需求分析
1、编写目的
本软件需求规格说明的目的在于为《员工管理系统》项目的开发提供:
a. 提出软件总体要求,作为软件开发人员和最终使用者之间相互了解的基础;
b. 提出软件功能要求、性能要求、接口要求、数据结构等要求,作为软件设计和程序编制的基础;
c. 为软件测试提供依;
本软件需求规格说明的读者对象主要是软件设计人员和最终用户;
2、项目概述
本项目的目的是完成一个计算机员工管理系统,实现员工信息管理的自动化,系统的主要功能包括员工信息的增加、删除、修改、查询操作以及员工薪水的改动和查询操作。
本系统提供交互友好的界面和用户选择菜单,具有一定的错误自检和修复能力。
3、总体数据流图
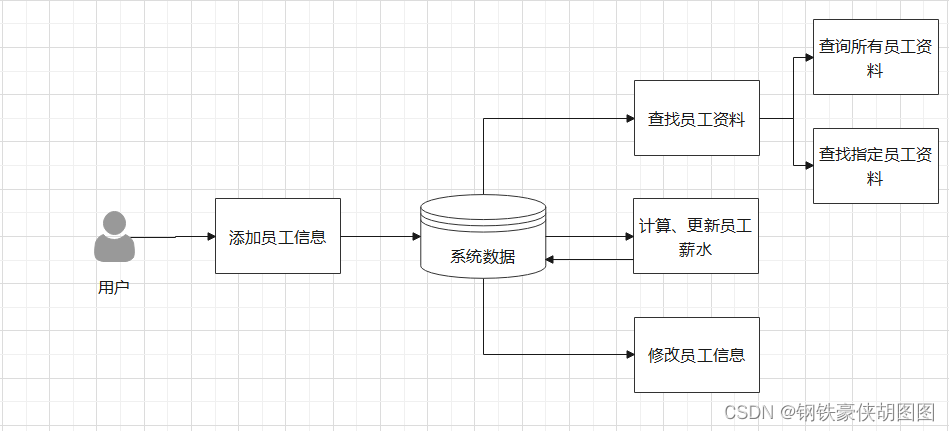
4、系统的数据库设计
员工表:
| 列名 | 数据类型 | 非空约束 | 主键约束 | 外键约束 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| eid | int | not null | primary key | |
| ename | varchar(20) | not null | ||
| age | int | |||
| sex | char(1) | |||
| hirdate | date |
创建数据库工具类
package com.工程名称.util;
import java.sql.*;
public class DBUtil {
//获取连接对象,我是自己手打的url,也可以读取db.properties配置文件
public static Connection getConnetion() {
Connection conn = null;
try {
//1、类加载,加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/emp_management?" +
"useSSL=false&user=root&password=159357&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF8";
//2、连接数据库,获取连接对象
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return conn;
}
//封装增删改操作(DMl) obj中保存的就是传递的参数
public static int exeUpdate(String sql, Object[] obj) {
Connection conn = getConnetion();
PreparedStatement pstm = null;
int update = 0;
try {
pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < obj.length; i++) {
pstm.setObject(i + 1, obj[i]);
}
update = pstm.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
closeAll(pstm, conn, null);
}
return update;
}
//抽取关闭组件
public static void closeAll(PreparedStatement pstm, Connection conn, ResultSet rs) {
try {
if (rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (pstm != null) {
pstm.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
5、主页设计
受个人知识面所限,本系统将使用控制台作为操控页面
设计思路:
使用 do{}-while(true) 循环加载菜单
在其中使用 switch-case 来添加主菜单的列表
根据判断用户输入的选项来执行相对应的功能
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
do {
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("*******欢迎进入员工管理系统*******");
System.out.println("\t1、查询所有员工");
System.out.println("\t2、查询指定编号的员工");
System.out.println("\t3、添加员工信息");
System.out.println("\t4、修改员工信息");
System.out.println("\t5、删除员工信息");
System.out.println("\t6、退出");
System.out.println("******************************");
System.out.print("请选择菜单:");
int choice = input.nextInt();
switch (choice) {
case 1:/*selectAll()*/
//查找所有员工信息
break;
case 2:/*selectById()*/
//根据eid查找特定员工信息
break;
case 3:/*addEmployee()*/
