一、AIDL
1.1 AIDL的作用
通过代码来实现这个数据传输过程是冗长乏味的,Android提供了AIDL工具来处理这项工作。
AIDL IPC机制是面向接口的,像COM或Corba一样,但是更加轻量级。它是使用代理类在客户端和实现端传递数据。
1.2 选择AIDL的使用场合
- Calls made from the local process are executed in the same thread that is making the call. If this is your main UI thread, that thread continues to execute in the AIDL interface. If it is another thread, that is the one that executes your code in the service. Thus, if only local threads are accessing the service, you can completely control which threads are executing in it (but if that is the case, then you shouldn't be using AIDL at all, but should instead create the interface byimplementing a Binder).
- Calls from a remote process are dispatched from a thread pool the platform maintains inside of your own process. You must be prepared for incoming calls from unknown threads, with multiple calls happening at the same time. In other words, an implementation of an AIDL interface must be completely thread-safe.
- The
onewaykeyword modifies the behavior of remote calls. When used, a remote call does not block; it simply sends the transaction data and immediately returns. The implementation of the interface eventually receives this as a regular call from theBinderthread pool as a normal remote call. Ifonewayis used with a local call, there is no impact and the call is still synchronous.
3. 抛出的异常是不能返回给调用者(跨进程抛异常处理是不可取的)。
1.3 使用AIDL
使用AIDL实现IPC服务的步骤是:
1. 创建.aidl文件-该文件(YourInterface.aidl)定义了客户端可用的方法和数据的接口。
2. 实现接口-AIDL编译器从AIDL接口文件中利用Java语言创建接口,该接口有一个继承的命名为Stub的内部抽象类(并且实现了一些IPC调用的附加方法),要做的就是创建一个继承于YourInterface.Stub的类并且实现在.aidl文件中声明的方法。
3. 向客户端公开接口-如果是编写服务,应该继承Service并且重载Service.onBind(Intent) 以返回实现了接口的对象实例
1.3.1 定义AIDL接口
- 每个aidl文件只能定义一个接口,而且只能是接口的声明和方法的声明。
- AIDL使用简单的语法来声明接口,描述其方法以及方法的参数和返回值。这些参数和返回值可以是任何类型,甚至是其他AIDL生成的接口。
- 其中对于Java编程语言的基本数据类型 (int, long, char, boolean等),String和CharSequence,集合接口类型List和Map,不需要import 语句。
- 而如果需要在AIDL中使用其他AIDL接口类型,需要import,即使是在相同包结构下。AIDL允许传递实现Parcelable接口的类,需要import.
- 需要特别注意的是,对于非基本数据类型,也不是String和CharSequence类型的,需要有方向指示,包括in、out和inout,in表示由客户端设置,out表示由服务端设置,inout是两者均可设置。
- AIDL只支持接口方法,不能公开static变量。
例如A应用通过服务Service方式向B应用提供通过书籍编号来查询书籍名称的服务)
A应用程序结构图如下:
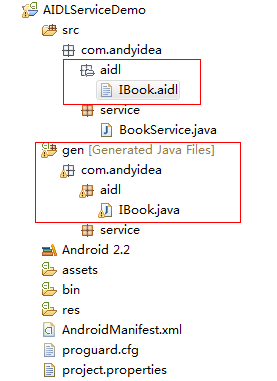
通过上面的结构图可以看到,在A应用程序中创建一个 aidl 的接口,然后系统在 gen 目录下自动生成相应的 java 文件。
package com.andyidea.aidl;
interface IBook {
String queryBook(int bookNo);
}
Android SDK tools就会在gen目录自动生成一个IBinder接口文件, 生成Proxy、Stub(抽象类)两个类。
Proxy
Proxy运行在客户端,它实现了IBook接口,并且持有一个远程代理IBinder mRemote,mRemote不做任何业务逻辑处理,仅仅通过IBinder接口的transact()方法,把客户端的调用参数序列化后transact到远程服务器。
Stub
- Stub运行在服务器端,继承自Binder,同样也实现了IBook接口,它的核心逻辑在onTransact方法中
- Stub中另外一个比较重要的接口就是asInterface()接口通过方法名字,我们大致可以猜出,它大概实现的功能,就是将一个IBinder对象转化为接口对象。
如果客户端和服务端在同一个进程下,那么asInterface()将返回Stub对象本身,否则返回Stub.Proxy对象。
也就是说asInterface()返回的对象有两种可能(实际上有三种,还有一种是null),Stub和Stub.Proxy。它们有什么区别呢?
