最新案例动态,请查阅【案例共创】基于华为开发者空间的RestNet50目标检测。小伙伴们快来领取华为开发者空间进行实操吧!
本案例由:梅科尔工作室提供
1 概述
1.1 案例介绍
ResNet50模型是一种深度卷积神经网络,它使用残差模块和跳跃连接来缓解梯度消失问题。反向传播算法在ResNet模型中同样起着到头重要的作用,它可以计算ResNet模型中各个权重的梯度,并更新权重,从而优化模型性能。本案例使用到开发者空间----工作台/AI Notebook。
本案例选择医院的病例数据作为示例,并借助开发者空间工作台提供的免费AI Notebook编辑器进行本地编辑函数、轻松部署上云,直观地展示Notebook支持AI训练模型的开发与调试能力和实际应用开发中为开发者带来的便利。
通过实际操作,让大家深入了解如何利用 Notebook开发并部署一个梯度与反向传播算法。在这个过程中,大家将学习到从函数创建、模型训练到应用部署以及与 API集成等一系列关键步骤,从而掌握ResNet50的基本使用方法,体验其在Notebook开发中的优势。
1.2 适用对象
-
企业
-
个人开发者
-
高校学生
1.3 案例时间
本案例总时长预计120分钟。
1.4 案例流程
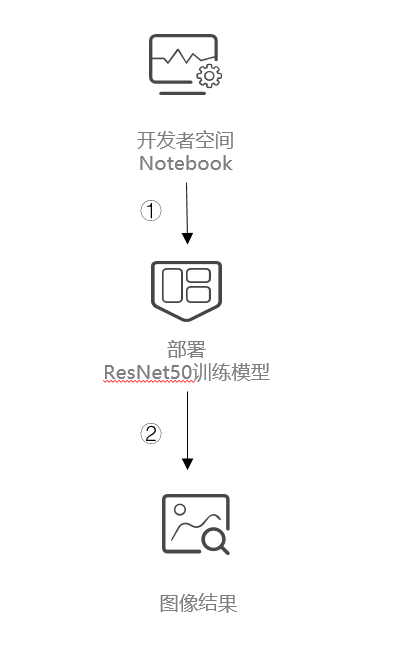
说明:
-
开发者空间进入Notebook;
-
在Notebook中用NPU训练模型,跑结果;
1.5 资源总览
| 资源名称 | 规格 | 单价(元) | 时长(分钟) |
| 开发者空间----工作台/AI Notebook | NPU basic · 1 * NPU 910B · 8v CPU · 24GB | 免费 | 120 |
2 梯度与反向传播算法
2.1 代码分析
环境配置
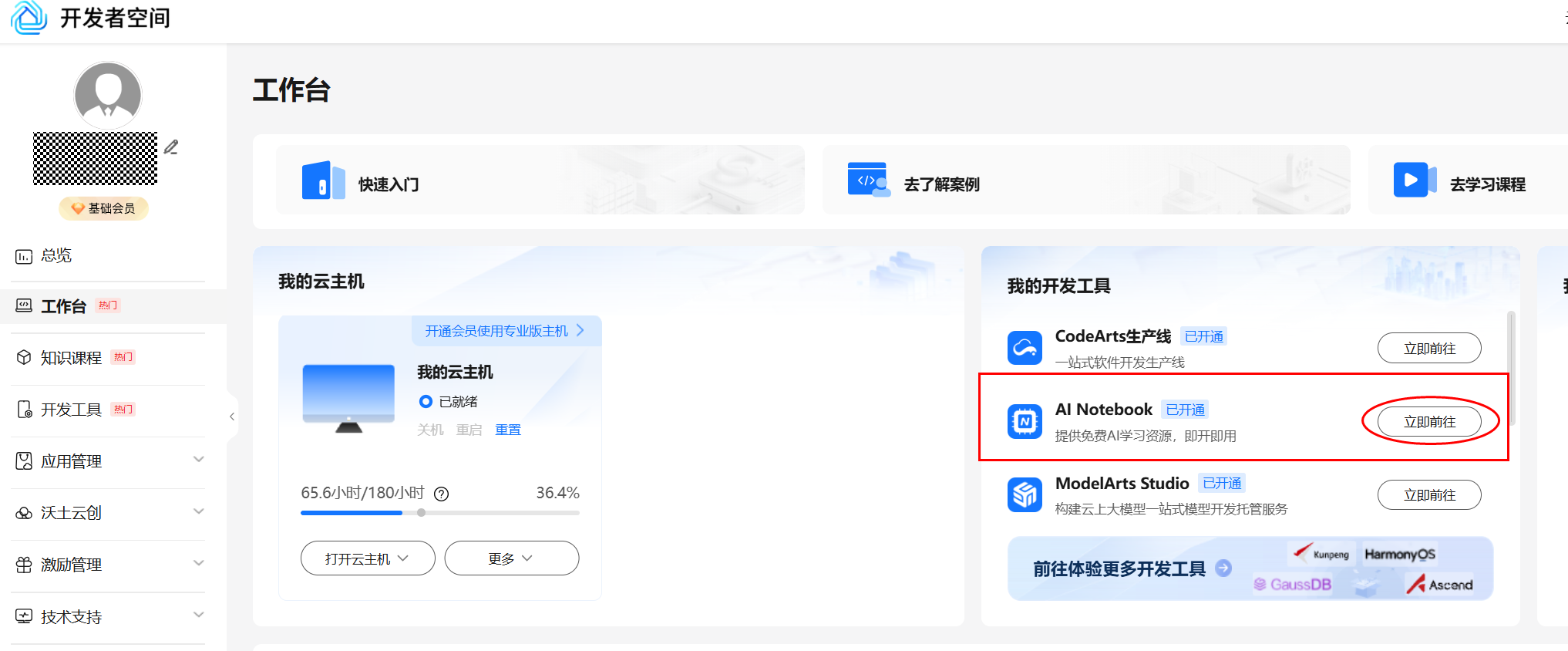
详细资源配置请参考案例华为开发者空间AI Notebook使用指导:步骤二。
进入华为开发者空间界面,进入AI Notebook页面。
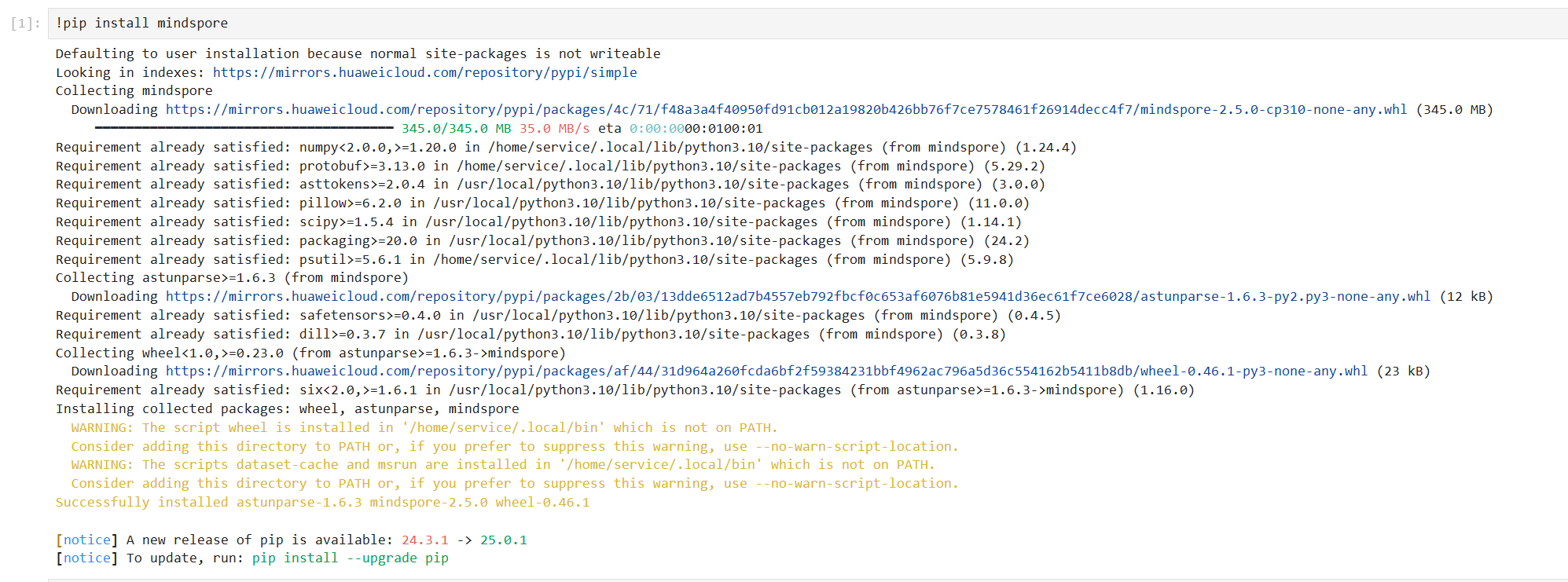
!pip install mindspore
!pip install numpy
说明numpy模块已经被安装了。
!pip install matplotlib
!pip install opencv-python

opencv模块在pip install安装失败,用-i指定其他下载源也安装失败,所以此处用yum install安装opencv模块。
!pip install pillow
MindSpore:深度学习框架,用于构建和训练模型。
NumPy:用于数值计算,处理数据。
Matplotlib:用于数据可视化,绘制图表。
OpenCV:用于图像处理,可能在数据预处理中使用。
Pillow:用于图像处理,加载和处理图像数据。
