大家好,今天我们聊聊Vue3的组合Composition API。
引言:为什么我们需要 Composition API?
在Vue2的Options API中,所有数据、方法及计算属性等都在一个抽屉里。当功能复杂时,相关的代码被分散在不同地方,改一个功能要在多个抽屉里翻找。
Composition API中,按功能把数据、方法、计算属性按功能打包在一起,改一个功能只需看一个地方(解决逻辑分散问题);写好的功能包可以直接在其他组件使用,更易复用(解决mixins 复用代码会带来命名冲突及来源不明问题);对TypeScript有更好的支持(解决类型支持差问题)。
文章目录
一、Composition API 核心概念详解
1.1 Options API vs Composition API
Options API(选项式 API)有固定的几个格子(data、methods、computed、watch),把代码按类型放进对应格子。
// Vue2 的 Options API - 逻辑分散
export default {
data() {
return {
users: [],
loading: false,
searchQuery: ''
}
},
computed: {
filteredUsers() {
return this.users.filter(user => user.name.includes(this.searchQuery))
}
},
methods: {
async fetchUsers() {
this.loading = true
// 获取用户逻辑
},
async addUser(user) {
// 添加用户逻辑
}
},
mounted() {
this.fetchUsers()
}
}
Composition API(组合式 API)按功能打包,一个功能的数据、方法、计算属性都在一起,把这些功能包组合成完整组件。
// Vue3 的 Composition API - 逻辑聚合
import { ref, computed, onMounted } from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
// 用户管理相关逻辑
const users = ref([])
const loading = ref(false)
const searchQuery = ref('')
const filteredUsers = computed(() => {
return users.value.filter(user => user.name.includes(searchQuery.value))
})
const fetchUsers = async () => {
loading.value = true
try {
users.value = await userApi.getUsers()
} finally {
loading.value = false
}
}
const addUser = async (user) => {
const newUser = await userApi.addUser(user)
users.value.push(newUser)
}
onMounted(fetchUsers)
return {
users,
loading,
searchQuery,
filteredUsers,
addUser
}
}
}
1.2 响应式系统的革命性升级
Options API的底层是基于“配置对象”的编译转换,在编译阶段将你的组件配置对象转换为渲染函数,将 data、methods、computed 等合并绑定到组件实例的 this 上。其响应式系统大致如下:
// vue2代码
data() {
return { count: 0 }
},
methods: {
increment() { this.count++ }
}
// 底层大致转换为
const instance = {
data: reactive({ count: 0 }), // 变为响应式
increment: function() { this.data.count++ }.bind(this)
}
Composition API的底层是基于“函数调用”的直接响应式,在组件创建前执行,setup将返回的数据直接暴露给模板。响应式系统直接调用,不依赖于this。
setup() {
// 直接调用响应式API,不依赖this
const count = ref(0)
const increment = () => { count.value++ }
return { count, increment }
}
1.3 生命周期钩子的新写法
Vue3的生命周期如下图:
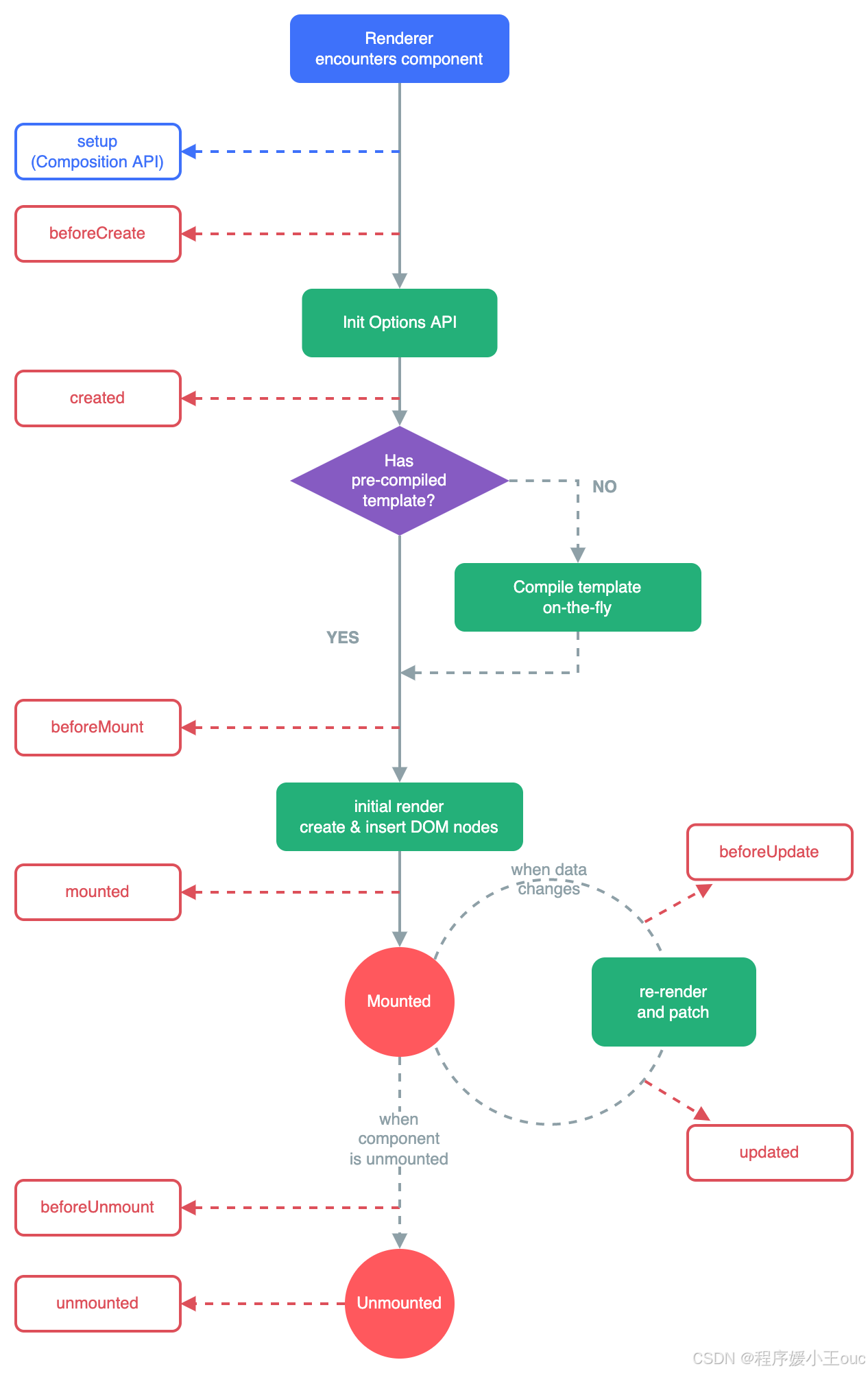
vue2 和 vue3 关于生命周期的对比
| Vue2 | Vue3 |
|---|---|
| beforeCreate created | setup,在 beforeCreate 和 created 前,因此一般在组合式 api 中使用它做一些前置处理。 |
| beforeMount | onBeforeMount |
| mounted | onMounted |
| updated | onUpdated |
| beforeDestroy | onBeforeUnmount |
| destroyed | onUnmounted |
1.4 计算属性与侦听器的威力
option API中所有计算属性挤在一起,与相关数据分离。
computed: {
// 只能定义在固定区域
fullName() {
return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName
},
discountedPrice() {
return this.price * this.discount
}
}
Composition API中的计算可以与相关数据放在一起,可以在任何逻辑中创建,更易于封装复用。
import { computed } from 'vue'
setup() {
