这篇笔记记录了连接跟踪子系统对L3和L4协议的管理,核心代码涉及如下文件:
| 代码路径 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| net/netfilter/nf_conntrack_l3proto.c | 对L3和L4协议的管理 |
| include/net/netfilter/nf_conntrack_l3proto.h | L3协议相关数据结构定义 |
| include/net/netfilter/nf_conntrack_l4proto.h | L4协议相关数据结构定义 |
1. L3协议管理
每个支持连接跟踪子系统的L3协议(或者说协议族),都必须先向连接跟踪子系统注册自己,实际上就是提供一个struct nf_conntrack_l3proto对象。
1.1 struct nf_conntrack_l3proto
L3协议在连接跟踪子系统中的定义如下:
struct nf_conntrack_l3proto
{
//L3协议号,就是用协议族表示,如PF_INET
u_int16_t l3proto;
//协议的名字,如AF_INET协议族为“ipv4”
const char *name;
//根据skb内容计算tuple,tuple可以理解为连接的地址,每一个连接有两个tuple,
//分别表示数据传输的两个方向。nhoff表示L3首部在skb中的偏移,如果计算成功,
//返回true,否则返回false(必选回调)
int (*pkt_to_tuple)(const struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int nhoff,
struct nf_conntrack_tuple *tuple);
//根据orig方向的tuple,计算其反方向的tuple
int (*invert_tuple)(struct nf_conntrack_tuple *inverse,
const struct nf_conntrack_tuple *orig);
int (*print_tuple)(struct seq_file *s, const struct nf_conntrack_tuple *);
//数据包进入连接跟踪子系统后,通过检查后,会调用该回调确定返回给Netfilter框架的值,
//一般来讲,连接跟踪子系统不应该过滤数据包,所以该函数大多数情况下应该返回NF_ACCEPT
int (*packet)(struct nf_conn *ct, const struct sk_buff *skb,
enum ip_conntrack_info ctinfo);
//如果输入的数据包属于一个新的连接,那么会调用该回调
int (*new)(struct nf_conn *ct, const struct sk_buff *skb);
//分析skb首部,解析出L4协议号保存在protonum中,L4报文开始位置距离skb第一个
//字节的偏移量保存在dataoff中,处理成功返回大于0(必选回调)
int (*get_l4proto)(const struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int nhoff,
unsigned int *dataoff, u_int8_t *protonum);
//下面三个字段和Netlink相关,用于和用户空间通信,先忽略
int (*tuple_to_nlattr)(struct sk_buff *skb,
const struct nf_conntrack_tuple *t);
int (*nlattr_to_tuple)(struct nlattr *tb[],
struct nf_conntrack_tuple *t);
const struct nla_policy *nla_policy;
#ifdef CONFIG_SYSCTL
//L3协议可以指定一些属于自己的系统配置参数
struct ctl_table_header *ctl_table_header;
struct ctl_path *ctl_table_path;
struct ctl_table *ctl_table;
#endif /* CONFIG_SYSCTL */
struct module *me;
};
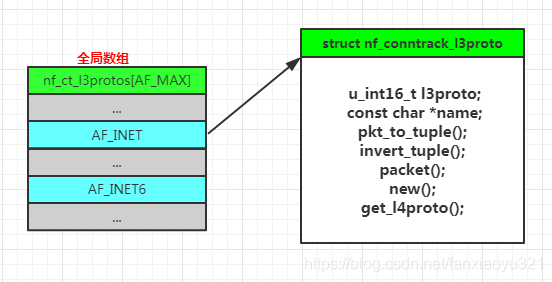
连接跟踪子系统用全局数组保存各个协议族注册的struct nf_conntrack_l3proto对象,每个协议族只能注册一个该对象。
struct nf_conntrack_l3proto *nf_ct_l3protos[AF_MAX] __read_mostly;
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(nf_ct_l3protos);
static DEFINE_MUTEX(nf_ct_proto_mutex);
L3协议的组织结构如下图所示:
1.2 L3协议的注册
上面也有提到过,支持连接跟踪子系统的协议族在其初始化过程中需要向连接跟踪子系统注册自己的struct nf_conntrack_l3proto对象,注册函数如下:
int nf_conntrack_l3proto_register(struct nf_conntrack_l3proto *proto)
{
int ret = 0;
//当前版本支持的协议族最大值为AF_MAX=34
if (proto->l3proto >= AF_MAX)
return -EBUSY;
mutex_lock(&nf_ct_proto_mutex);