注:如果存在软件包下载失败,可以添加参数-i指定华为云的安装源。例如:
!pip install matplotlib -i https://repo.huaweicloud.com/repository/pypi/simple/
数据获取和准备
!wget <https://dtse-mirrors.obs.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com/case/0036/skin-cancer-detection.tar>
!mkdir pifudata_Maker
!tar -xvf skin-cancer-detection.tar -C pifudata_Maker/
注释:使用git命令克隆数据集仓库,并解压数据集到指定文件夹。
分析:数据集是项目的基础,克隆和解压操作确保了数据的可用性。
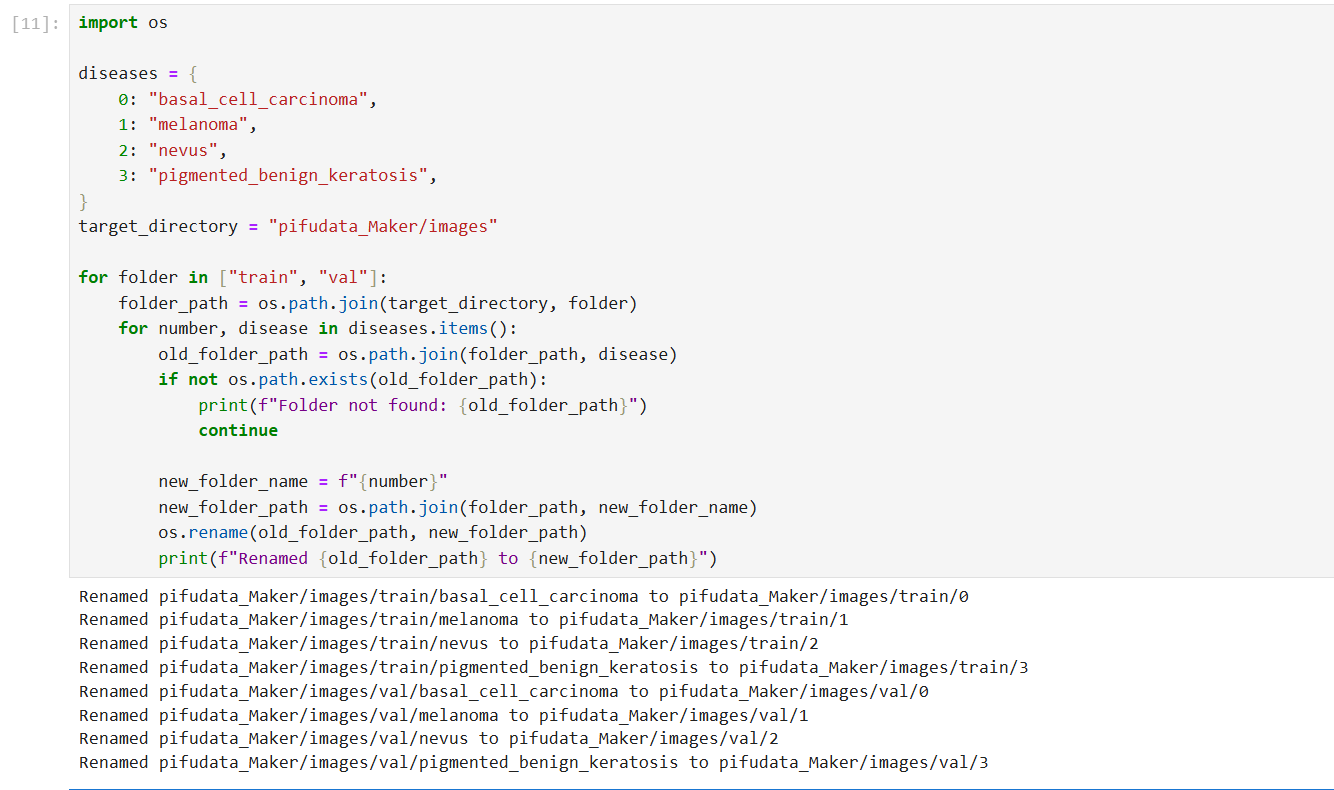
import os
diseases = {
0: "basal_cell_carcinoma",
1: "melanoma",
2: "nevus",
3: "pigmented_benign_keratosis",
}
target_directory = "pifudata_Maker/images"
for folder in ["train", "val"]:
folder_path = os.path.join(target_directory, folder)
for number, disease in diseases.items():
old_folder_path = os.path.join(folder_path, disease)
if not os.path.exists(old_folder_path):
print(f"Folder not found: {old_folder_path}")
continue
new_folder_name = f"{number}"
new_folder_path = os.path.join(folder_path, new_folder_name)
os.rename(old_folder_path, new_folder_path)
print(f"Renamed {old_folder_path} to {new_folder_path}")
注释:定义疾病名称和编号的映射,并对训练和验证数据集的文件夹进行重命名,方便后续处理。
分析:数据组织结构的调整有助于模型训练时的数据加载和管理。
预训练模型准备
在工程文件下新建文件夹,命名为:pretrainmodel,然后在命令行中输入:
!mkdir pretrainmodel
