前言
说道Javaagent是最近经常在使用这个技术,顺便了解了原理与根源,实际上就是jvm开个代理字节码修改的instrument接口。但实际上使用,根据使用的方式不同而略有区别。
1. Javaagent使用
实际上,笔者在前段时间写了arthas的启动原理(83条消息) arthas 启动原理分析_fenglllle的博客-优快云博客,简单的说明了Javaagent的2种方式,jvm参数方式与动态attach。
以动态attach为例,实际上以jvm参数的agent类似,动态attach支持远程attach。
1.1 agent jar,demo
public class AgentMainDemo {
private static synchronized void main(String args, Instrumentation inst) {
try {
System.out.println("agent exec ......");
inst.addTransformer(new ClassFileTransformer() {
@Override
public byte[] transform(ClassLoader loader, String className, Class<?> classBeingRedefined, ProtectionDomain protectionDomain, byte[] classfileBuffer) throws IllegalClassFormatException {
//字节码修改,替换
System.out.println("------ byte instead -----");
return new byte[0];
}
}, true);
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.feng.agent.demo.ReTransformDemo");
inst.retransformClasses(clazz);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | UnmodifiableClassException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void premain(String args, Instrumentation inst) {
main(args, inst);
}
public static void agentmain(String args, Instrumentation inst) {
main(args, inst);
}
}pom打包manifest支持
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-assembly-plugin</artifactId>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>single</goal>
</goals>
<phase>package</phase>
<configuration>
<descriptorRefs>
<descriptorRef>jar-with-dependencies</descriptorRef>
</descriptorRefs>
<archive>
<manifestEntries>
<Premain-Class>com.feng.agent.demo.AgentMainDemo</Premain-Class>
<Agent-Class>com.feng.agent.demo.AgentMainDemo</Agent-Class>
<Can-Retransform-Classes>true</Can-Retransform-Classes>
</manifestEntries>
</archive>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>1.2 运行的Java应用&tools.jar