- 如果在同一个进程下的话,那么asInterface()将返回服务端的Stub对象本身,因为此时根本不需要跨进称通信,那么直接调用Stub对象的接口就可以了,返回的实现就是服务端的Stub实现,也就是根本没有跨进程通信;
- 如果不是同一个进程,那么asInterface()返回是Stub.Proxy对象,该对象持有着远程的Binder引用,因为现在需要跨进程通信,所以如果调用Stub.Proxy的接口的话,那么它们都将是IPC调用,它会通过调用transact方法去与服务端通信。
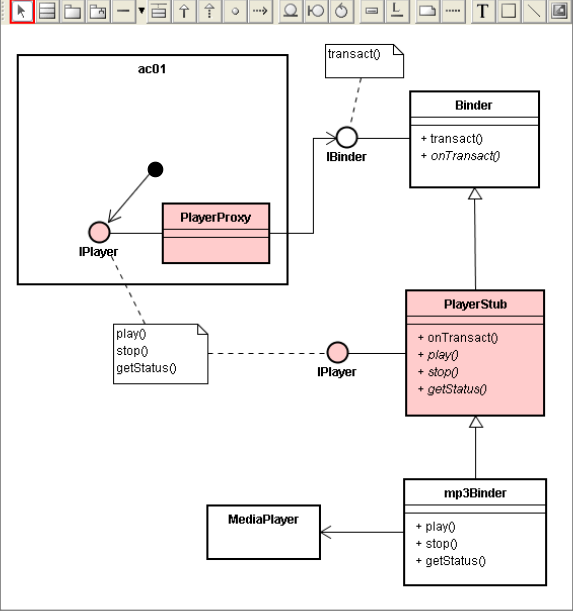
1)定义IPlayer接口:定义了play,stop的接口,确定client和remote端需要实现的接口。
2)实现mp3Binder的Stub和Proxy:Stub和Proxy都封装play,stop接口。
3)myActivity通过startService,获取到mp3Binder的proxy对象
4)myActivity调用proxy的play或者stop,proxy通过transact将参数传递给Stub的OnTranstact
5)Stub的OnTranstact解析参数,并执行响应的动作
1.3.2 实现接口
package com.andyidea.service;
import com.andyidea.aidl.IBook;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
/**
* 查询书籍的服务
* @author Andy
*
*/
public class BookService extends Service {
private String[] bookNames = {"Java编程思想","设计模式","Android开发设计"};
private IBinder mIBinder = new BookBinder();
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return mIBinder;
}
/**
* 服务中交互的方法
* @param bookNo
* @return
*/
public String queryBookName(int bookNo){
if(bookNo > 0 && bookNo <= bookNames.length){
return bookNames[bookNo-1];
}
return null;
}
private class BookBinder extends IBook.Stub{
@Override
public String queryBook(int bookNo) throws RemoteException {
return queryBookName(bookNo);
}
}
} 这里会看到有一个名为IBook.Stub类,查看aidl文件生成的Java文件源代码就能发现有这么一段代码:
/** Local-side IPC implementation stub class. */
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements com.demo.IBook原来Stub类就是继承于Binder类,也就是说BookService类和普通的Service类没什么不同,只是所返回的IBinder对象比较特别,是一个实现了AIDL接口的Binder。
同时别忘了在 Manifest.xml中配置该服务对象(标红色的部分),建议采用隐式方式激活该服务,适合不同的进程的意图。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.andyidea.service"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8" />
<application
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<service android:name=".BookService">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.andyidea.aidl.bookservice"/>
</intent-filter>
</service></span>
</application>
</manifest> 1.3.3 客户端获取接口
以上我们已经实现了A应用程序提供服务的功能,下面我们来实现B应用(或者其它需要用到A应用提供服务的应用程序)
B应用程序结构图如下:
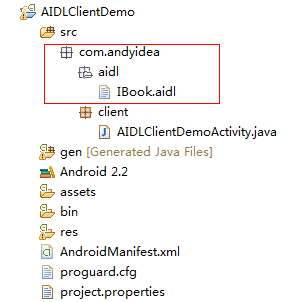
我们看到B应用程序也要和服务端同样的 .aidl 文件,我们可以从A应用程序中把该 aidl 文件中拷贝过来就是了
其中AIDLClientDemoActivity.java源码如下:【注:其中该客户端类要通过 bindService 方式来启动另外一个进程的服务,这样才能实现和服务进行交互。如果通过startService方式来启动服务,则不能与服务进行交互】
import com.andyidea.aidl.IBook;
public class AIDLClientDemoActivity extends Activity {
private EditText numberText;
private TextView resultView;
private Button query;
private IBook bookQuery;
private BookConnection bookConn = new BookConnection();
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
numberText = (EditText) this.findViewById(R.id.number);
resultView = (TextView) this.findViewById(R.id.resultView);
query = (Button)findViewById(R.id.query);
Intent service = new Intent("com.andyidea.aidl.bookservice");
bindService(service, bookConn, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
query.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
String number = numberText.getText().toString();
int num = Integer.valueOf(number);
try {
resultView.setText(bookQuery.queryBook(num));
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
unbindService(bookConn);
super.onDestroy();
}
private final class BookConnection implements ServiceConnection{