!wget -P pretrainmodel <https://mindspore-website.obs.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com/notebook/models/application/resnet50_224_new.ckpt>
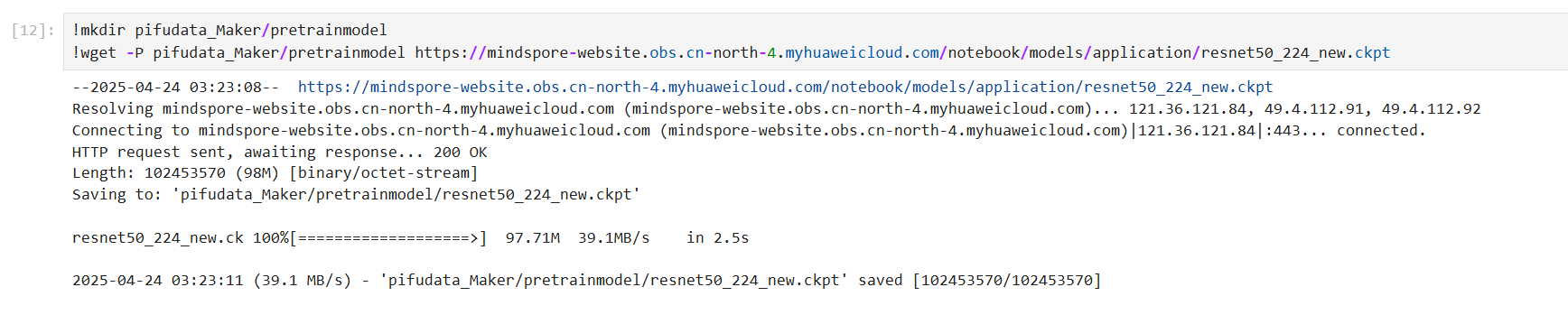
注意:如果系统中没有wget环境请先安装:
sudo apt-get install wget
数据可视化
注意:下面Python代码中,data_path_train和data_path_val需要根据实际位置进行修改。
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
diseases = {
0: "basal_cell_carcinoma",
1: "melanoma",
2: "nevus",
3: "pigmented_benign_keratosis",
}
data_path_train = "pifudata_Maker/images/train"
data_path_val = "pifudata_Maker/images/val"
file_counts_train = {}
file_counts_val = {}
for folder_name in os.listdir(data_path_train):
folder_path = os.path.join(data_path_train, folder_name)
if os.path.isdir(folder_path):
count = len(os.listdir(folder_path))
file_counts_train[diseases.get(folder_name, folder_name)] = count
for folder_name in os.listdir(data_path_val):
folder_path = os.path.join(data_path_val, folder_name)
if os.path.isdir(folder_path):
count = len(os.listdir(folder_path))
file_counts_val[diseases.get(folder_name, folder_name)] = count
train_categories = list(file_counts_train.keys())
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
train_bars = plt.bar(train_categories, file_counts_train.values(), width=0.4, color='blue', label='Train')