//同一协议族不允许重复注册,如下面的初始化过程,nf_ct_l3_protos[]的每个元素
//在初始化时都被设置成了nf_conntrack_l3proto_generic,表示尚未注册
if (nf_ct_l3protos[proto->l3proto] != &nf_conntrack_l3proto_generic) {
ret = -EBUSY;
goto out_unlock;
}
//注册L3协议可能存在的系统参数
ret = nf_ct_l3proto_register_sysctl(proto);
if (ret < 0)
goto out_unlock;
//将proto记录到全局数组的对应位置,完成注册
rcu_assign_pointer(nf_ct_l3protos[proto->l3proto], proto);
out_unlock:
mutex_unlock(&nf_ct_proto_mutex);
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(nf_conntrack_l3proto_register);
nf_conntrack_l3proto_unregister()是对应的去注册函数,不再赘述。
2. L4协议的管理
类似于L3协议的管理,连接跟踪子系统也使用一个全局的数组管理支持的L4协议,不过这个数组是二维数组。
//和L3协议使用同一把互斥锁
static struct nf_conntrack_l4proto **nf_ct_protos[PF_MAX] __read_mostly;
static DEFINE_MUTEX(nf_ct_proto_mutex);
其实使用二维数组的原因也很简单,因为一种L3协议可以支持多种L4协议,所以该二维数组的一维索引就是协议族,然后二维长度可变,视不同协议族的支持情况而定。
2.1 struct nf_conntrack_l4proto
L4协议在连接跟踪子系统中的定义如下:
struct nf_conntrack_l4proto
{
/* L3 Protocol number. */
u_int16_t l3proto;
/* L4 Protocol number. */
u_int8_t l4proto;
//根据skb内容生成tuple,tuple用于标示一条连接。nhoff表示L4首部在skb中的偏移;
//如果转换成功,返回true,否则返回false(必选回调)。连接跟踪子系统会优先调用
//L3协议的pkt_to_tuple()生成tuple,只有L3协议生成失败时才会调用L4协议的回调
int (*pkt_to_tuple)(const struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int dataoff,
struct nf_conntrack_tuple *tuple);
int (*invert_tuple)(struct nf_conntrack_tuple *inverse,
const struct nf_conntrack_tuple *orig);
int (*packet)(struct nf_conn *ct, const struct sk_buff *skb,
unsigned int dataoff, enum ip_conntrack_info ctinfo,
int pf, unsigned int hooknum);
int (*new)(struct nf_conn *ct, const struct sk_buff *skb,
unsigned int dataoff);
/* Called when a conntrack entry is destroyed */
void (*destroy)(struct nf_conn *ct);
//L4协议可以通过该回调校验skb,校验通过返回大于0(可选回调)
int (*error)(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int dataoff,
enum ip_conntrack_info *ctinfo,
int pf, unsigned int hooknum);
int (*print_tuple)(struct seq_file *s, const struct nf_conntrack_tuple *);
/* Print out the private part of the conntrack. */
int (*print_conntrack)(struct seq_file *s, const struct nf_conn *);
//netlink相关
int (*to_nlattr)(struct sk_buff *skb, struct nlattr *nla,
const struct nf_conn *ct);
int (*from_nlattr)(struct nlattr *tb[], struct nf_conn *ct);
int (*tuple_to_nlattr)(struct sk_buff *skb,
const struct nf_conntrack_tuple *t);
int (*nlattr_to_tuple)(struct nlattr *tb[],
struct nf_conntrack_tuple *t);
const struct nla_policy *nla_policy;
#ifdef CONFIG_SYSCTL
struct ctl_table_header **ctl_table_header;
struct ctl_table *ctl_table;
unsigned int *ctl_table_users;