public class DemoMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("I'm a app");
Thread.sleep(100000000000l);
}
}执行,可以debug执行都行。执行后pid笔者为 3041
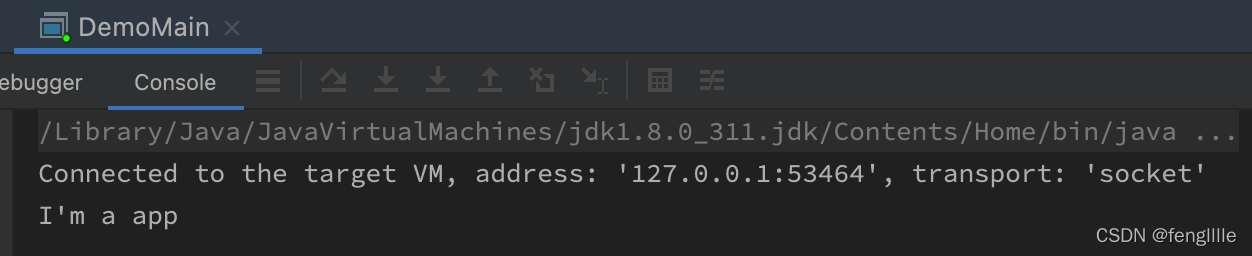
tools.jar,需要载入才行
public class AttachMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, AttachNotSupportedException, AgentLoadException, AgentInitializationException {
VirtualMachine machine = null;
try {
machine = VirtualMachine.attach("3041");
machine.loadAgent("/Users/huahua/IdeaProjects/java-agent-demo/attach-demo/src/main/resources/agent-demo-jar-with-dependencies.jar");
} finally {
if (machine != null) {
machine.detach();
}
}
}
}1.3 执行结果
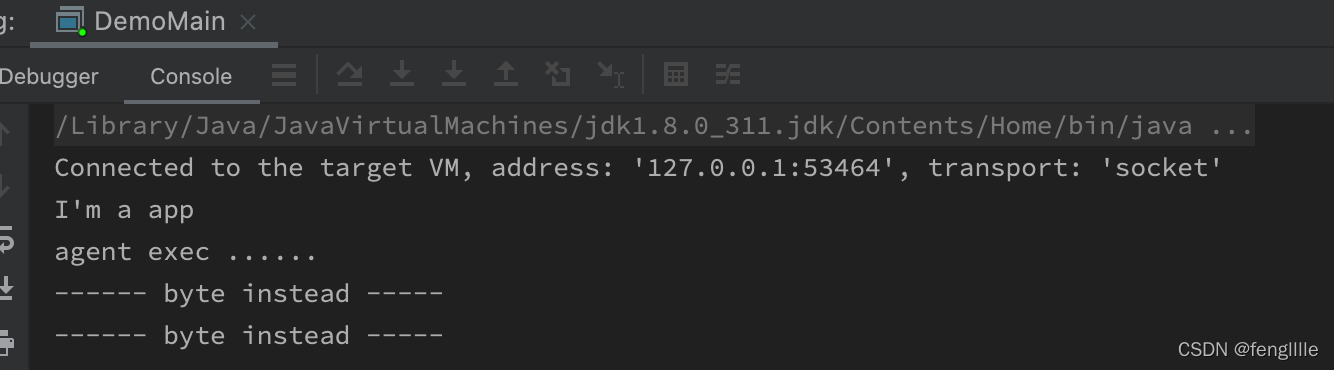
可以看到agent exec 的字样,说明agent已经load了,且进行了字节码替换。实际上transform的ClassFileTransformer可以形成调用链,一个类可以被多次transform。transform默认是有
ClassFileTransformer的。
2. Javaagent原理
简单介绍Javaagent的原理:Javaagent分为jvm参数方式与动态attach方式
jvm参数方式:这种方式比较常用,因为可以通过启动参数内置
动态attach:这种方式比较灵活,可以多次attach,且可以销毁attach的agent。
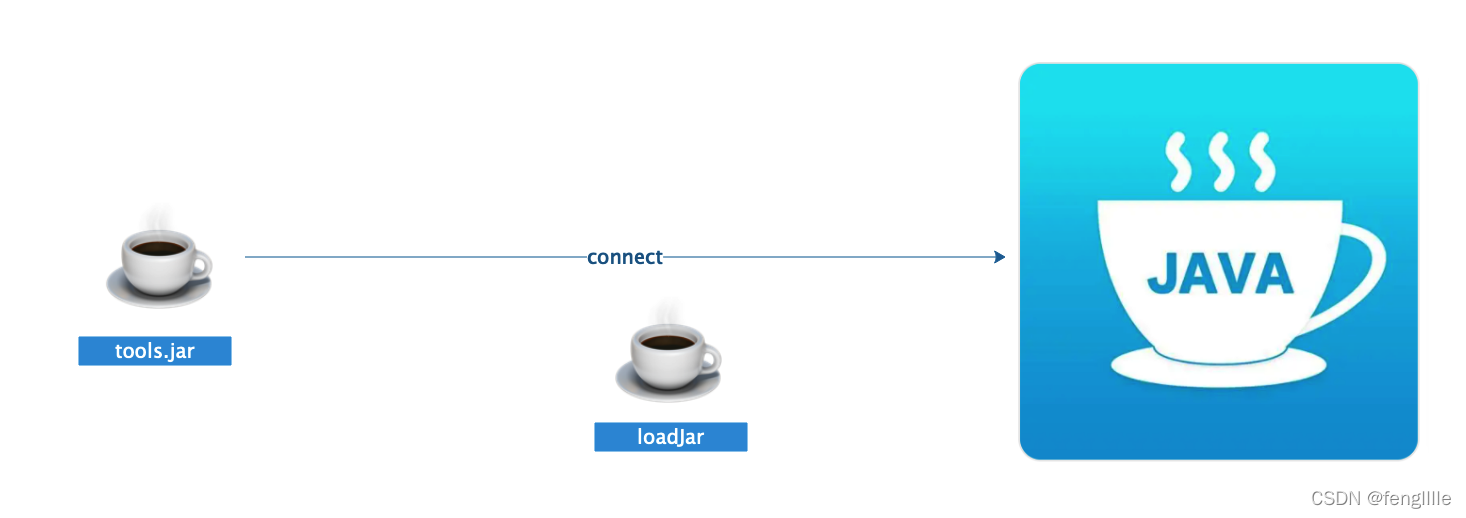
实际上jvm加载逻辑差不多,这里以复杂的动态attach为例
关键还是:provider.attachVirtualMachine(id);
public static VirtualMachine attach(String id)
throws AttachNotSupportedException, IOException
{
if (id == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("id cannot be null");
}
List<AttachProvider> providers = AttachProvider.providers();
if (providers.size() == 0) {
throw new AttachNotSupportedException("no providers installed");
}
AttachNotSupportedException lastExc = null;
for (AttachProvider provider: providers) {
try {
return provider.attachVirtualMachine(id);
} catch (AttachNotSupportedException x) {
lastExc = x;
}
}
throw lastExc;
}然后进一步跟踪:
可以看到使用了SPI技术,笔者Mac系统,如果是Linux或者win,这里是不同的
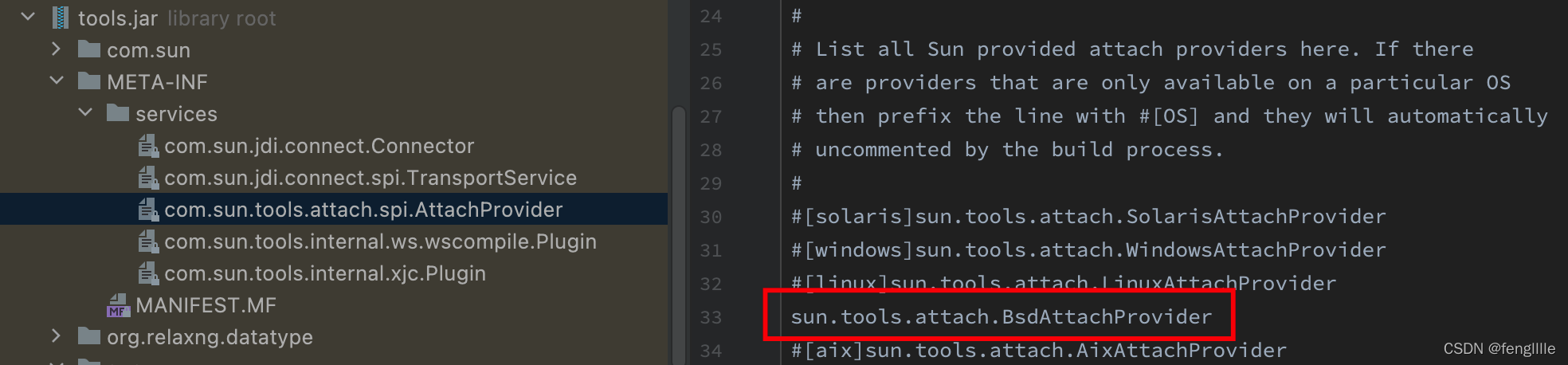
