反转链表是一个很常见的面试题,一般来说,可以借助栈做反转,利用栈先进后出的特点,反转很容易理解,今天要介绍的是剑指Offer名企面试上的一种做法。这种做法是使用两个指针pre,cur,两者相差1个节点的位置,当我们遍历的时候,就把原来next的关系给调转一下,cur.next=pre。这样当链表头部遍历到尾部的时候,新的链表就诞生了,而且链表的关系也切换了。主要的代码如下:
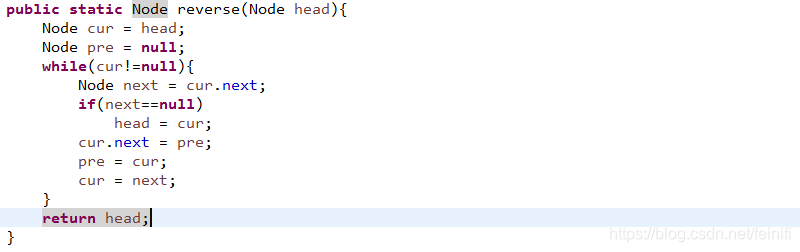
这个做法很精妙,一次遍历就可以搞定,就是需要把握头结点的位置,以及每个节点的next关系。不能简单的将next修改,否则容易形成一个环形链表。
完整代码:
package com.xxx.algorithm.sort;
import java.util.Stack;
public class LinkedListReverse {
public static Node reverseLinkedList(Node head){
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
while(head!=null){
stack.push(head);
head = head.next;
}
if(!stack.isEmpty())
head = stack.pop();
Node cur = head;
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
Node node = stack.pop();
node.next = null;
cur.next = node;
cur = node;
}
return head;
}
public static Node reverse(Node head){
Node cur = head;
Node pre = null;
while(cur!=null){
Node next = cur.next;
if(next==null)
head = cur;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return head;
}
public static void display(Node head){
System.out.print("list:");
Node cur = head;
while(cur!=null){
System.out.print(cur+"->");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node a = new Node("a");
Node b = new Node("b");
Node c = new Node("c");
Node d = new Node("d");
Node e = new Node("e");
Node f = new Node("f");
Node g = new Node("g");
a.next = b;
b.next = c;
c.next = d;
d.next = e;
e.next = f;
f.next = g;
System.out.println("原始链表:");
display(a);
Node head = reverse(a);
System.out.println("反转之后的链表:");
display(head);
}
}
class Node{
String val;
Node next;
public Node(String val) {
this.val = val;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node("+this.val+")";
}
}
运行之后,打印信息如下所示:
原始链表:
list:Node(a)->Node(b)->Node(c)->Node(d)->Node(e)->Node(f)->Node(g)->
反转之后的链表:
list:Node(g)->Node(f)->Node(e)->Node(d)->Node(c)->Node(b)->Node(a)->
这就是剑指Offer面试题16的解决办法的Java实现。





 本文介绍了剑指Offer中链表反转的经典解法,通过双指针pre和cur,仅需一次遍历即可完成链表的反转,避免了使用栈的空间复杂度。此方法巧妙地调整了链表节点的next指向,确保新链表正确生成。
本文介绍了剑指Offer中链表反转的经典解法,通过双指针pre和cur,仅需一次遍历即可完成链表的反转,避免了使用栈的空间复杂度。此方法巧妙地调整了链表节点的next指向,确保新链表正确生成。

















 389
389

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