val_bars = plt.bar([train_categories.index(cat) + 0.4 for cat in train_categories], [file_counts_val.get(cat, 0) for cat in train_categories], width=0.4, color='green', label='Validation')
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel('labels')
plt.ylabel('Number of Images')
plt.title('Training and Validation Datasets')
train_list = [diseases[int(i)] for i in train_categories]
plt.xticks([train_categories.index(cat) + 0.2 for cat in train_categories], train_list, rotation=30, fontsize='small')
for i, (train_bar, val_bar) in enumerate(zip(train_bars, val_bars)):
train_height = train_bar.get_height()
val_height = val_bar.get_height() if val_bar else 0
plt.text(train_bar.get_x() + train_bar.get_width() / 2, train_height, '{}'.format(train_height), ha='center', va='bottom')
plt.text(val_bar.get_x() + val_bar.get_width() / 2, val_height, '{}'.format(val_height), ha='center', va='bottom') if val_bar else None
plt.show()
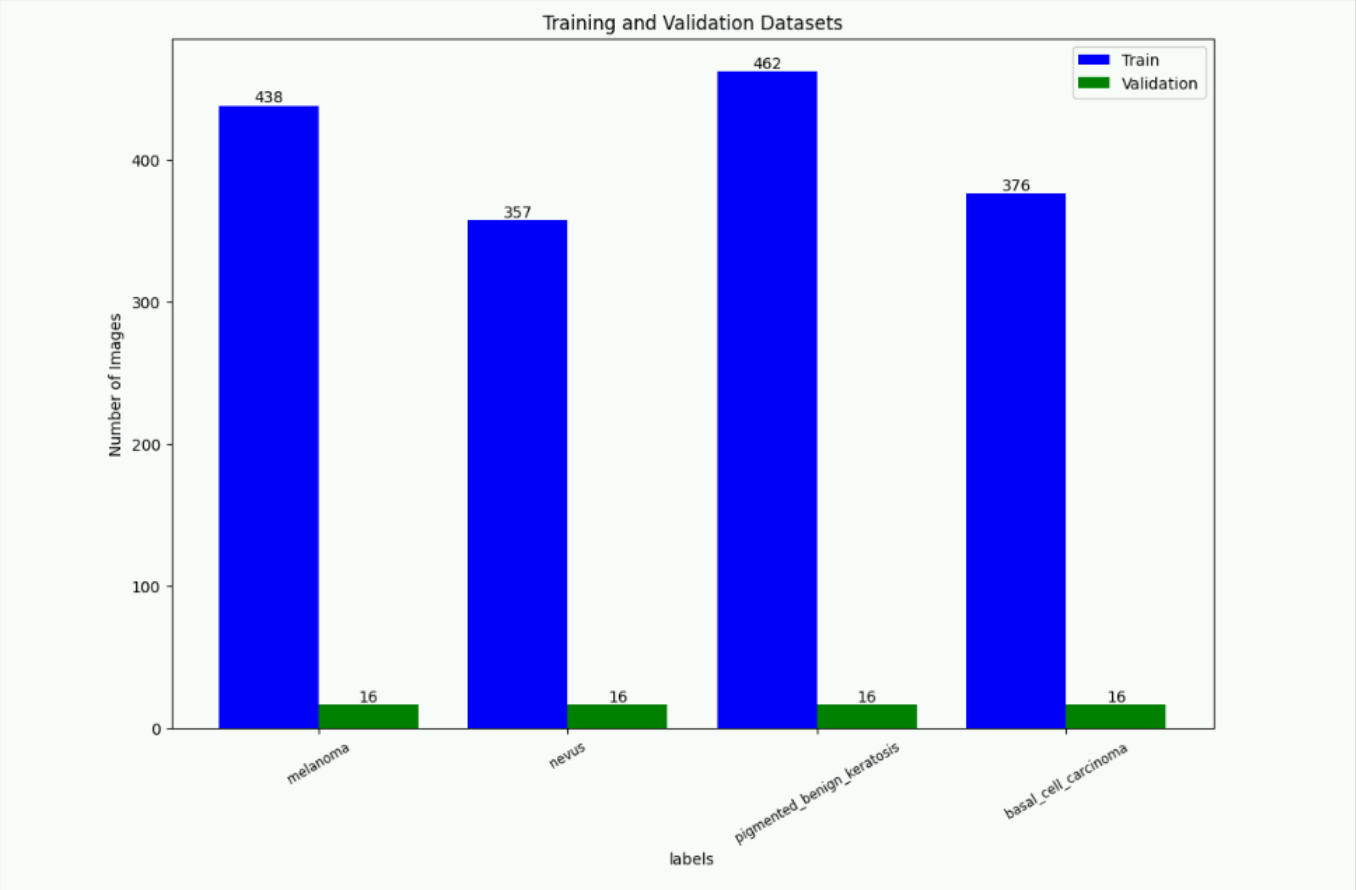
注释:统计训练和验证数据集中各类别的样本数量,并生成条形图进行可视化。
分析:数据分布的可视化有助于了解数据的平衡性,为模型训练提供参考。
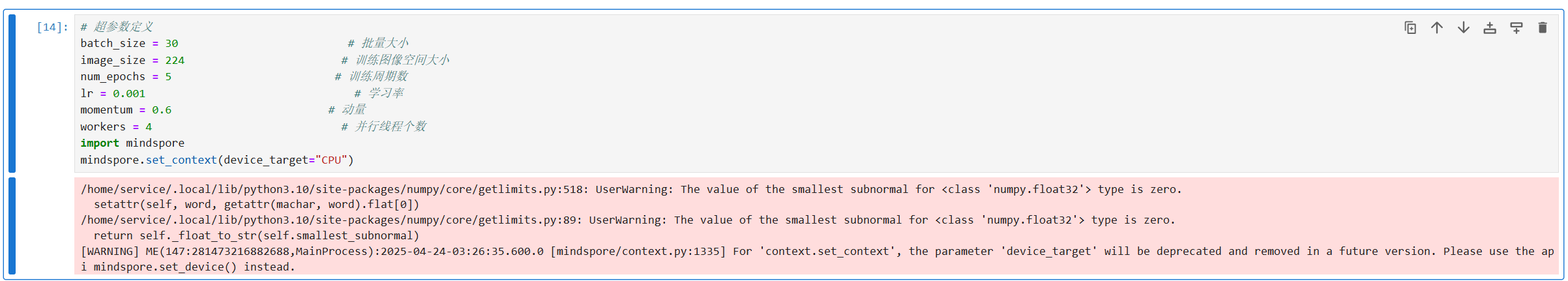
超参数定义
# 超参数定义
batch_size = 30 # 批量大小
image_size = 224 # 训练图像空间大小
num_epochs = 5 # 训练周期数
lr = 0.001 # 学习率
momentum = 0.6 # 动量
