2:
o1 = Cropping2D(cropping=((0, 0), (0, cx)),
data_format="channels_last")(o1)
else:
o2 = Cropping2D(cropping=((0, 0), (0, cx)),
data_format="channels_last")(o2)
if output_height1 > output_height2:
o1 = Cropping2D(cropping=((0, cy), (0, 0)),
data_format="channels_last")(o1)
else:
o2 = Cropping2D(cropping=((0, cy), (0, 0)),
data_format="channels_last")(o2)
return o1, o2
def fcn_8(n_classes, encoder=None, input_height=416,
input_width=608, channels=3):
img_input, levels = encoder(
input_height=input_height, input_width=input_width, channels=channels)
[f1, f2, f3, f4, f5] = levels
o = f5
o = (Conv2D(4096, (7, 7), activation='relu',
padding='same', data_format="channels_last"))(o)
o = Dropout(0.5)(o)
o = (Conv2D(4096, (1, 1), activation='relu',
padding='same', data_format="channels_last"))(o)
o = Dropout(0.5)(o)
o = (Conv2D(n_classes, (1, 1), kernel_initializer='he_normal',
data_format="channels_last"))(o)
o = Conv2DTranspose(n_classes, kernel_size=(4, 4), strides=(
2, 2), use_bias=False, data_format="channels_last")(o)
o2 = f4
o2 = (Conv2D(n_classes, (1, 1), kernel_initializer='he_normal',
data_format="channels_last"))(o2)
o, o2 = crop(o, o2, img_input)
o = Add()([o, o2])
o = Conv2DTranspose(n_classes, kernel_size=(4, 4), strides=(
2, 2), use_bias=False, data_format="channels_last")(o)
o2 = f3
o2 = (Conv2D(n_classes, (1, 1), kernel_initializer='he_normal',
data_format="channels_last"))(o2)
o2, o = crop(o2, o, img_input)
o = Add( name="seg_feats" )([o2, o])
o = Conv2DTranspose(n_classes, kernel_size=(16, 16), strides=(
8, 8), use_bias=False, data_format="channels_last")(o)
model = get_segmentation_model(img_input, o)
model.model_name = "fcn_8"
return model
def fcn_8_mobilenet(n_classes, input_height=224, input_width=224, channels=3):
model = fcn_8(n_classes, get_mobilenet_encoder,
input_height=input_height, input_width=input_width, channels=channels)
model.model_name = "fcn_8_mobilenet"
return model
模型训练结果
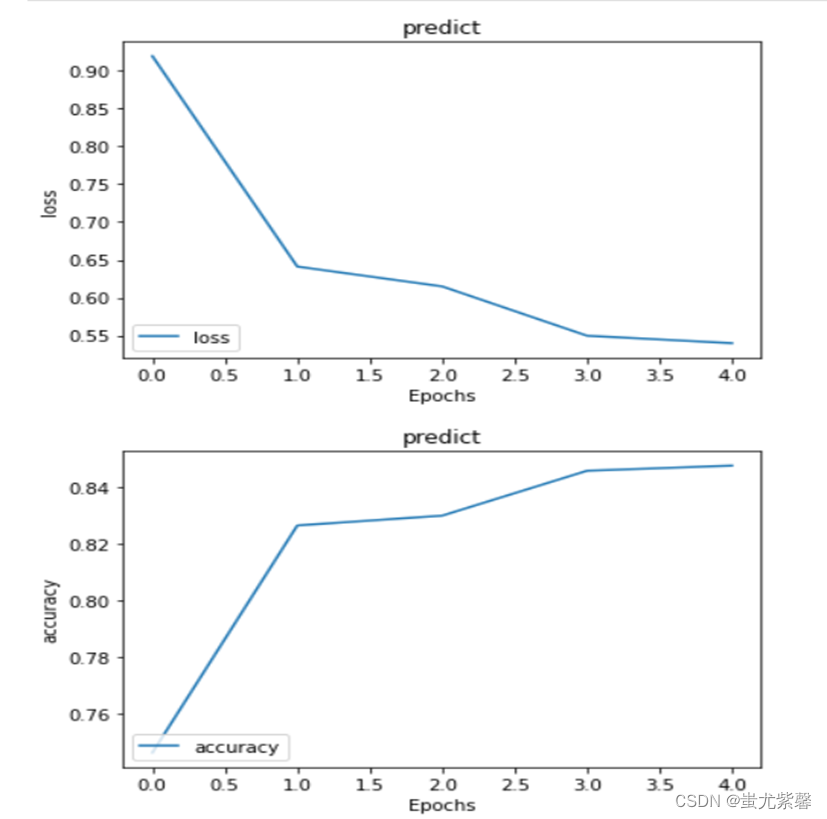
总结:
模型缺陷与后续改进:
- 1、得到的结果还是不够精细。进行8倍上采样虽然比32倍的效果好了很多,但是上采样的结果还是比较模糊和平滑,对图像中的细节不敏感
- 2、对各个像素进行分类,没有充分考虑像素与像素之间的关系。忽略了在通常的基于像素分类的分割方法中使用的空间规整(spatial regularization)步骤,缺乏空间一致性




 博客介绍了用于自动驾驶等领域的CNN、FCN和MobileNet模型。CNN适用于图像分类回归,FCN可解决语义级图像分割问题,MobileNet是轻量级深层神经网络。还给出实验环境、主要代码和模型训练结果,指出模型存在结果不够精细、未充分考虑像素关系等缺陷。
博客介绍了用于自动驾驶等领域的CNN、FCN和MobileNet模型。CNN适用于图像分类回归,FCN可解决语义级图像分割问题,MobileNet是轻量级深层神经网络。还给出实验环境、主要代码和模型训练结果,指出模型存在结果不够精细、未充分考虑像素关系等缺陷。
















 1286
1286










