面向高光谱图像的多特征融合哈希
I. Introduction
The existing methods for multiple feature fusion are mainly
focused on improving their classification accuracy without con- sidering the computational and storage cost. However,
动机:现存多特征融合方法主要致力于提高分类精度,没有考虑计算和存储开销。
As a powerful technique to obtain compact features and fast nearest neighbor search, hashing has not been introduced in remote sensing processing until very recently, where it is adopted for large-scale remote sensing image retrieval. To the best of our knowledge, it has not been used in hyperspectral image classification.
哈希作为一种获取紧凑特征和快速近邻搜索的强大技术,直到最近才被引入到遥感处理中,被用于大规模遥感图像检索。据我们所知,它还没有被用于高光谱图像的分类。
The main contributions of our work are summarized as follows.
- We propose an MFH framework to use hash technique in fusing multiple features for hyperspectral image classification and show encouraging results.
- We conduct an extensive performance evaluation of different hashing methods on fusing multiple features for classification on four popular hyperspectral data sets. Based on the evaluation results, we supply with an indepth discussion on the advantages, disadvantages, and availability of different hashing methods in this task.
- We conduct comparative experiments with five classical subspace-based dimension reduction methods and six different multiple feature fusion methods. Experiments show that, when equipped with a proper hashing learning strategy, the proposed MFH method can achieve comparable or even competitive performance. Meanwhile, the obtained binary features require much less storage and classification time.
本文的主要贡献如下:
- 提出了一种MFH(Multiple feature Fision Hashing)框架,将哈希技术引用到多特征融合的高光谱图像分类中;
- 在4个流行高光谱数据集上进行了性能评估,探讨哈希方法在本课题中的优缺点;
- 对五种经典的基于子空间的降维方法和六种不同的多特征融合方法进行了对比实验。
II. MFH Framework
The proposed MFH framework can be divided into three steps: 1) perform feature extraction in the hyperspectral image via efficient approaches, and concatenate multiple features into a long feature vector for each pixel; 2) perform hashing learning on these feature vectors with or without class label information, and map the original float-type feature vectors into compact binary codes; and 3) perform classification with the obtained binary codes, and output the final classification results. The flowchart of MFH is shown in Fig. 1.
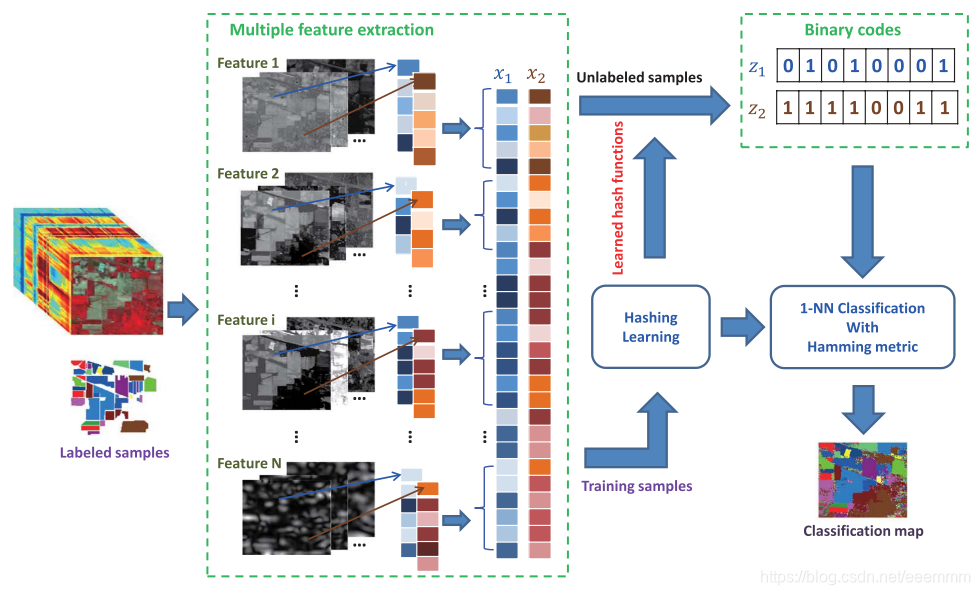
MFH框架分为三个步骤:
- 对高光谱图像进行特征提取,并将每个像素的多个特征拼接成一个长特征向量;
- 对特征向量进行哈希学习,将浮点特征映射为二进制哈希码;
- 利用得到的哈希码进行分类,输出分类结果。
MFH方法简单地将多特征拼接,它忽略了不同视图之间的潜在相关性。
III. Feature Hashing
本节介绍了几个代表性监督和非监督的哈希算法。
(1)无监督哈希
- LSH
- KLSH
- SH
(2)监督哈希
- KSH
- FastHash
- CCA-Based ITQ:当标签信息可用时,可以用典型相关分析(CCA)[46]代替PCA,从而产生基于CCA的ITQ算法(CCA-ITQ)。如[45]所示,CCA-ITQ是非常有效的,可以显著提高图像检索的性能。
[45] Y. Gong and S. Lazebnik, “Iterative quantization: A Procrustean approach to learning binary codes,” in Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recog., 2011, pp. 817–824.