workers = 4 # 并行线程个数
import mindspore
mindspore.set_context(device_target="CPU")
注释:定义模型训练的超参数,包括批量大小、图像大小、训练周期数、学习率、动量和并行线程个数。
分析:超参数的选择对模型的训练效果和效率有重要影响,需要根据具体任务进行调整。
数据加载和预处理
import mindspore as ms
import mindspore.dataset as ds
import mindspore.dataset.vision as vision
# 数据集目录路径
data_path_train = "pifudata_Maker/images/train"
data_path_val = "pifudata_Maker/images/val"
# 创建训练数据集
def create_dataset_canidae(dataset_path, usage):
"""数据加载"""
data_set = ds.ImageFolderDataset(dataset_path,
num_parallel_workers=workers,
shuffle=True,)
# 数据增强操作
mean = [0.485 * 255, 0.456 * 255, 0.406 * 255]
std = [0.229 * 255, 0.224 * 255, 0.225 * 255]
scale = 32
if usage == "train":
# Define map operations for training dataset
trans = [
vision.RandomCropDecodeResize(size=image_size, scale=(0.08, 1.0), ratio=(0.75, 1.333)),
vision.RandomHorizontalFlip(prob=0.5),
vision.Normalize(mean=mean, std=std),
vision.HWC2CHW()
]
else:
# Define map operations for inference dataset
trans = [
vision.Decode(),
vision.Resize(image_size + scale),
vision.CenterCrop(image_size),
vision.Normalize(mean=mean, std=std),
vision.HWC2CHW()
]
# 数据映射操作
data_set = data_set.map(
operations=trans,
input_columns='image',
num_parallel_workers=workers)
# 批量操作
data_set = data_set.batch(batch_size)
