Description
Stan has n sticks of various length. He throws them one at a time on the floor in a random way. After finishing throwing, Stan tries to find the top sticks, that is these sticks such that there is no stick on top of them. Stan has noticed that the last thrown stick is always on top but he wants to know all the sticks that are on top. Stan sticks are very, very thin such that their thickness can be neglected.
Input
Input consists of a number of cases. The data for each case start with 1 <= n <= 100000, the number of sticks for this case. The following n lines contain four numbers each, these numbers are the planar coordinates of the endpoints of one stick. The sticks are listed in the order in which Stan has thrown them. You may assume that there are no more than 1000 top sticks. The input is ended by the case with n=0. This case should not be processed.
Output
For each input case, print one line of output listing the top sticks in the format given in the sample. The top sticks should be listed in order in which they were thrown.
The picture to the right below illustrates the first case from input.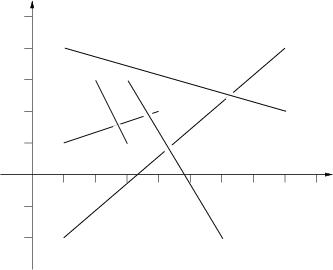
The picture to the right below illustrates the first case from input.

Sample Input
5 1 1 4 2 2 3 3 1 1 -2.0 8 4 1 4 8 2 3 3 6 -2.0 3 0 0 1 1 1 0 2 1 2 0 3 1 0
Sample Output
Top sticks: 2, 4, 5. Top sticks: 1, 2, 3.
Hint
Huge input,scanf is recommended.
Source
//题意:往地上随机的扔木棍,问有哪些木棍上面没有压着木棍。直接遍历看当前木棍(线段)与后面的木棍(线段)是否相交!
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 100005
struct point
{
double x,y;
};
struct line
{
point sp,ep;
}L[maxn];
int n;
bool used[maxn];
double x_multi(point p1,point p2,point p3)
{
return (p2.x-p1.x)*(p3.y-p1.y)-(p3.x-p1.x)*(p2.y-p1.y);
}
bool Onsegment(point p1,point p2,point p3)
{
double min_x=min(p1.x,p2.x);
double min_y=min(p1.y,p2.y);
double max_x=max(p1.x,p2.x);
double max_y=max(p1.y,p2.y);
if(p3.x>=min_x&&p3.x<=max_x&&p3.y>=min_y&&p3.y<=max_y)
return true;
return false;
}
bool Is_intersected(point p1,point p2,point p3,point p4)
{
double d1=x_multi(p1,p2,p3);
double d2=x_multi(p1,p2,p4);
double d3=x_multi(p3,p4,p1);
double d4=x_multi(p3,p4,p2);
if(d1*d2<0.0&&d3*d4<0.0)
return true;
if(d1==0.0&&Onsegment(p1,p2,p3))
return true;
if(d2==0.0&&Onsegment(p1,p2,p4))
return true;
if(d3==0.0&&Onsegment(p3,p4,p1))
return true;
if(d4==0.0&&Onsegment(p3,p4,p2))
return true;
return false;
}
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d",&n),n)
{
int i,j;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf",&L[i].sp.x,&L[i].sp.y,&L[i].ep.x,&L[i].ep.y);
memset(used,false,sizeof(used));
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(j=i+1;j<=n;j++)
if(Is_intersected(L[i].sp,L[i].ep,L[j].sp,L[j].ep))
{
used[i]=true;
break;
}
printf("Top sticks: ");
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(!used[i])
{
if(i<n)
printf("%d, ",i);
else
printf("%d.\n",i);
}
}
return 0;
}




 本文详细阐述了如何通过编程解决木棍堆叠问题,即确定哪些木棍位于堆叠顶部,没有其他木棍覆盖它们。通过输入一系列木棍的坐标,程序能够识别并输出所有处于顶部的木棍,按照它们被投掷的顺序列出。
本文详细阐述了如何通过编程解决木棍堆叠问题,即确定哪些木棍位于堆叠顶部,没有其他木棍覆盖它们。通过输入一系列木棍的坐标,程序能够识别并输出所有处于顶部的木棍,按照它们被投掷的顺序列出。
















 481
481

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