const firstName = ref('张')
const lastName = ref('三')
// 威力1:与相关数据放在一起
const fullName = computed(() => `${firstName.value} ${lastName.value}`)
// 威力2:可以在任何逻辑中创建
const price = ref(100)
const discount = ref(0.8)
const discountedPrice = computed(() => price.value * discount.value)
// 威力3:易于封装复用
const { filteredList, search } = useSearchComputed(list)
return { fullName, discountedPrice }
}
Options API 的侦听器只能监听 this 上的属性且深度监听写法繁琐。
watch: {
'user.id'(newVal, oldVal) {
this.fetchUser(newVal)
},
// 深度监听
someObject: {
handler(newVal) { /* ... */ },
deep: true,
immediate: true
}
}
Composition API 的侦听器可以直接监听响应式变量,自动追踪依赖变化,可精细控制(手动停止)。
import { watch, watchEffect } from 'vue'
setup() {
const userId = ref(1)
const user = reactive({ info: { name: '' } })
// 威力1:直接监听响应式变量
watch(userId, (newId) => {
fetchUser(newId)
})
// 威力2:watchEffect - 自动追踪依赖
watchEffect(() => {
// 自动追踪 user.info.name 的变化
console.log('用户名变更:', user.info.name)
})
// 威力3:灵活的监听选项
watch(() => user.info.name, // 可以监听嵌套属性
(newName) => { /* ... */ },
{ immediate: true, deep: true }
)
// 威力4:可以停止监听
const stop = watch(userId, callback)
stop() // 手动停止
}
二、构建可复用的组合式函数
组合式函数就是把一段相关逻辑打包成可复用的“工具箱“。
// useMouse.js - 创建一个“鼠标工具箱”
import { ref, onMounted, onUnmounted } from 'vue'
export function useMouse() {
// 工具箱里的工具
const x = ref(0)
const y = ref(0)
// 工具的功能
function update(event) {
x.value = event.pageX
y.value = event.pageY
}
// 安装工具
onMounted(() => window.addEventListener('mousemove', update))
// 卸载工具
onUnmounted(() => window.removeEventListener('mousemove', update))
// 把工具暴露出去
return { x, y }
}
在组件中使用:
<template>
<div>鼠标位置:{{ x }}, {{ y }}</div>
</template>
<script setup>
// 导入并直接使用“鼠标工具箱”
import { useMouse } from './useMouse'
// 像调用函数一样使用,自动获得所有功能
const { x, y } = useMouse()
</script>
三、实际项目应用场景-数据请求与状态管理
useFetch - 数据请求封装
// composables/useFetch.ts
import { ref, computed, onUnmounted } from 'vue'
/**
* 数据请求组合式函数
* 特点:复用请求逻辑,统一错误处理,自动清理
*/
export function useFetch<T>(url: string, options?: RequestInit) {
// 响应式状态
const data = ref<T | null>(null) // 数据
const loading = ref(false) // 加载状态
const error = ref<Error | null>(null) // 错误信息
// 取消请求的控制器
const controller = new AbortController()
/**
* 执行请求
*/
const execute = async () => {
loading.value = true
error.value = null
try {
const response = await fetch(url, {
...options,
signal: controller.signal // 支持取消请求
})
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`HTTP ${response.status}`)
}
data.value = await response.json()
} catch (err) {
// 如果是取消请求的错误,不设置 error
if (err.name !== 'AbortError') {
error.value = err as Error
}
} finally {
loading.value = false
}
}
/**
* 取消请求
*/
const cancel = () => {
controller.abort()
}
// 自动清理:组件卸载时取消请求
onUnmounted(cancel)