return data_set
dataset_train = create_dataset_canidae(data_path_train, "train")
step_size_train = dataset_train.get_dataset_size()
dataset_val = create_dataset_canidae(data_path_val, "val")
step_size_val = dataset_val.get_dataset_size()
print(step_size_train)
print(step_size_val)
data = next(dataset_val.create_dict_iterator())
images = data["image"]
labels = data["label"]
# print(data["image"][0])
print("Tensor of image", images.shape)
print("Labels:", labels)
注释:定义数据加载和预处理函数,对训练和验证数据集进行不同的数据增强操作,并批量加载数据。
分析:数据增强可以提高模型的泛化能力,预处理操作确保输入数据的格式和分布符合模型的要求。

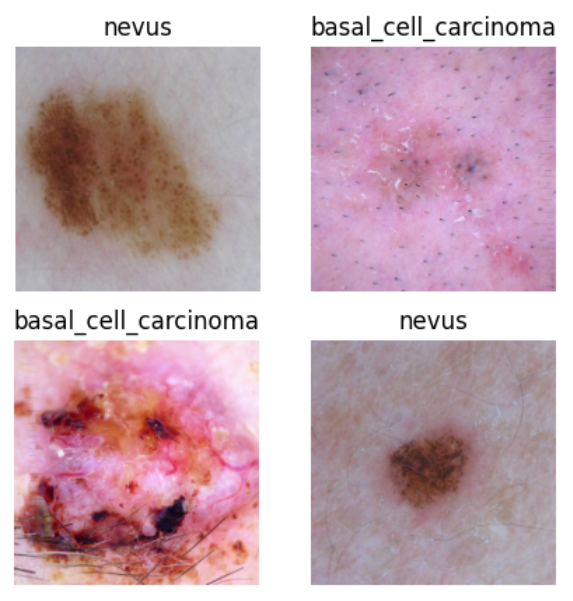
数据集可视化
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# class_name对应label,按文件夹字符串从小到大的顺序标记label
class_name = {
0: "basal_cell_carcinoma",
1: "melanoma",
2: "nevus",
3: "pigmented_benign_keratosis",
}
# print(images[0])
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
for i in range(4):
# 获取图像及其对应的label
# print(images[i])
data_image = images[i].asnumpy()
data_label = labels[i]
# 处理图像供展示使用
data_image = np.transpose(data_image, (1, 2, 0))
mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
std = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
data_image = std * data_image + mean