#ifdef CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK_PROC_COMPAT
struct ctl_table_header *ctl_compat_table_header;
struct ctl_table *ctl_compat_table;
#endif
#endif
//L4协议名字
const char *name;
struct module *me;
};
可见,L4协议的内容和L3协议基本类似,其含义和调用场景也相同。
2.2 L4协议的注册
int nf_conntrack_l4proto_register(struct nf_conntrack_l4proto *l4proto)
{
int ret = 0;
//当前版本L4协议号不能超过PF_MAX=34
if (l4proto->l3proto >= PF_MAX)
return -EBUSY;
mutex_lock(&nf_ct_proto_mutex);
//注册L3协议的第一个L4协议,在全局结构nf_ct_protos[]中分配空间
if (!nf_ct_protos[l4proto->l3proto]) {
/* l3proto may be loaded latter. */
struct nf_conntrack_l4proto **proto_array;
int i;
//最多分配256个,也就是说每个L3协议在连接跟踪子系统中最多可以支持256个L4协议
proto_array = kmalloc(MAX_NF_CT_PROTO *
sizeof(struct nf_conntrack_l4proto *), GFP_KERNEL);
if (proto_array == NULL) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto out_unlock;
}
//分配完毕,将该L3协议的所有L4协议初始化为nf_conntrack_l4proto_generic,
//和L3协议的含义一样,这表示一种未注册状态
for (i = 0; i < MAX_NF_CT_PROTO; i++)
proto_array[i] = &nf_conntrack_l4proto_generic;
//nf_ct_protos[]指向新分配的空间
nf_ct_protos[l4proto->l3proto] = proto_array;
} else if (nf_ct_protos[l4proto->l3proto][l4proto->l4proto] !=
&nf_conntrack_l4proto_generic) {
//不是第一次注册L4协议,检查该L4协议之前是否已经注册过了
ret = -EBUSY;
goto out_unlock;
}
//注册该L4协议可能支持的sysctl系统参数
ret = nf_ct_l4proto_register_sysctl(l4proto);
if (ret < 0)
goto out_unlock;
//注册成功,保存L4协议到全局数组nf_ct_protos[]中
rcu_assign_pointer(nf_ct_protos[l4proto->l3proto][l4proto->l4proto], l4proto)
out_unlock:
mutex_unlock(&nf_ct_proto_mutex);
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(nf_conntrack_l4proto_register);
对应的去注册函数为nf_conntrack_l4proto_unregister(),不再赘述。
3. 初始化
L3和L4协议管理由一个单独的模块实现,其初始化是由连接跟踪子系统的初始化函数nf_conntrack_init()调用的,初始化函数如下:
int nf_conntrack_proto_init(void)
{
unsigned int i;
int err;
//为默认的L4协议注册sysctl控制参数
err = nf_ct_l4proto_register_sysctl(&nf_conntrack_l4proto_generic);
if (err < 0)
return err;
//将每个层三协议族初始化为一个默认的非法struct nf_conntrack_l3proto对象
for (i = 0; i < AF_MAX; i++)
rcu_assign_pointer(nf_ct_l3protos[i], &nf_conntrack_l3proto_generic);
return 0;
}










 本文详细介绍了连接跟踪子系统中L3和L4协议的管理,包括struct nf_conntrack_l3proto和struct nf_conntrack_l4proto的结构,以及它们的注册和初始化过程。L3协议的全局数组保存各协议族注册的对象,L4协议则使用二维数组管理,以支持多协议。初始化过程由nf_conntrack_init()调用。
本文详细介绍了连接跟踪子系统中L3和L4协议的管理,包括struct nf_conntrack_l3proto和struct nf_conntrack_l4proto的结构,以及它们的注册和初始化过程。L3协议的全局数组保存各协议族注册的对象,L4协议则使用二维数组管理,以支持多协议。初始化过程由nf_conntrack_init()调用。
















 1263
1263

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