逻辑大同小异:
static {
System.loadLibrary("attach");
tmpdir = getTempDir();
}
先load c的lib,然后获取临时目录
BsdVirtualMachine(AttachProvider provider, String vmid)
throws AttachNotSupportedException, IOException
{
super(provider, vmid);
// This provider only understands pids
int pid;
try {
pid = Integer.parseInt(vmid);
} catch (NumberFormatException x) {
throw new AttachNotSupportedException("Invalid process identifier");
}
//这段注释很明显,先找socket文件,找不到就创建attach文件,发送quit信号,再试查找socket文件
// Find the socket file.
// If not found then we attempt to start the attach mechanism in the target VM by sending it a QUIT signal.
// Then we attempt to find the socket file again.
//查找socket文件
path = findSocketFile(pid);
if (path == null) {
File f = new File(tmpdir, ".attach_pid" + pid);
//创建attach文件
createAttachFile(f.getPath());
try {
//发送退出信号,启动attach mechanism连接途径
sendQuitTo(pid);
// give the target VM time to start the attach mechanism
int i = 0;
long delay = 200;
int retries = (int)(attachTimeout() / delay);
do {
try {
Thread.sleep(delay);
} catch (InterruptedException x) { }
//多次查找socket文件
path = findSocketFile(pid);
i++;
} while (i <= retries && path == null);
if (path == null) {
throw new AttachNotSupportedException(
"Unable to open socket file: target process not responding " +
"or HotSpot VM not loaded");
}
} finally {
f.delete();
}
}
// Check that the file owner/permission to avoid attaching to
// bogus process
checkPermissions(path);
// Check that we can connect to the process
// - this ensures we throw the permission denied error now rather than
// later when we attempt to enqueue a command.
//socket创建
int s = socket();
try {
//连接socket,相当于远程(另一个jvm进程)连上了pid
connect(s, path);
} finally {
close(s);
}
}
// Return the socket file for the given process.