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
bookQuery = IBook.Stub.asInterface(service);
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
bookQuery = null;
}
}
} 客户端如何获取AIDL接口呢?通过IBook.Stub.asInterface(service)来得到IBook对象:在生成的IBook.java里面会找到这样的代码:
/**
* Cast an IBinder object into an com.demo.IMyService interface,
* generating a proxy if needed.
*/
public static com.demo.IBook asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj) {...}
1.3.4 通过IPC调用/传递数据
1.3.5 自定义类型Bean
1) void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) 将需要序列化存储的数据写入外部提供的Parcel对象dest。而看了网上的代码例子,个人猜测,读取Parcel数据的次序要和这里的write次序一致,否则可能会读错数据。具体情况我没试验过!
2) describeContents() 没搞懂有什么用,反正直接返回0也可以
3) static final Parcelable.Creator对象CREATOR 这个CREATOR命名是固定的,而它对应的接口有两个方法:
createFromParcel(Parcel source) 实现从source创建出JavaBean实例的功能
newArray(int size) 创建一个类型为T,长度为size的数组,仅一句话(return new T[size])即可。估计本方法是供外部类反序列化本类数组使用。
public class Person implements Parcelable {
private String name;
private String telNumber;
private int age;
public Person() {}
public Person(Parcel pl){
name = pl.readString();
telNumber = pl.readString();
age = pl.readInt();
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getTelNumber() {
return telNumber;
}
public void setTelNumber(String telNumber) {
this.telNumber = telNumber;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) {
dest.writeString(name);
dest.writeString(telNumber);
dest.writeInt(age);
}
public static final Parcelable.Creator<Person> CREATOR = new Parcelable.Creator<Person>() {
@Override
public Person createFromParcel(Parcel source) {
return new Person(source);
}
@Override
public Person[] newArray(int size) {
return new Person[size];
}
};
}
package com.demo;
parcelable Person;1.3.6 远程服务
Permission权限
如果Service在AndroidManifest.xml中声明了全局的强制的访问权限,其他引用必须声明权限才能来start,stop或bind这个service.
另外,service可以通过权限来保护她的IPC方法调用,通过调用checkCallingPermission(String)方法来确保可以执行这个操作。
AndroidManifest.xml的Service元素
<service android:name=".BookService" android:process=":remote">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="xxx" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
android:process
The name of the process where the service is to run. Normally, all components of an application run in the default process created for the application. It has the same name as the application package. The <application> element's process attribute can set a different default for all components. But component can override the default with its own process attribute, allowing you to spread your application across multiple processes.If the name assigned to this attribute begins with a colon (':'), a new process, private to the application, is created when it's needed and the service runs in that process. If the process name begins with a lowercase character, the service will run in a global process of that name, provided that it has permission to do so. This allows components in different applications to share a process, reducing resource usage.





 本文详细介绍了Android接口定义语言(AIDL)的使用方法,包括AIDL的作用、适用场景、接口定义及其实现过程。此外,还讲解了如何在客户端和服务端之间进行进程间通信(IPC)以及如何传递自定义数据。
本文详细介绍了Android接口定义语言(AIDL)的使用方法,包括AIDL的作用、适用场景、接口定义及其实现过程。此外,还讲解了如何在客户端和服务端之间进行进程间通信(IPC)以及如何传递自定义数据。
















 3084
3084

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








