
//预备知识:二叉树的构造
#include <stdio.h>
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
void preorder_print(TreeNode* node, int layer) {
if (!node) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < layer; i++) {
printf("------");//根据层数打印------
}
printf("[%d]\n", node->val);
preorder_print(node->left, layer + 1);
preorder_print(node->right, layer + 1);
}
void traversal(TreeNode* node) {
if (!node) {
return;
}
//前序遍历
printf("[%d]\n", node->val);
traversal(node->left);
traversal(node->right);
// //中序遍历
// traversal(node->left);
// printf("[%d]\n", node->val);
// traversal(node->right);
//
// //后序遍历
// traversal(node->left);
// traversal(node->right);
// printf("[%d]\n", node->val);
}
int main() {
TreeNode a(1);
TreeNode b(2);
TreeNode c(5);
TreeNode d(3);
TreeNode e(4);
TreeNode f(6);
a.left = &b;
a.right = &c;
b.left = &d;
b.right = &e;
c.right = &f;
preorder_print(&a, 0);
return 0;
}
例一:LeetCode113
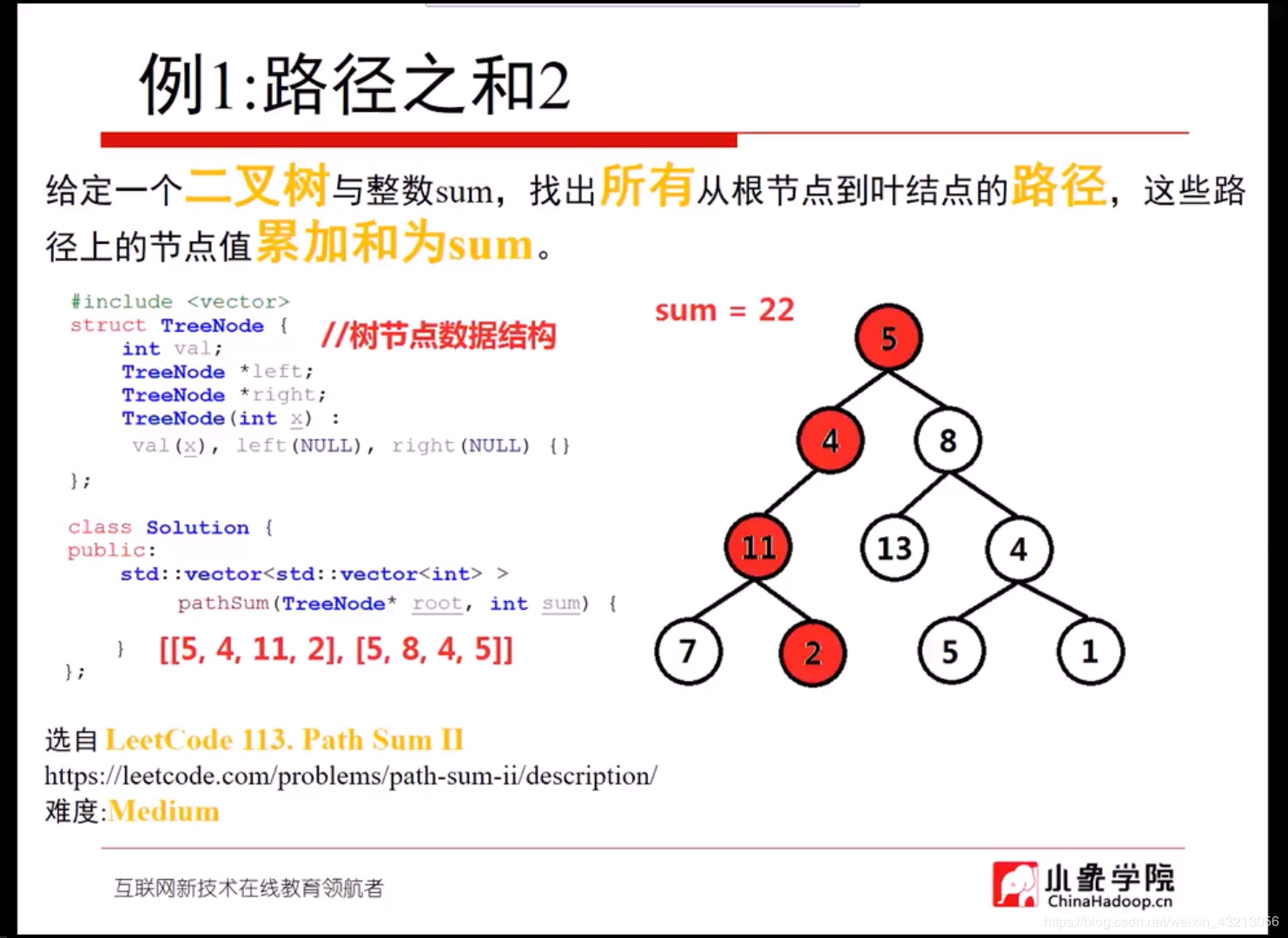