// Checks temp directory for .java_pid<pid>.
private String findSocketFile(int pid) {
String fn = ".java_pid" + pid;
File f = new File(tmpdir, fn);
return f.exists() ? f.getPath() : null;
}建立socket连接,就进行下一步,loadjar
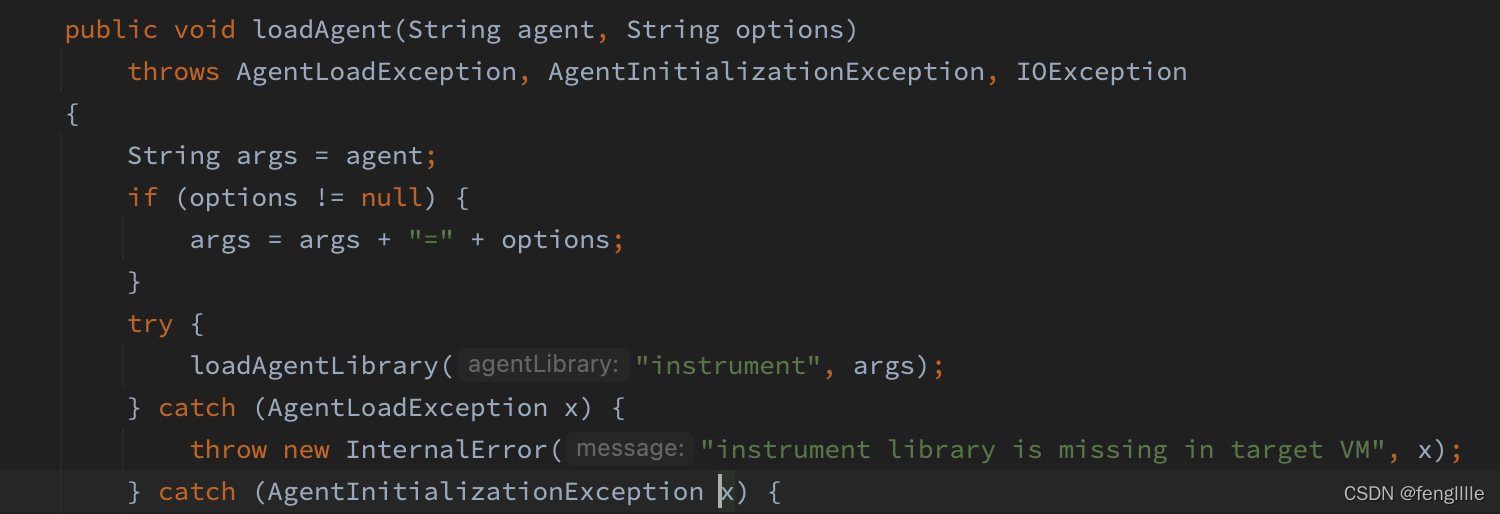
实际上这里就可以看到是要加载instrument。执行load指令,拿到结果,实际上load jar加载结束,agent就注入生效了,这个过程是JDK触发完成
private void loadAgentLibrary(String agentLibrary, boolean isAbsolute, String options)
throws AgentLoadException, AgentInitializationException, IOException
{
InputStream in = execute("load",
agentLibrary,
isAbsolute ? "true" : "false",
options);
try {
int result = readInt(in);
if (result != 0) {
throw new AgentInitializationException("Agent_OnAttach failed", result);
}
} finally {
in.close();
}
}继续load
InputStream execute(String cmd, Object ... args) throws AgentLoadException, IOException {
assert args.length <= 3; // includes null
// did we detach?
String p;
synchronized (this) {
if (this.path == null) {
throw new IOException("Detached from target VM");
}
p = this.path;
}
// create UNIX socket
int s = socket();
// connect to target VM
try {
connect(s, p);
} catch (IOException x) {
close(s);
throw x;
}
IOException ioe = null;
// connected - write request
// <ver> <cmd> <args...>
try {
writeString(s, PROTOCOL_VERSION);
writeString(s, cmd);
for (int i=0; i<3; i++) {
if (i < args.length && args[i] != null) {
//把jar的路径写给JVM,就结束了,JVM指令执行load指令
writeString(s, (String)args[i]);
} else {
writeString(s, "");
}
}
} catch (IOException x) {
ioe = x;
}
// Create an input stream to read reply
SocketInputStream sis = new SocketInputStream(s);
// Read the command completion status
int completionStatus;
try {
completionStatus = readInt(sis);
} catch (IOException x) {
sis.close();
if (ioe != null) {
throw ioe;
} else {
throw x;
}
}
if (completionStatus != 0) {
sis.close();
// In the event of a protocol mismatch then the target VM
// returns a known error so that we can throw a reasonable
// error.
if (completionStatus == ATTACH_ERROR_BADVERSION) {
throw new IOException("Protocol mismatch with target VM");
}
// Special-case the "load" command so that the right exception is
// thrown.