break;
case 5:/*delete()*/
break;
case 6:/*退出系统*/
System.out.println("谢谢使用");
System.exit(1);
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入错误");
}
System.out.print("按任意键继续..........");
input.nextLine();
input.nextLine();
} while (true);
6、接口设计
设计思路
根据需求分析,本系统主要实现的功能是对员工信息表的增删改查
因此可以根据数据流图来进行EmployeeDao的接口设计
package com.cslwb.dao;
import com.cslwb.entity.Employee;
import java.util.List;
public interface EmployeeDao {
//1、查询所有员工信息的实现 select * from employee 参数:无 返回值:employeeList
List<Employee> selectAll();
//根据eid查询单个员工的实现 参数:int eid 返回值: Employee对象
Employee selectById(int eid);
//添加员工的实现 参数:Employee对象 返回值: Boolean
public Boolean addEmployee(Employee employee);
}
7、查询所有员工信息功能实现
功能流程:
首先,用户在主页从键盘输入数字1选项,选择查询所有用户功能
主页switch执行case 1段代码
调用EmployeeDao的实现类EmployeeDaoImpl中selectAll()方法,获取所有员工信息的List列表
循环遍历列表,打印所有员工信息
代码如下:
//switch部分
case 1:/*selectAll()*/
employeeList = employeeDao.selectAll();
for (Employee emp : employeeList) {
System.out.println(emp);
}//查找所有员工信息
break;
//EmployeeDaoImpl部分
@Override
public List<Employee> selectAll() {
Connection conn = DBUtil.getConnetion();
PreparedStatement pstm = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
String sql = "select * from employee";
List<Employee> employeeList = new ArrayList<>();
try {
pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = pstm.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
//1、这一步就是把数据从ResultSet中取出来
int eid = rs.getInt(1);
String ename = rs.getString(2);
int age = rs.getInt(3);
String sex = rs.getString(4);
Date hirdate = rs.getDate(5);
//2、把取出来的数据保存到对象中
Employee employee = new Employee(eid, ename, age, sex, hirdate);
//3、把所有的对象保存到集合中
employeeList.add(employee);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.closeAll(pstm, conn, rs);
}
return employeeList;
}
演示效果:
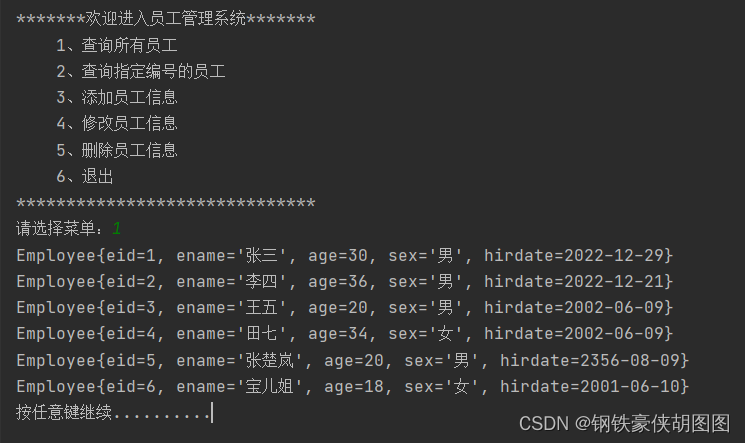
8、根据Id查找指定员工的实现
//switch部分
case 2:/*selectById()*/
System.out.print("请输入需要查找的员工id:");
eid = input.nextInt();
employee = employeeDao.selectById(eid);
System.out.println(employee);
break;
调用EmployeeDaoImpl中的selectById方法,传入参数为eid
@Override
public Employee selectById(int eid) {
Connection conn = DBUtil.getConnetion();
PreparedStatement pstm = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
String sql = "select * from employee where eid = " + eid;
Employee employee = null;
try {
pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = pstm.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
//1、从Resultset中取出数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String ename = rs.getString(2);
int age = rs.getInt(3);
String sex = rs.getString(4);
Date hirdate = rs.getDate(5);
//2、把数据存到对象中
employee = new Employee(id, ename, age, sex, hirdate);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.closeAll(pstm, conn, rs);
}
return employee;
}
演示效果:
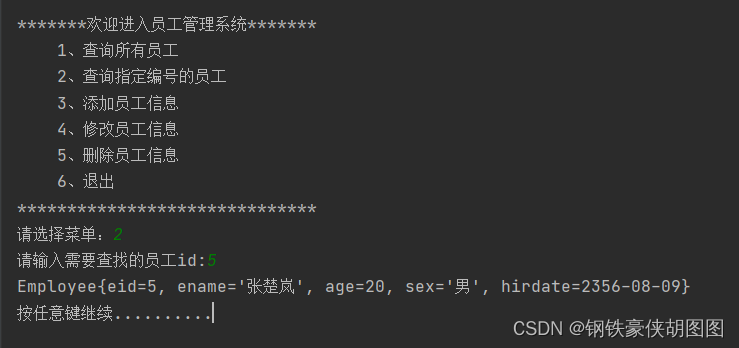
9、添加员工方法
由用户在主页输入新员工信息,封装至Employee对象中,作为参数传入EmployeeDaoImpl.addEmployee()中
//switch部分
case 3:/*addEmployee()*/
System.out.print("请输入插入员工的id:");
eid = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
System.out.print("请输入插入员工的姓名:");
ename = input.nextLine();
System.out.print("请输入插入员工的年龄:");
age = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
System.out.print("请输入插入员工的性别:");
sex = input.nextLine();
System.out.print("请输入插入员工的生日:");
hirdate = Date.valueOf(input.nextLine());
employee = new Employee(eid, ename, age, sex, hirdate);
if(employeeDao.addEmployee(employee)){
System.out.println("插入成功");
}else{
System.out.println("插入失败");
}
break;
public Boolean addEmployee(Employee employee)
@Override
public Boolean addEmployee(Employee employee) {
Boolean ans = true;
Connection conn = DBUtil.getConnetion();
PreparedStatement pstm = null;
String sql = "insert employee values(?,?,?,?,?)";
List<Employee> employeeList = null;
try {
pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstm.setObject(1, employee.getEid());
pstm.setObject(2, employee.getEname());
pstm.setObject(3, employee.getAge());
pstm.setObject(4, employee.getSex());
pstm.setObject(5, employee.getHirdate());
pstm.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("插入成功");
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
Employee e = selectById(employee.getEid());
if(e == null){
ans = false;
return ans;
}
System.out.println(e);
DBUtil.closeAll(pstm, conn, null);
return ans;
}
}
演示效果:
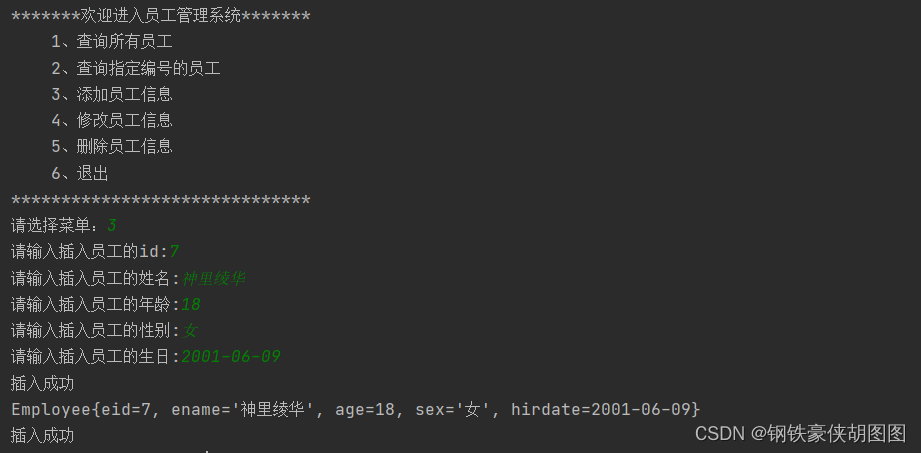
其余功能在一周之内开发完毕





 本文档详细描述了一个员工管理系统的软件需求规格,包括系统的目的、功能、数据库设计、接口设计及主要功能的实现,如员工信息的增删改查。系统采用控制台交互界面,数据库使用MySQL,通过DBUtil工具类进行连接操作。此外,还展示了查询所有员工和根据ID查询员工的实现过程。
本文档详细描述了一个员工管理系统的软件需求规格,包括系统的目的、功能、数据库设计、接口设计及主要功能的实现,如员工信息的增删改查。系统采用控制台交互界面,数据库使用MySQL,通过DBUtil工具类进行连接操作。此外,还展示了查询所有员工和根据ID查询员工的实现过程。
















 1094
1094

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








