手写简易的 Vuex
1.基本骨架
1.1 目录结构
1.2 src/store/index.js文件
这是本项目的src/store/index.js文件,看看一般vuex的使用。
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from './myvuex' // 引入自己写的 vuex
import * as getters from './getters'
import * as actions from './actions'
import state from './state'
import mutations from './mutations'
Vue.use(Vuex) // Vue.use(plugin)方法使用vuex插件
// vuex 导出一个类叫Store,并传入对象作为参数
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters,
})
1.3 Vue.use的用法
安装 Vue.js 插件。如果插件是一个对象,必须提供 install 方法。如果插件是一个函数,它会被作为 install 方法。install 方法调用时,会将 Vue 作为参数传入。这个方法的第一个参数是 Vue 构造器,第二个参数是一个可选的选项对象。
- 该方法需要在调用 new Vue() 之前被调用。
- 当 install 方法被同一个插件多次调用,插件将只会被安装一次。
即是我们需要在./myvuex.js中导出 install方法,同时导出一个类Store,于是第一步可以写出代码:
let Vue = null
class Store {
constructor(options) {}
}
function install(_Vue) {
Vue = _Vue // 上面Store类需要能获取到Vue
}
export default {
Store,
install,
}
2.实现思路
2.1 install方法
当我们使用 vuex 的时候,每一个组件上面都有一个this.$store属性,里面包含了 state,mutations, actions, getters 等,所以我们也需要在每个组件上都挂载一个$store 属性,要让每一个组件都能获取到,这里我们使用Vue.mixin(mixin),用法介绍如下:
全局注册一个混入,影响注册之后所有创建的每个 Vue 实例。可以使用混入向组件注入自定义的行为,它将影响每一个之后创建的 Vue 实例。
function install(_Vue) {
Vue = _Vue // install方法调用时,会将Vue作为参数传入(上面Store类需要用到Vue)
// 实现每一个组件,都能通过this调用$store
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
// 通过this.$options可以获取new Vue({参数}) 传递的参数
if (this.$options && this.$options.store) {
// 证明这个this是根实例,也就是new Vue产生的那个实例
this.$store = this.$options.store
} else if (this.$parent && this.$parent.$store) {
// 子组件获取父组件的$store属性
this.$store = this.$parent.$store
}
},
})
}
2.2 state方法
由于 Vuex 是基于 Vue 的响应式原理基础,所以我们要让数据改变可刷新视图,则需要创建一个 vue 实例。
class Store {
// options 即是 Vuex.Store({})传入的参数
constructor(options) {
// vuex 的核心就是借用了vue的实例,因为vue的实例数据变化,会刷新视图
let vm = new Vue({
data: {
state: options.state,
},
})
// state
this.state = vm.state
}
}
2.3 commit方法
我们使用vuex改变数据时,是触发 commit 方法,即是这样使用的:
this.$store.commit('eventName', '参数' );
所以我们要实现一个commit方法,把 Store 构造函数传入的 mutations 做下处理:
class Store {
constructor(options) {
// 实现 state ...
// mutations
this.mutations = {} // 存储传进来的mutations
let mutations = options.mutations || {}
// 循环取出事件名进行处理(mutations[事件名]: 执行方法)
Object.keys(mutations).forEach(key => {
this.mutations[key] = params => {
mutations[key].call(this, this.state, params) // 修正this指向
}
})
}
commit = (key, params) => {
// key为要触发的事件名
this.mutations[key](params)
}
}
2.4 dispatch方法
跟上面的commit流程同理。
class Store {
constructor(options = {}) {
// ...
// actions
this.actions = {}
let actions = options.actions || {}
Object.keys(actions).forEach(key => {
this.actions[key] = params => {
actions[key].call(this, this, params)
}
})
}
dispatch = (type, payload) => {
this.actions[type](payload)
}
}
2.5 getters方法
getters 实际就是返回 state 的值,在使用的时候是放在 computed 属性,每一个 getter 都是函数形式;
getters 是需要双向绑定的。但不需要双向绑定所有的 getters,只需要绑定项目中事件使用的 getters。
这里使用Object.defineProperty()方法,它会直接在一个对象上定义一个新属性,或者修改一个对象的现有属性,并返回此对象。
class Store {
constructor(options = {}) {
// ...