data_image = np.clip(data_image, 0, 1)
# 显示图像
plt.subplot(2, 2, i+1)
plt.imshow(data_image)
plt.title(class_name[int(labels[i].asnumpy())])
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
注释:定义残差网络的基本模块、构建ResNet模型,并定义ResNet50的函数,支持加载预训练模型。
分析:ResNet模型通过残差连接解决了深度网络中的梯度消失问题,预训练模型的加载可以加速训练并提高模型性能。
**注意:**该部分Python代码最好与第5部分代码合在一起运行,以免报asnumpy()函数引用问题。
模型网络搭建
from typing import Type, Union, List, Optional
from mindspore import nn, train
from mindspore.common.initializer import Normal
weight_init = Normal(mean=0, sigma=0.02)
gamma_init = Normal(mean=1, sigma=0.02)
class ResidualBlockBase(nn.Cell):
expansion: int = 1 # 最后一个卷积核数量与第一个卷积核数量相等
def __init__(self, in_channel: int, out_channel: int,
stride: int = 1, norm: Optional[nn.Cell] = None,
down_sample: Optional[nn.Cell] = None) -> None:
super(ResidualBlockBase, self).__init__()
if not norm:
self.norm = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
else:
self.norm = norm
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
weight_init=weight_init)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel,
kernel_size=3, weight_init=weight_init)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.down_sample = down_sample
def construct(self, x):
"""ResidualBlockBase construct."""