// 计算属性:是否成功获取数据
const hasData = computed(() => !loading.value && data.value !== null)
// 计算属性:是否出错
const hasError = computed(() => !loading.value && error.value !== null)
return {
// 响应式数据
data,
loading,
error,
// 计算属性
hasData,
hasError,
// 方法
execute,
cancel
}
}
在组件中使用
<!-- UserList.vue -->
<template>
<div>
<!-- 加载状态 -->
<div v-if="loading">加载中...</div>
<!-- 错误状态 -->
<div v-else-if="error" class="error">
错误: {{ error.message }}
<button @click="retry">重试</button>
</div>
<!-- 数据展示 -->
<div v-else-if="hasData">
<ul>
<li v-for="user in data" :key="user.id">
{{ user.name }} - {{ user.email }}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<!-- 初始状态 -->
<div v-else>
<button @click="fetchUsers">获取用户列表</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { useFetch } from './composables/useFetch'
// 使用组合式函数 - 逻辑集中,复用性强
interface User {
id: number,
name: string,
email: string
}
const {
data: users,
loading,
error,
hasData,
execute: fetchUsers,
cancel
} = useFetch<User[]>('/api/users')
// 重试功能
const retry = () => {
fetchUsers()
}
// 页面卸载时自动取消请求(已在 useFetch 中实现)
</script>
四、常用工具函数
4.1 inject/provide 依赖注入
provide/inject 是 Vue 3 中实现依赖注入的核心 API,用于在组件树中跨层级传递数据,避免了逐层传递 props 的繁琐。
<!-- ❌ Props 逐层传递(Props Drilling) -->
<GrandParent>
<Parent :data="data" /> // 中间组件只是转发,不关心数据
<Child :data="data" /> // 中间组件只是转发,不关心数据
<GrandChild :data="data" /> // 实际使用者
</GrandParent>
<!-- ✅ Provide/Inject 直接注入 -->
<GrandParent>
<Parent> // 不需要传递 props
<Child> // 不需要传递 props
<GrandChild /> // 直接注入使用
</Child>
</Parent>
</GrandParent>
inject/provide使用示例
<!-- Parent 祖先组件提供数据 -->
<script setup>
import { provide } from 'vue'
// 提供静态数据
provide('appName', 'My Awesome App')
provide('version', '1.0.0')
</script>
<!-- GrandChild 后代组件注入数据 -->
<script setup>
import { inject } from 'vue'
// 注入数据
const appName = inject('appName')
const version = inject('version')
console.log(appName) // 'My Awesome App'
console.log(version) // '1.0.0'
</script>
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{ appName }} v{{ version }}</h1>
</div>
</template>
4.2 getCurrentInstance 获取当前组件
getCurrentInstance 是 Vue 3 的一个内部 API,用于获取当前组件的实例。
注意:它仅在 setup 函数或生命周期钩子中可用。不推荐使用,存在安全隐患。
<template>
<div>
<p>当前组件的 uid: {{ uid }}</p>
<p>父组件是否存在: {{ hasParent }}</p>
<p>根组件是否存在: {{ hasRoot }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { getCurrentInstance, onMounted } from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'MyComponent',
setup() {
// 获取当前组件实例
const instance = getCurrentInstance()
// 从实例中获取一些属性
const uid = instance.uid
const hasParent = !!instance.parent
const hasRoot = !!instance.root
// 生命周期钩子中也可以使用
onMounted(() => {
console.log('组件已挂载')
})
return {
uid,
hasParent,
hasRoot
}
}
}
</script>