// getters
this.getters = {}
let getters = options.getters || {}
Object.keys(getters).forEach(key => {
Object.defineProperty(this.getters, key, {
get: () => {
return getters[key].call(this, this.state)
},
})
})
}
}
到此为止,已经可以使用我们自己写的 vuex 做一些基本操作了,但只能通过this.$store.xx的形式调用,故需要再实现方法。
2.6 map辅助函数
先来说说 mapState,没有 map 辅助函数之前这样使用:
computed: {
count () {
return this.$store.state.count
}
}
当映射的计算属性的名称与 state 的子节点名称相同时,给 mapState 传一个字符串数组。
computed: {
// 使用对象展开运算符将此对象混入到外部对象中
...mapState(['count'])
}
我们这里简单就只实现数组的情况:
export const mapState = args => {
let obj = {}
args.forEach(item => {
obj[item] = function () {
return this.$store.state[item]
}
})
return obj
}
之后几个 map 辅助函数都是类似。
//mapGetters
export const mapGetters = args => {
let obj = {}
args.forEach(item => {
obj[item] = function () {
return this.$store.getters[item]
}
})
return obj
}
//mapMutations
export const mapMutations = args => {
let obj = {}
args.forEach(item => {
obj[item] = function (params) {
return this.$store.commit(item, params)
}
})
return obj
}
//mapActions
export const mapActions = args => {
let obj = {}
args.forEach(item => {
obj[item] = function (payload) {
return this.$store.dispatch(item, payload)
}
})
return obj
}
3.完整代码
//myvuex.js
let Vue = null
class Store {
constructor(options) {
// vuex 的核心就是借用了vue的实例,因为vue的实例数据变化,会刷新视图
let vm = new Vue({
data: {
state: options.state,
},
})
// state
this.state = vm.state
// mutations
this.mutations = {} // 存储传进来的mutations
let mutations = options.mutations || {}
Object.keys(mutations).forEach(key => {
this.mutations[key] = params => {
mutations[key].call(this, this.state, params)
}
})
// actions
this.actions = {}
let actions = options.actions || {}
Object.keys(actions).forEach(key => {
this.actions[key] = params => {
actions[key].call(this, this, params)
}
})
// getters
this.getters = {}
let getters = options.getters || {}
Object.keys(getters).forEach(key => {
Object.defineProperty(this.getters, key, {
get: () => {
return getters[key].call(this, this.state)
},
})
})
}
commit = (key, params) => {
this.mutations[key](params)
}
dispatch = (type, payload) => {
this.actions[type](payload)
}
}
export const mapState = args => {
let obj = {}
args.forEach(item => {
obj[item] = function () {
return this.$store.state[item]
}
})
return obj
}
export const mapGetters = args => {
let obj = {}
args.forEach(item => {
obj[item] = function () {
return this.$store.getters[item]
}
})
return obj
}
export const mapMutations = args => {
let obj = {}
args.forEach(item => {
obj[item] = function (params) {
return this.$store.commit(item, params)
}
})
return obj
}
export const mapActions = args => {
let obj = {}
args.forEach(item => {
obj[item] = function (payload) {
return this.$store.dispatch(item, payload)
}
})
return obj
}
function install(_Vue) {
Vue = _Vue // install方法调用时,会将Vue作为参数传入(上面Store类需要用到Vue)
// 实现每一个组件,都能通过this调用$store
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
// 通过this.$options可以获取new Vue({参数}) 传递的参数