//给定一个二叉树与整数sum,找出所有从根节点到叶节点的路径,这些路径上累加值为sum
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
std::vector<std::vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
std::vector<std::vector<int>> result;
std::vector<int> path;
int path_value = 0;
preorder(root, path_value, sum, path, result);
return result;
}
private:
void preorder(TreeNode* node, int& path_value, int sum, std::vector<int>& path, std::vector<std::vector<int>>& result) {
if (!node) {
return;
}
path_value += node->val;
path.push_back(node->val);
if (!node->left && !node->right && path_value == sum) {
result.push_back(path);
}
preorder(node->left, path_value, sum, path, result);
preorder(node->right, path_value, sum, path, result);
path_value -= node->val;
path.pop_back();
}
};
int main() {
TreeNode a(5);
TreeNode b(4);
TreeNode c(8);
TreeNode d(11);
TreeNode e(13);
TreeNode f(4);
TreeNode g(7);
TreeNode h(2);
TreeNode x(5);
TreeNode y(1);
a.left = &b;
a.right = &c;
b.left = &d;
c.left = &e;
c.right = &f;
d.left = &g;
d.left = &h;
f.left = &x;
f.right = &y;
Solution solve;
std::vector<std::vector<int>> result = solve.pathSum(&a, 22);
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < result[i].size(); j++) {
printf("[%d]", result[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
例二:LeetCode236



//已知二叉树,求二叉树中给定的两个节点的最近公共祖先
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
std::vector<TreeNode*> path;
std::vector<TreeNode*> node_p_path;
std::vector<TreeNode*> node_q_path;
int finish = 0;
preorder(root, p, path, node_p_path, finish);
path.clear();
finish = 0;
preorder(root, q, path, node_q_path, finish);
int path_len = 0;
if (node_p_path.size() < node_q_path.size()) {
path_len = node_p_path.size();
}
else {
path_len = node_q_path.size();
}
TreeNode* result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < path_len; i++) {
if (node_p_path[i] == node_q_path[i]) {
result = node_p_path[i];
}
}
return result;
}
private:
void preorder(TreeNode* node, TreeNode* search, std::vector<TreeNode*>& path,
std::vector<TreeNode*>& result, int& finish) {
if (!node || finish) {
return;
}
path.push_back(node);
if (node == search) {
finish = 1;
result = path;
}
preorder(node->left, search, path, result, finish);
preorder(node->right, search, path, result, finish);
path.pop_back();
}
};
int main() {
TreeNode a(3);
TreeNode b(5);
TreeNode c(1);
TreeNode d(6);
TreeNode e(2);
TreeNode f(0);
TreeNode x(8);
TreeNode y(7);
TreeNode z(4);
a.left = &b;
a.right = &c;
b.left = &d;
b.right = &e;
c.left = &f;
c.right = &x;
e.left = &y;
e.right = &z;
Solution solve;
TreeNode* result = solve.lowestCommonAncestor(&a, &b, &f);
printf("lowestCommonAncestor = %d\n", result->val);
result = solve.lowestCommonAncestor(&a, &d, &z);
printf("lowestCommonAncestor = %d\n", result->val);
result = solve.lowestCommonAncestor(&a, &b, &y);
printf("lowestCommonAncestor = %d\n", result->val);
return 0;
}
例三:LeetCode114




//给定一个二叉树,将该二叉树"就地"转化为单链表。
//单链表中节点序为前序遍历的顺序。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
void flatten(TreeNode* root) {
TreeNode* last = NULL;
preorder(root, last);
}
private:
void preorder(TreeNode* node, TreeNode*& last) {
if (!node) {
return;
}
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) {
last = node;
return;
}
TreeNode* left = node->left;
TreeNode* right = node->right;
TreeNode* left_last = NULL;
TreeNode* right_last = NULL;
if (left) {
preorder(left, left_last);
node->left = NULL;
node->right = left;
last = left_last;
}
if (right) {
preorder(right, right_last);
if (left_last) {
left_last->right = right;
}
last = right_last;
}
}
};
int main() {
TreeNode a(1);
TreeNode b(2);
TreeNode c(5);
TreeNode d(3);
TreeNode e(4);
TreeNode f(6);
a.left = &b;
a.right = &c;
b.left = &d;
b.right = &e;
c.right = &f;
Solution solve;
solve.flatten(&a);
TreeNode* head = &a;
while (head) {
if (head->left) {
printf("ERROR\n");
}
printf("[%d]", head->val);
head = head->right;
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}