4.3 useSlots/useAttrs 插槽和属性
Composition API中用于访问组件的插槽和属性的API。注意:它们只能在setup函数或<script setup>中使用。
useSlots访问插槽
<!-- SlotDemo.vue -->
<script setup>
import { useSlots, h } from 'vue'
// 获取插槽
const slots = useSlots()
// 检查插槽是否存在
console.log('默认插槽存在?', !!slots.default)
console.log('header插槽存在?', !!slots.header)
console.log('footer插槽存在?', !!slots.footer)
// 检查是否有作用域插槽
const hasScopedSlot = computed(() => {
return !!slots.default && slots.default.length > 0
})
// 渲染插槽内容
const renderSlots = () => {
// 如果没有默认插槽,返回提示
if (!slots.default) {
return h('div', '没有提供插槽内容')
}
// 渲染插槽
return slots.default()
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="slot-demo">
<!-- 直接在模板中使用 -->
<header v-if="slots.header">
<slot name="header" />
</header>
<main>
<slot>默认内容</slot>
</main>
<footer v-if="slots.footer">
<slot name="footer" />
</footer>
</div>
</template>
useAttrs访问非Props属性
<!-- AttrsDemo.vue -->
<script setup>
import { useAttrs, computed } from 'vue'
// 定义 props(声明的 props 不会出现在 attrs 中)
const props = defineProps({
title: String,
disabled: Boolean
})
// 获取所有非 props 属性
const attrs = useAttrs()
// 监听 attrs 变化
watch(() => attrs, (newAttrs) => {
console.log('属性变化:', newAttrs)
}, { deep: true })
// 分类处理 attrs
const classAttrs = computed(() => {
const { class: className, style, ...rest } = attrs
return { className, style, rest }
})
// 合并类名
const mergedClasses = computed(() => {
const baseClass = 'base-component'
const customClass = attrs.class || ''
const disabledClass = props.disabled ? 'disabled' : ''
return [baseClass, customClass, disabledClass].filter(Boolean).join(' ')
})
// 合并样式
const mergedStyles = computed(() => {
const baseStyle = {
padding: '16px',
borderRadius: '4px'
}
const customStyle = typeof attrs.style === 'object' ? attrs.style : {}
return { ...baseStyle, ...customStyle }
})
</script>
<template>
<div :class="mergedClasses" :style="mergedStyles" v-bind="attrs">
<h3 v-if="title">{{ title }}</h3>
<slot />
</div>
</template>
五、高频面试解析
问题:Composition API 与 Options API 的主要区别?
参考答案:
· 代码组织方式:Composition API 按逻辑关注点组织,Options API 按选项类型组织
· 逻辑复用:Composition API 通过组合式函数更好复用,Options API 主要通过 mixins(来源不清晰问题)
· TypeScript 支持:Composition API 有更好的类型推断
· 灵活性:Composition API 更灵活,适合复杂组件
六、总结
Compositon API优势
更好的逻辑复用:Composable 函数
更好的开发体验:组合式 API
核心思想转变:从思考"这个数据放哪里?这个方法放哪里?“到思考"这个功能需要哪些数据和方法?”
迁移建议
✅ 推荐做法:
新项目直接使用 Vue3 + Composition API
老项目逐步迁移,可以先在部分组件试用
充分利用 Composable 函数复用逻辑
使用 <script setup>语法糖简化代码
❌ 避免做法:
不要为了用新特性而过度设计
不要混合使用 Options API 和 Composition API 的编码风格
下一期预告
下一篇我们将深入探讨Vue的响应式原理Object.defineProperty VS Proxy, 理解底层原理能提升我们的开发效率、减少bug、写出更可靠的代码。
如果觉得有帮助,请关注+点赞+收藏,这是对我最大的鼓励! 如有问题,请评论区留言























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