if (cmd.equals("load")) {
throw new AgentLoadException("Failed to load agent library");
} else {
throw new IOException("Command failed in target VM");
}
}
// Return the input stream so that the command output can be read
return sis;
}jdk里面如何执行的呢,打开OpenJDK InvocationAdapter.c,jvm参数加载的agent执行
Agent_OnLoad函数
而动态attach的agent,执行
Agent_OnAttach函数

之所以读取manifest文件是jdk定义的,这个是动态attach,读取Agent-Class,另外还有 boot-class-path

下面才是核心
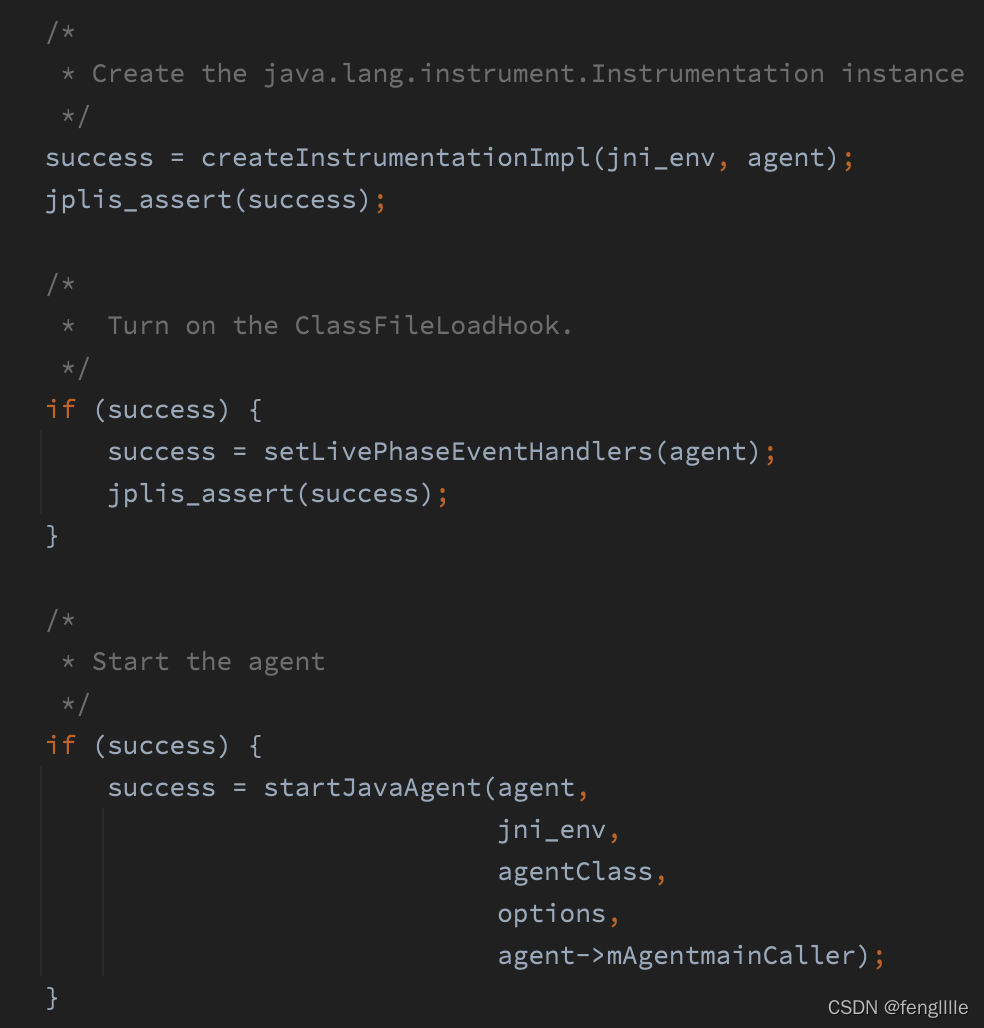
3部曲