//二叉树的广度优先遍历,利用队列
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
void BFS_print(TreeNode* root) {
std::queue<TreeNode*> Q;
Q.push(root);
while (!Q.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = Q.front();
Q.pop();
printf("[%d]\n", node->val);
if (node->left) {
Q.push(node->left);
}
if (node->right) {
Q.push(node->right);
}
}
}
int main() {
TreeNode a(1);
TreeNode b(2);
TreeNode c(5);
TreeNode d(3);
TreeNode e(4);
TreeNode f(6);
a.left = &b;
a.right = &c;
b.left = &d;
b.right = &e;
c.right = &f;
BFS_print(&a);
return 0;
}
例四:LeetCode199


//给定一个二叉树,假设从该二叉树的右侧观察它
//将观察到的节点按照从上到下的顺序输出。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
std::vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
std::vector<int> view;
std::queue<std::pair<TreeNode*, int>> Q;
if (root) {
Q.push(std::make_pair(root, 0));
}
while (!Q.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = Q.front().first;
int depth = Q.front().second;
Q.pop();
if (view.size() == depth) {
view.push_back(node->val);
}
else {
view[depth] = node->val;
}
if (node->left) {
Q.push(std::make_pair(node->left, depth + 1));
}
if (node->right) {
Q.push(std::make_pair(node->right, depth + 1));
}
}
return view;
}
};
int main() {
TreeNode a(1);
TreeNode b(2);
TreeNode c(5);
TreeNode d(3);
TreeNode e(4);
TreeNode f(6);
a.left = &b;
a.right = &c;
b.left = &d;
b.right = &e;
c.right = &f;
Solution solve;
std::vector<int> result = solve.rightSideView(&a);
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
printf("[%d]\n", result[i]);
}
return 0;
}

//图的邻接矩阵数据结构
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
int main() {
const int MAX_N = 5;
int Graph[MAX_N][MAX_N] = { 0 };
Graph[0][2] = 1;
Graph[0][4] = 1;
Graph[1][0] = 1;
Graph[1][2] = 1;
Graph[2][3] = 1;
Graph[3][4] = 1;
Graph[4][4] = 1;
printf("Graph\n");
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < MAX_N; j++) {
printf("%d ", Graph[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
//图的邻接表数据结构
struct GraphNode {
int label;
std::vector<GraphNode*> neighbors;
GraphNode(int x) : label(x) {}
};
int main() {
const int MAX_N = 5;
GraphNode* Graph[MAX_N];
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++) {
Graph[i] = new GraphNode(i);
}
Graph[0]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[2]);
Graph[0]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[4]);
Graph[1]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[0]);
Graph[1]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[2]);
Graph[2]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[3]);
Graph[3]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[4]);
Graph[4]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[3]);
printf("Graph:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++) {
printf("label[%d]:", i);
for (int j = 0; j < Graph[i]->neighbors.size(); j++) {
printf(" %d", Graph[i]->neighbors[j]->label);
}
printf("\n");
}
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++) {
delete Graph[i];
}
return 0;
}


