url 模块:
1、用于解析和处理URL的字符串
2、处理带参数的请求
比如这个请求:http://localhost:8990/news?newsid=1&author=zs,带有参数:newsid=1&author=zs
引入模块:require('url');
url.parse();
parse函数:接受一个URL字符串,解析它,然后返回一个URL对象
const urlString = url.parse('http://www.nodejs.org/some/url/?with=query¶m=that#about');
console.log(urlString);
/*
Url {
protocol: 'http:',
slashes: true,
auth: null,
host: 'www.nodejs.org',
port: null,
hostname: 'www.nodejs.org',
hash: '#about',
search: '?with=query¶m=that',
query: 'with=query¶m=that',
pathname: '/some/url/',
path: '/some/url/?with=query¶m=that',
href: 'http://www.nodejs.org/some/url/?with=query¶m=that#about'
}
*/
protocol: 'http:', ------------------------------------ url协议
slashes: true, ---------------------------------------- 斜杠
auth: null, ------------------------------------------ 用户认证
host: 'www.nodejs.org', ------------------------- 主机
port: null, --------------------------------------------- 端口
hostname: 'www.nodejs.org', ------------------主机名
hash: '#about', ------------------------------------- 片段部分,也就是URL#之后的部分search: '?
with=query¶m=that', ---------- -url中HTTP GET的信息,包含了 ?
query: 'with=query¶m=that', ----------- 和 search一样,但是不包含 ?
pathname: '/some/url/', ----------------- 跟在host之后的整个文件路径。但是不包含 ? 及 ?之后的字符串。
path: '/some/url/?with=query¶m=that', ---- 和pathname一样,但是包含 ? 及之后的字符串,但是不包含hash
href: 'http://www.nodejs.org/some/url/?with=query¶m=that#about' ---- 原始的url
url.format();
format函数 的作用与parse相反,它的参数是一个JSON对象,返回一个组装好的url地址
var urlObj = {
protocol: 'http:',
slashes: true,
auth: null,
host: 'www.nodejs.org',
port: null,
hostname: 'www.nodejs.org',
hash: '#about',
search: '?with=query¶m=that',
query: 'with=query¶m=that',
pathname: '/some/url/',
path: '/some/url/?with=query¶m=that',
href: 'http://www.nodejs.org/some/url/?with=query¶m=that#about'
};
console.log(url.format(urlObj)); // http://www.nodejs.org/some/url/?with=query¶m=that#about
url.resolve(from,to)
url.resolve(from,to) ;用于拼接URL, 它根据相对URL拼接成新的URL;
var str1 = url.resolve('/data/xx/text', 'my');
console.log(str1); // /data/xx/my
const str2 = url.resolve('http://www.baidu.com', 'my');
console.log(str2); // http://www.baidu.com/my
const str3 = url.resolve('http://www.baidu.com/', '/my');
console.log(str3); // 输出 http://www.baidu.com/my
2、处理带参数的请求
在页面中输入请求路径:http://localhost:8990/news?newsid=1&author=zs
【例 3:】url.parse()方法:接受一个URL字符串,解析它,然后返回一个URL对象
const http = require('http');
const url = require('url');//当请求带参数时使用 url模块,用于处理请求路径
http.createServer(function(request,response){
const strurl = request.url;//请求路径
//response.write(strurl);
const resultUrl = url.parse(strurl);
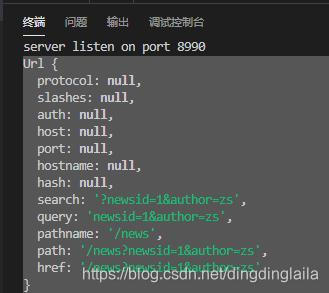
console.log(resultUrl);//结果是一个url对象,如下图
console.log(resultUrl.query);//newsid=1&author=zs
response.end();
}).listen(8990,function(err){
if(err){
console.log(err)
}else{
console.log('server listen on port 8990')
}
})
这时候运行的结果是这样的:如图
如果要将参数和值取出来,就得通过截取字符串形式来获取,为了方便我们直接取值。url.parse()里面可以在接收第二个参数 是个布尔值。因为true时会自动帮我们获取到参数值。来看代码
const http = require('http');
const url = require('url');//当请求带参数时使用 url模块,用于处理请求路径
http.createServer(function(request,response){
const strurl = request.url;//请求路径
//response.write(strurl);
/*
const resultUrl = url.parse(strurl);
console.log(resultUrl.query);//newsid=1&author=zs
*/
//在url.parse()加了一个参数true后 方便拿取我们传递的参数 表示把query部分解析成对象
const resultUrl = url.parse(strurl,true);
console.log(resultUrl.query.newsid,resultUrl.query.author);//1 zs
response.end();
}).listen(8990,function(err){
if(err){
console.log(err)
}else{
console.log('server listen on port 8990')
}
})
【例 2:】将一个解析后的URL对象,转成 一个格式化的URL字符串
format函数 的作用 与 parse函数 相反,它的参数是一个JSON对象,返回一个组装好的url地址
const url = require('url');
const urlobj = {
protocol: 'http:',
host: 'www.qq.com',
port: null,
hostname: null,
search: '?newsid=1&author=zs',
query: { newsid: '1', author: 'zs' },
pathname: '/news',
path: '/news?newsid=1&author=zs',
href: '/news?newsid=1&author=zs'
}
let strurl = url.format(urlobj);
console.log(strurl);//http://www.qq.com/news?newsid=1&author=zs
好啦 这一篇先到这里。
我的文章都是学习过程中的总结,如果发现错误,欢迎留言指出,我及时更正





 本文介绍了Node.js中的url模块,主要用于解析和处理URL字符串。内容包括:1) 使用url.parse()解析URL,返回URL对象,详细展示了各项属性如protocol、hostname、pathname等;2) url.format()函数将URL对象格式化为字符串;3) url.resolve()用于拼接URL;4) 解析带参数的请求,并演示了如何通过url.parse()获取参数值。
本文介绍了Node.js中的url模块,主要用于解析和处理URL字符串。内容包括:1) 使用url.parse()解析URL,返回URL对象,详细展示了各项属性如protocol、hostname、pathname等;2) url.format()函数将URL对象格式化为字符串;3) url.resolve()用于拼接URL;4) 解析带参数的请求,并演示了如何通过url.parse()获取参数值。
















 801
801

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