1. 创建InstrumentationImpl实例
2. 打开ClassFileLoadHook,这个与字节码替换回调相关
3. 启动agent,实际上是调用第一步创建InstrumentationImpl实例的loadClassAndCallAgentmain方法
private void loadClassAndCallPremain(String var1, String var2) throws Throwable {
this.loadClassAndStartAgent(var1, "premain", var2);
}
private void loadClassAndCallAgentmain(String var1, String var2) throws Throwable {
this.loadClassAndStartAgent(var1, "agentmain", var2);
}另一个方法就是jvm参数方式的调用函数
3. idea debug
之所以说idea的debug能力是笔者在使用jmx技术时,发现😋
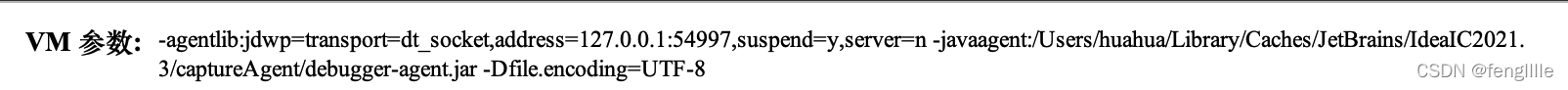
是不是很有意思,-javaagent
前面是jvmti的能力,开启debug,后面居然是一个agent,有意思
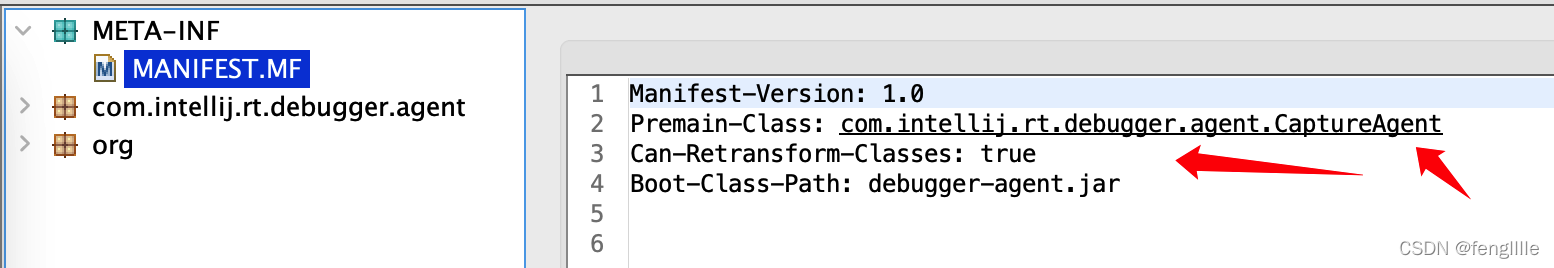
然后查看这个premain的class
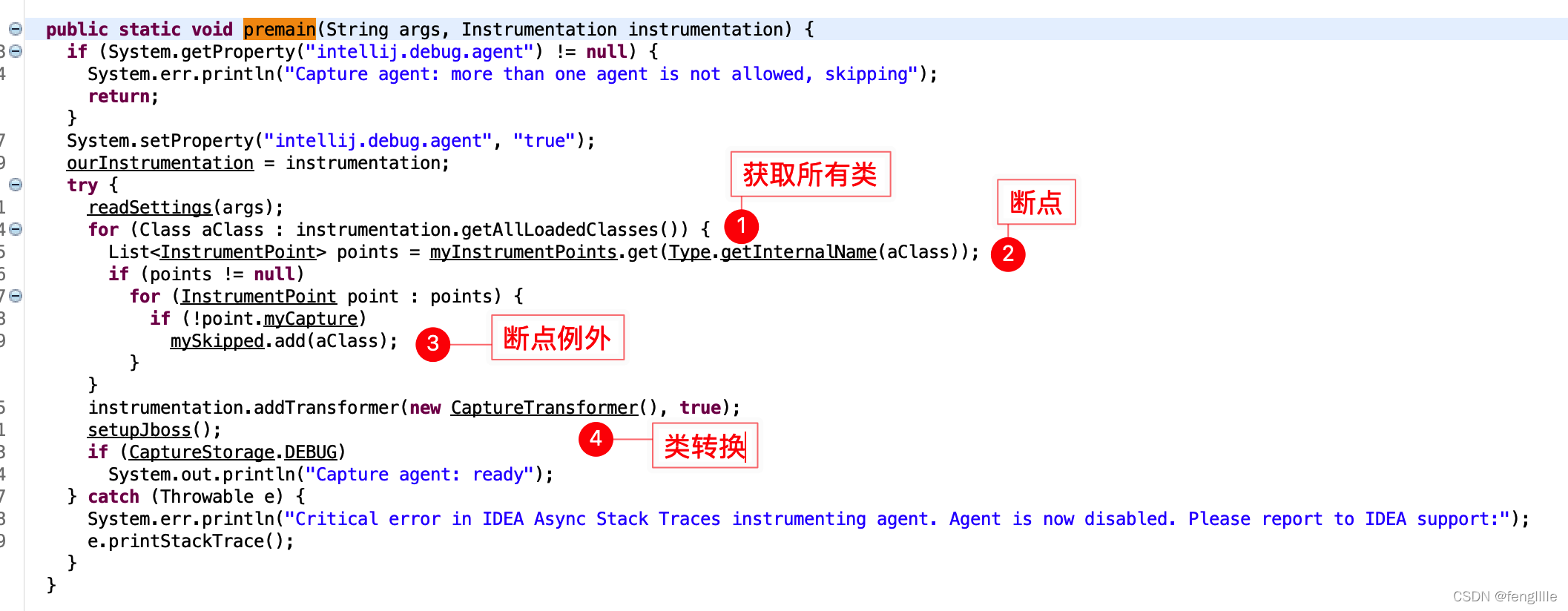
idea转换器,关键类
CaptureInstrumentor来capture方法
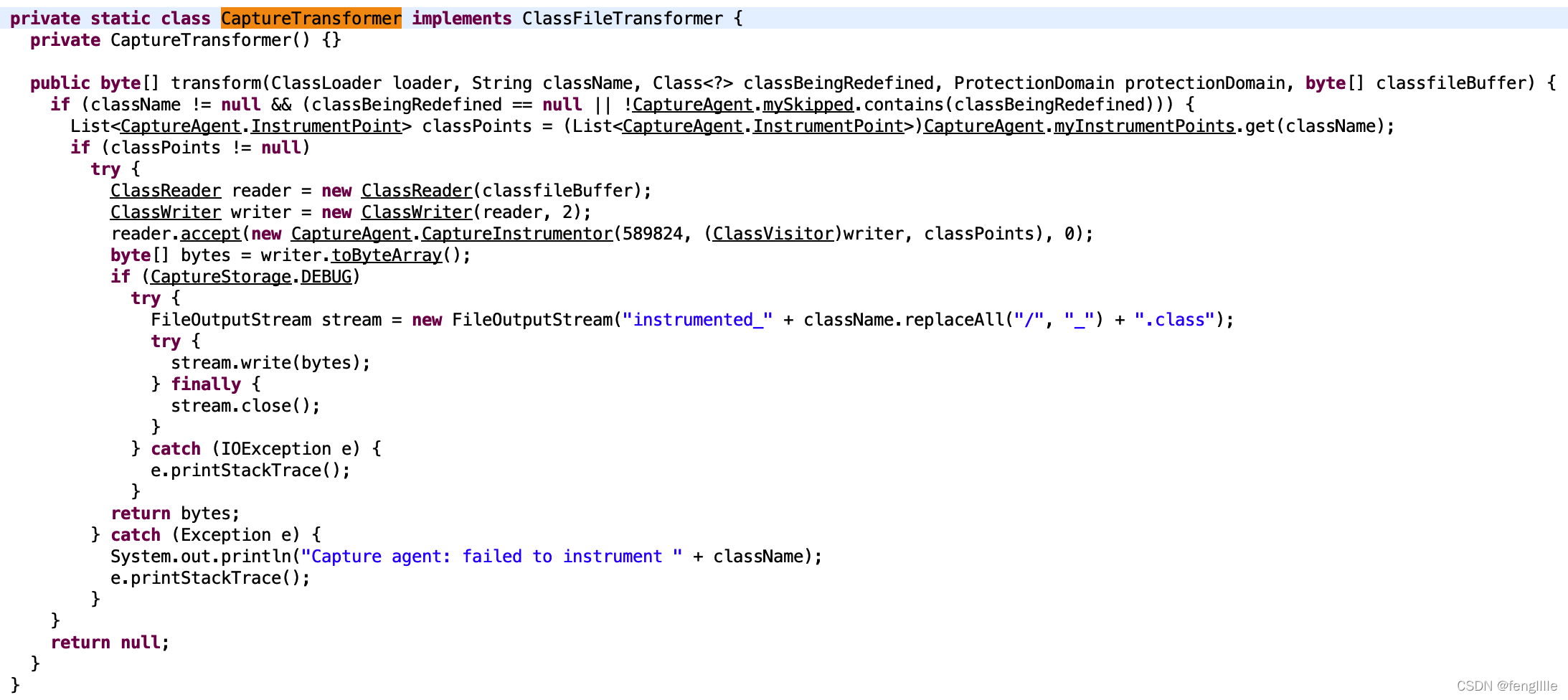
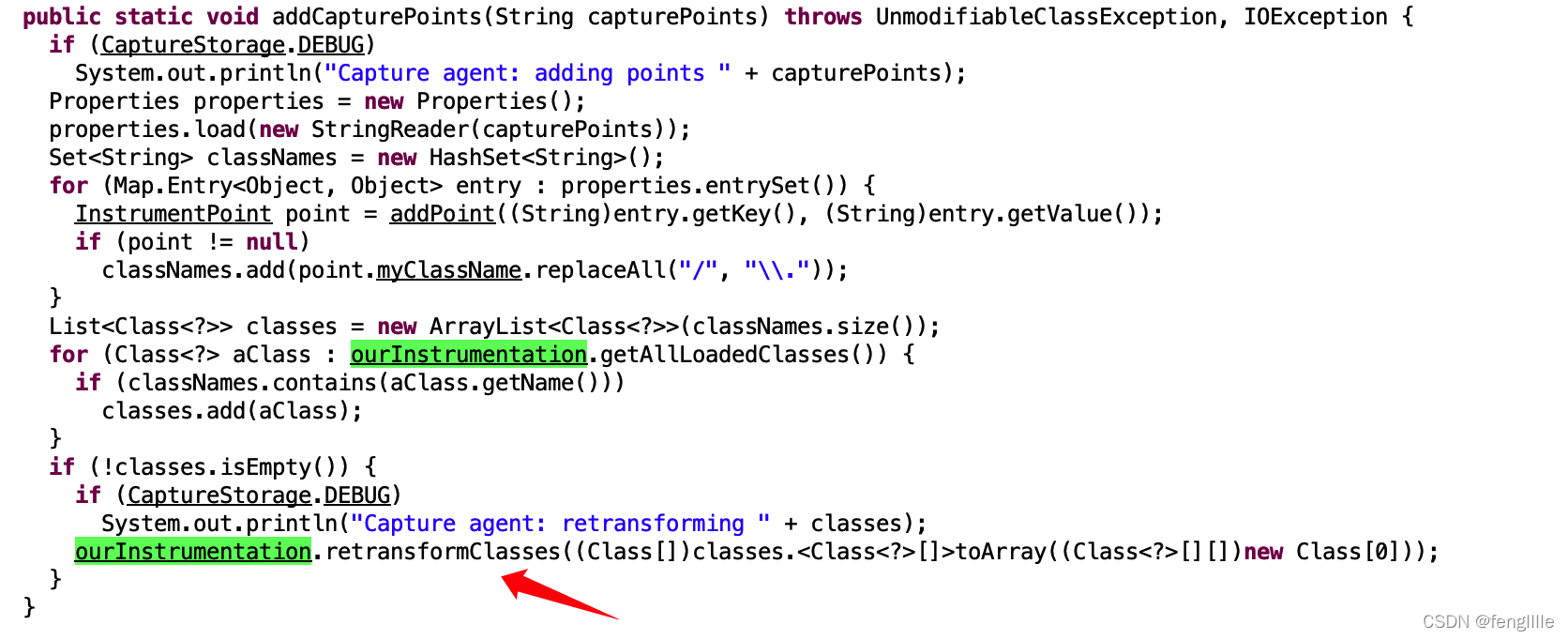
打断点的时候,类转换了
总结
实际上Javaagent类似一个sidecar的能力,不侵入应用代码即可实现字节码替换的原理,执行前检查,通过字节码修改的方式。
如果配合jmx技术,那么可以用来做APM系统非常nice,实际上pinpoint skywalking等也是使用的这种技术实现的,本次讲解了Javaagent的实现原理,现在使用就会非常明白。







 本文详细介绍了Javaagent的使用和原理,包括动态attach方式加载agent,通过字节码修改实现类的增强。通过示例代码展示了如何创建agentjar,如何使用attach工具远程加载,并解析了JVM的加载逻辑。最后,讨论了IDEA中的debug与Javaagent的关系,揭示了Javaagent在APM系统中的应用潜力。
本文详细介绍了Javaagent的使用和原理,包括动态attach方式加载agent,通过字节码修改实现类的增强。通过示例代码展示了如何创建agentjar,如何使用attach工具远程加载,并解析了JVM的加载逻辑。最后,讨论了IDEA中的debug与Javaagent的关系,揭示了Javaagent在APM系统中的应用潜力。
















 8853
8853

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