[46] H. Hotelling, “Relations between two sets of variates,” Biometrika, vol. 28, no. 3/4, pp. 321–377, Dec. 1936.
IV. Experiment Setting
A. Data Sets
Indian Pines: This data set was captured by the Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometry (AVIRIS) sensor over a mixed agricultural/forested region in Northwest Indiana, on June 12, 1992. This data set has a spatial size of 145×145 pixels and 220 spectral bands with a spatial resolution of 20 m/pixel. It has 16 land-cover classes, whose sizes of labeled samples disproportionately range from 20 to 2468 pixels. In the experi- ments, we remove 20 noisy bands (104–108, 150–163, and 220) due to water absorption and use the remaining 200 bands.
Indian Pine :该数据集具有145*145像素的空间大小和220个光谱波段,空间分辨率为20m/piexl。该数据集包含16个土地覆盖类别,可用于分类的样本分布极不均匀,数量从20到2468个不等。实验中去掉了20个(104-108,150-163和220)被水吸收的噪声频段,使用了剩下的200个频段。
University of Pavia: This data set was acquired by the Reflective Optics System Imaging Spectrometry (ROSIS), covering an urban area of the University of Pavia, Italy. Originally, the ROSIS sensor provided 115 bands from 0.43 to 0.86 μm. After removing the 12 most noisy bands, the remaining 103 bands are used for experiments. The spatial size of this data set is 610 × 340 pixels, and its spatial resolution is 1.3 m/pixel. There are 9 classes, with sizes of labeled samples ranging from 1026 to 18686.
University of Pavia:该数据集包含115个波段,去除12个噪声最大的波段后,剩下的103个波段用于实验。该数据集的空间大小为610*340像素,空间分辨率为1.3m/pixel。包含9个类别,样本像素数量从1026到18686个不等。
Salinas: This data set was captured by the AVIRIS sensor over Salinas Valley, CA, USA, with a spatial resolution of 3.7 m/pixel. This data set has a spatial size of 512 × 217 with 224 spectral bands. In our experiments, 20 water absorption bands (108–112, 154–167, and 224) are discarded. This data set has 16 classes, whose sample sizes range from 916 to 11271.
Salinas:该数据集空间分辨率大小为3.7m/pixel,包含有224个波段,空间大小为512*217的像素。实验中忽略了20个被水吸收的波段(108–112, 154–167和224)。该数据集包含16个类别,样本像素数量从916到11271个不等。
Houston: This data set was initially distributed in the 2013 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Data Fusion Contest, which includes an urban hyperspectral data set and light detection and ranging (LiDAR) derived digital surface model. Both are geographically referenced and at the same spatial resolution (2.5 m). The hyperspectral data set has 144 bands in the 380–1050-nm spectral region. There are 15 classes of interest selected by the organizers.
Houston:该数据集包括一个城市高光谱数据集和一个由光探测和测距(LiDAR)得出的数字地表模型。两者的空间分辨率均为2.5m/pixel。高光谱数据集在380-1050 nm的光谱区域中有144个波段。实验中选取了15个感兴趣的类别。
B. Multiple Feature Extraction
Four kinds of commonly used features in hyperspectral image processing are extracted for each pixel, including the following: 1) the original spectral feature (denoted as Spectral); 2) the EMP feature (denoted as EMP) [19]; 3) the EAP feature (denoted as EAP) [20], [21]; and 4) the Gabor filtering feature (denoted as Gabor).
对于每个像素,实验提取了高光谱图像处理中常用的四种特征,包括:
- 原始光谱特征(Spectral),记为 x s p e ∈ R d 1 x_{spe}\in\mathbb{R}^{d_1} xspe∈Rd





 本文提出了一种名为MFH的框架,将哈希技术应用于高光谱图像的多特征融合,以提高分类性能并降低计算和存储成本。通过在四个典型高光谱数据集上的实验,比较了多种监督和非监督哈希方法,结果显示,如FastHash和CCA-ITQ等监督哈希方法能取得良好的分类效果。实验还强调了哈希码在保持数据相似性的同时,能实现高效处理和存储优势。
本文提出了一种名为MFH的框架,将哈希技术应用于高光谱图像的多特征融合,以提高分类性能并降低计算和存储成本。通过在四个典型高光谱数据集上的实验,比较了多种监督和非监督哈希方法,结果显示,如FastHash和CCA-ITQ等监督哈希方法能取得良好的分类效果。实验还强调了哈希码在保持数据相似性的同时,能实现高效处理和存储优势。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 3万+
3万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