//图的邻接矩阵数据结构
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
int main() {
const int MAX_N = 5;
int Graph[MAX_N][MAX_N] = { 0 };
Graph[0][2] = 1;
Graph[0][4] = 1;
Graph[1][0] = 1;
Graph[1][2] = 1;
Graph[2][3] = 1;
Graph[3][4] = 1;
Graph[4][4] = 1;
printf("Graph\n");
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < MAX_N; j++) {
printf("%d ", Graph[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
图的邻接表数据结构
struct GraphNode {
int label;
std::vector<GraphNode*> neighbors;
GraphNode(int x) : label(x) {}
};
int main() {
const int MAX_N = 5;
GraphNode* Graph[MAX_N];
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++) {
Graph[i] = new GraphNode(i);
}
Graph[0]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[2]);
Graph[0]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[4]);
Graph[1]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[0]);
Graph[1]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[2]);
Graph[2]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[3]);
Graph[3]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[4]);
Graph[4]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[3]);
printf("Graph:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++) {
printf("label[%d]:", i);
for (int j = 0; j < Graph[i]->neighbors.size(); j++) {
printf(" %d", Graph[i]->neighbors[j]->label);
}
printf("\n");
}
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++) {
delete Graph[i];
}
return 0;
}
// DFS深度搜索邻接表
void DFS_graph(GraphNode* node, int visit[]) {
visit[node->label] = 1;
printf("%d ", node->label);
for (int i = 0; i < node->neighbors.size(); i++) {
if (visit[node->neighbors[i]->label] == 0) {
DFS_graph(node->neighbors[i], visit);
}
}
}
int main() {
const int MAX_N = 5;
GraphNode* Graph[MAX_N];
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++) {
Graph[i] = new GraphNode(i);
}
Graph[0]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[4]);
Graph[0]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[2]);
Graph[1]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[0]);
Graph[1]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[2]);
Graph[2]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[3]);
Graph[3]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[4]);
Graph[4]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[3]);
int visit[MAX_N] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++) {
if (visit[i] == 0) {
printf("From label(%d):", Graph[i]->label);
DFS_graph(Graph[i], visit);
printf("\n");
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++) {
delete Graph[i];
}
return 0;
}
// 图的广度优先遍历
void BFS_graph(GraphNode* node, int visit[]) {
std::queue<GraphNode*> Q;
Q.push(node);
visit[node->label] = 1;
while (!Q.empty()) {
GraphNode* node = Q.front();
Q.pop();
printf("%d ", node->label);
for (int i = 0; i < node->neighbors.size(); i++) {
if (visit[node->neighbors[i]->label] == 0) {
Q.push(node->neighbors[i]);
visit[node->neighbors[i]->label] = 1;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
const int MAX_N = 5;
GraphNode* Graph[MAX_N];
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++) {
Graph[i] = new GraphNode(i);
}
Graph[0]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[4]);
Graph[0]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[2]);
Graph[1]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[0]);
Graph[1]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[2]);
Graph[2]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[3]);
Graph[3]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[4]);
Graph[4]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[3]);
int visit[MAX_N] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++) {
if (visit[i] == 0) {
printf("From Label(%d):", Graph[i]->label);
BFS_graph(Graph[i], visit);
printf("\n");
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++) {
delete Graph[i];
}
return 0;
}
例五:LeetCode207



//已知有n门课程,标记从0至n-1,课程之间是有依赖关系的,
//例如希望完成A课程,可能需要完成B课程。已知n个课程的依赖关系,
//可否将n门课程学完。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
struct GraphNode {
int label;
std::vector<GraphNode*> neighbors;
GraphNode(int x) : label(x) {}
};
//深度优先算法
class Solution{
public:
bool canFinish(int numCourses, std::vector<std::vector<int>> &prerequisites){
std::vector<GraphNode*> graph;
std::vector<int> visit;
for(int i=0; i<numCourses; i++){
graph.push_back(new GraphNode(i));
visit.push_back(-1);
}
for(int i=0; i<prerequisites.size(); i++){
GraphNode *begin = graph[prerequisites[i][1]];
GraphNode *end = graph[prerequisites[i][0]];
begin->neighbors.push_back(end);
}
for(int i=0; i<graph.size(); i++){
if(visit[i] == -1 && !DFS_graph(graph[i], visit)){
return false;
}
}
for(int i=0; i<numCourses; i++){
delete graph[i];
}
return true;
}
private:
bool DFS_graph(GraphNode* node, std::vector<int> &visit){
visit[node->label] = 0;
for(int i=0; i<node->neighbors.size(); i++){
if(visit[node->neighbors[i]->label] == -1){
if(DFS_graph(node->neighbors[i], visit) == 0){
return false;
}
}
else if(visit[node->neighbors[i]->label] == 0){
return false;
}
}
visit[node->label] = 1;
return true;
}
};


//广度搜索算法
class Solution{
public:
bool canFinish(int numCourses, std::vector<std::vector<int>> &prerequisites){
std::vector<GraphNode*> graph;
std::vector<int> degree;
for(int i=0; i<numCourses; i++){
degree.push_back(0);
graph.push_back(new GraphNode(i));
}
for(int i=0; i<prerequisites.size(); i++){
GraphNode *begin = graph[prerequisites[i][1]];
GraphNode *end = graph[prerequisites[i][0]];
begin->neighbors.push_back(end);
degree[prerequisites[i][0]]++;
}
std::queue<GraphNode*> Q;
for(int i=0; i<numCourses; i++){
if(degree[i] == 0){
Q.push(graph[i]);
}
}
while(!Q.empty()){
GraphNode* node = Q.front();
Q.pop();
for(int i=0; i<node->neighbors.size(); i++){
degree[node->neighbors[i]->label]--;
if(degree[node->neighbors[i]->label] == 0){
Q.push(node->neighbors[i]);
}
}
}
for(int i=0; i<graph.size(); i++){
delete graph[i];
}
for(int i=0; i<degree.size(); i++){
if(degree[i]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};












































 317
317

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