if (this.$options && this.$options.store) {
// 证明这个this是根实例,也就是new Vue产生的那个实例
this.$store = this.$options.store
} else if (this.$parent && this.$parent.$store) {
// 子组件获取父组件的$store属性
this.$store = this.$parent.$store
}
},
})
}
export default {
Store,
install,
}
4.测试使用
src/store/state.js:
const state = {
count: 1,
title: 'initial',
}
export default state
src/store/getters.js:
export const count = state => state.count
export const title = state => state.title
src/store/mutations.js:
import { ADD_COUNT, REDUCE_COUNT, SET_TITLE } from './mutation-types'
const mutations = {
[ADD_COUNT](state, payload) {
state.count += payload
},
[REDUCE_COUNT](state, payload) {
state.count -= payload
},
[SET_TITLE](state, payload) {
state.title = payload
},
}
export default mutations
src/store/mutation-types.js:
export const ADD_COUNT = 'ADD_COUNT'
export const REDUCE_COUNT = 'REDUCE_COUNT'
export const SET_TITLE = 'SET_TITLE'
src/store/actions.js:
import { SET_TITLE } from './mutation-types'
import axios from 'axios'
export const getTitle = async ({ commit }) => {
const result = await axios.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1')
commit(SET_TITLE, result.data.title)
}
然后在main.js中引入:
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from './store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
src/App.vue:
<template>
<div id="app">
<counter></counter>
<art-title></art-title>
<div class="wrapper">
<h3>App组件</h3>
<div>count: {{ count }}</div>
<div>title: {{ title }}</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapGetters } from './store/myvuex'
import Counter from './components/Counter'
import ArtTitle from './components/ArtTitle'
export default {
name: 'App',
created() {
console.log(this)
},
computed: {
...mapState(['count']),
...mapGetters(['title']),
},
components: {
Counter,
ArtTitle,
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.wrapper {
width: 100%;
padding: 10px;
border: 1px solid red;
}
</style>
src/components/ArtTitle.vue:
<template>
<div class="wrapper">
<h3>ArtTitle 组件</h3>
<button @click="getTitle">获取title</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'ArtTitle',
methods: {
...mapActions(['getTitle']),
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.wrapper {
width: 100%;
padding: 10px;
border: 1px solid red;
}
</style>
src/components/Counter.vue:
<template>
<div class="count-wrapper">
<h3>Counter 组件</h3>
<button @click="ADD_COUNT(10)">count 加10</button>
<button @click="REDUCE_COUNT(10)">count 减10</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapMutations } from '../store/myvuex'
export default {
name: 'Counter',
methods: {
...mapMutations(['ADD_COUNT', 'REDUCE_COUNT']),
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.count-wrapper {
width: 100%;
padding: 10px;
border: 1px solid red;
}
</style>
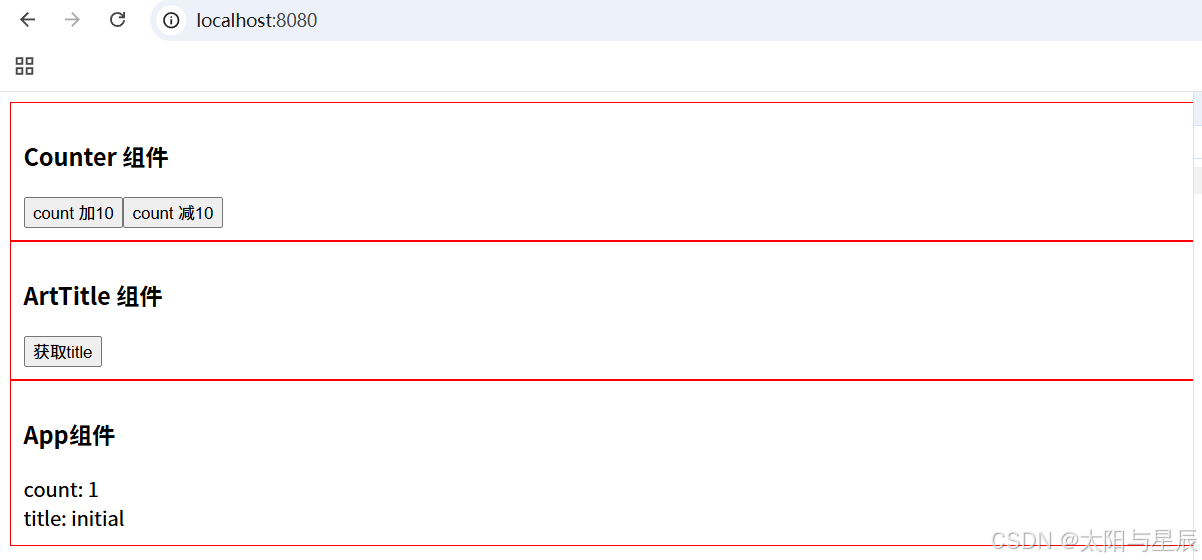
测试一下:
























 923
923

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










