浅谈springMVC中的设计模式(1)——责任链模式
2018年03月17日 13:02:31 春天写下一个bug 阅读数:2481 标签: 设计模式springMVC责任链模式 更多
个人分类: 专题
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/ljw761123096/article/details/79591133
最近终于闲了下来,准备自己记录些东西。网上关于springMVC的资料很多,但关于设计模式的还有限,我就想把springMVC源码中的设计模式抽出来做成一个系列,简单的谈一下其中的实现原理,作为一种学习分享,以后有更深的感悟也会更新。
先从一张图对整个springMVC的运作流程有一个大致的了解,图片侵删。 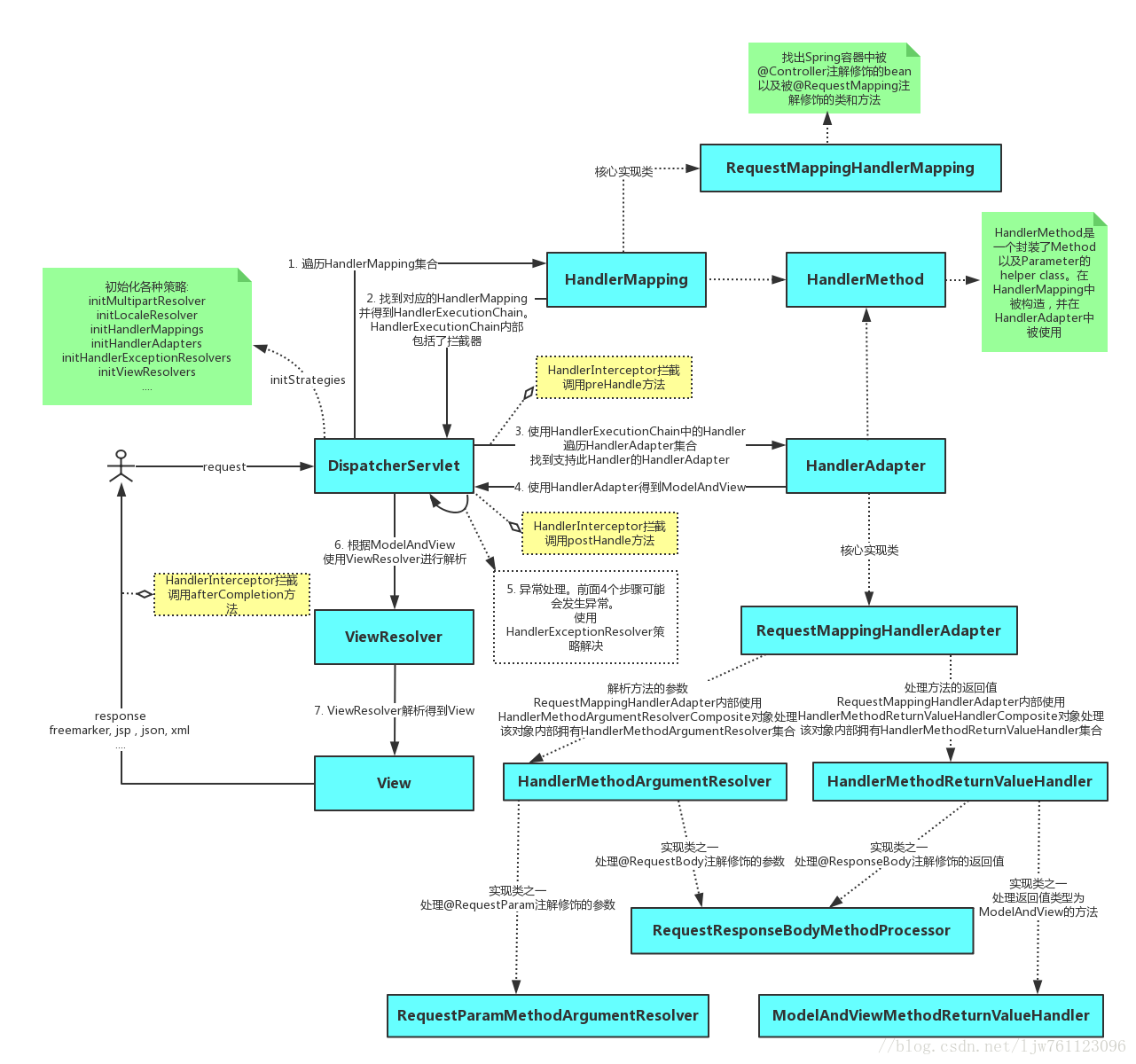
HandlerExecutionChain
其中我们可以看到,在springMVC中,DispatcherServlet这个核心类中使用到了HandlerExecutionChain这个类,他就是责任链模式实行的具体类。在DispatcherServlet的doDispatch这个方法中,我们可以看到它贯穿了整个请求dispatch的流程:
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 获取该请求的handler,每个handler实为HandlerExecutionChain,它为一个处理链,负责处理整个请求
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 责任链执行预处理方法,实则是将请求交给注册的请求拦截器执行
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// 实际的执行逻辑的部分,也就是你加了@RequestMapping注解的方法
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// 责任链执行后处理方法,实则是将请求交给注册的请求拦截器执行
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
// 处理返回的结果,触发责任链上注册的拦截器的AfterCompletion方法,其中也用到了HandlerExecutionChain注册的handler来处理错误结果
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// 触发责任链上注册的拦截器的AfterCompletion方法
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
从上面的代码中我们可以看到,HandlerExecutionChain主要负责请求的拦截器的执行和请求的处理,但是他本身不处理请求,只是将请求分配给在链上注册的处理器执行,这是一种责任链的实现方式,减少了责任链本身与处理逻辑之间的耦合的同时,规范了整个处理请求的流程,下面我们看一下上面代码中涉及到的方法在HandlerExecutionChain类中对应的代码。
boolean applyPreHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {
for (int i = 0; i < interceptors.length; i++) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
if (!interceptor.preHandle(request, response, this.handler)) {
triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
return false;
}
this.interceptorIndex = i;
}
}
return true;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
void applyPostHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ModelAndView mv) throws Exception {
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {
for (int i = interceptors.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
interceptor.postHandle(request, response, this.handler, mv);
}
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
void triggerAfterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Exception ex)
throws Exception {
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {
for (int i = this.interceptorIndex; i >= 0; i--) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
try {
interceptor.afterCompletion(request, response, this.handler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex2) {
logger.error("HandlerInterceptor.afterCompletion threw exception", ex2);
}
}
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
代码很容易理解,这里不详细说明。需要注意的是,HandlerExecutionChain维护了HandlerInterceptor(拦截器)的集合,可以向其中注册相应的HandlerInterceptor。
总结
个人的理解,责任链模式可以很好的将原本耦合的顺序过程处理的代码和逻辑,解耦成执行的顺序逻辑,和一个个相对应的处理器(责任人),对应的责任链只需要关心责任处理的顺序,而不需要关心具体的处理逻辑,将这些逻辑交给注册的责任人去处理。从springMVC的源码中,我们可以看到这一设计模式的应用,将原本复杂的请求处理逻辑表现的清楚明白。





 本文深入探讨SpringMVC框架中的责任链模式应用,通过分析HandlerExecutionChain类,揭示了请求处理流程如何通过责任链模式解耦,使得处理逻辑清晰且模块化。
本文深入探讨SpringMVC框架中的责任链模式应用,通过分析HandlerExecutionChain类,揭示了请求处理流程如何通过责任链模式解耦,使得处理逻辑清晰且模块化。
















 808
808

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