identity = x # shortcuts分支
out = self.conv1(x) # 主分支第一层:3*3卷积层
out = self.norm(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out) # 主分支第二层:3*3卷积层
out = self.norm(out)
if self.down_sample is not None:
identity = self.down_sample(x)
out += identity # 输出为主分支与shortcuts之和
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class ResidualBlock(nn.Cell):
expansion = 4 # 最后一个卷积核的数量是第一个卷积核数量的4倍
def __init__(self, in_channel: int, out_channel: int,
stride: int = 1, down_sample: Optional[nn.Cell] = None) -> None:
super(ResidualBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel,
kernel_size=1, weight_init=weight_init)
self.norm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(out_channel, out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
weight_init=weight_init)
self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(out_channel, out_channel * self.expansion,
kernel_size=1, weight_init=weight_init)
self.norm3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel * self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.down_sample = down_sample
def construct(self, x):
identity = x # shortscuts分支
out = self.conv1(x) # 主分支第一层:1*1卷积层
out = self.norm1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out) # 主分支第二层:3*3卷积层
out = self.norm2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out) # 主分支第三层:1*1卷积层
out = self.norm3(out)
if self.down_sample is not None:
identity = self.down_sample(x)
out += identity # 输出为主分支与shortcuts之和
out = self.relu(out)
return out
def make_layer(last_out_channel, block: Type[Union[ResidualBlockBase, ResidualBlock]],
channel: int, block_nums: int, stride: int = 1):
down_sample = None # shortcuts分支
if stride != 1 or last_out_channel != channel * block.expansion:
down_sample = nn.SequentialCell([
nn.Conv2d(last_out_channel, channel * block.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=stride, weight_init=weight_init),
nn.BatchNorm2d(channel * block.expansion, gamma_init=gamma_init)
])
layers = []
layers.append(block(last_out_channel, channel, stride=stride, down_sample=down_sample))
in_channel = channel * block.expansion
# 堆叠残差网络
for _ in range(1, block_nums):
layers.append(block(in_channel, channel))
return nn.SequentialCell(layers)
from mindspore import load_checkpoint, load_param_into_net
class ResNet(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self, block: Type[Union[ResidualBlockBase, ResidualBlock]],
layer_nums: List[int], num_classes: int, input_channel: int) -> None:
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
# 第一个卷积层,输入channel为3(彩色图像),输出channel为64
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, weight_init=weight_init)
self.norm = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
# 最大池化层,缩小图片的尺寸
self.max_pool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, pad_mode='same')
# 各个残差网络结构块定义,
self.layer1 = make_layer(64, block, 64, layer_nums[0])
self.layer2 = make_layer(64 * block.expansion, block, 128, layer_nums[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = make_layer(128 * block.expansion, block, 256, layer_nums[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = make_layer(256 * block.expansion, block, 512, layer_nums[3], stride=2)
# 平均池化层
self.avg_pool = nn.AvgPool2d()
# flattern层
self.flatten = nn.Flatten()
# 全连接层
self.fc = nn.Dense(in_channels=input_channel, out_channels=num_classes)
def construct(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.norm(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.max_pool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.avg_pool(x)
x = self.flatten(x)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def download_pretrained_model(url, save_path):
# 创建目录
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(save_path), exist_ok=True)
# 下载文件
urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, save_path)
print(f"预训练模型已下载到: {save_path}")
def _resnet(model_url: str, block: Type[Union[ResidualBlockBase, ResidualBlock]],
layers: List[int], num_classes: int, pretrained: bool, pretrianed_ckpt: str,
input_channel: int):
model = ResNet(block, layers, num_classes, input_channel)
if pretrained:
# 加载预训练模型
# download(url=model_url, path=pretrianed_ckpt, replace=True)
param_dict = load_checkpoint(pretrianed_ckpt)
load_param_into_net(model, param_dict)
return model
def resnet50(num_classes: int = 1000, pretrained: bool = False):
"ResNet50模型"
resnet50_url = "https://mindspore-website.obs.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com/notebook/models/application/resnet50_224_new.ckpt"
resnet50_ckpt = "./pretrainmodel/resnet50_224_new.ckpt"
return _resnet(resnet50_url, ResidualBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes,
pretrained, resnet50_ckpt, 2048)
注释:定义残差网络的基本模块、构建ResNet模型,并定义ResNet50的函数,支持加载预训练模型。
分析:ResNet模型通过残差连接解决了深度网络中的梯度消失问题,预训练模型的加载可以加速训练并提高模型性能。
模型训练(训练时长预计40min)
先导入预训练模型文件:新建pretrainmodel文件夹,将以下文件导入:
resnet50_224_new.ckpt
命令如下
!mkdir pretrainmodel
!wget -P pretrainmodel <https://mindspore-website.obs.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com/notebook/models/application/resnet50_224_new.ckpt>
# 代码中首先导入了必要的MindSpore模块和函数,并设置了运行环境。
import mindspore
from mindspore import nn, train
from mindspore.nn import Loss, Accuracy
!pip install download
import mindspore as ms
from download import download
network = resnet50(pretrained=True)
# 通过替换ResNet50的原始全连接层和平均池化层来适配新的任务
# 全连接层输入层的大小
in_channels = network.fc.in_channels
# 输出通道数大小为皮肤肿瘤分类数4
head = nn.Dense(in_channels, 4)
# 重置全连接层
network.fc = head
# 平均池化层kernel size为7
avg_pool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=7)
# 重置平均池化层
network.avg_pool = avg_pool
import mindspore as ms
import mindspore
# 定义优化器和损失函数
opt = nn.Momentum(params=network.trainable_params(), learning_rate=lr, momentum=momentum)
loss_fn = nn.SoftmaxCrossEntropyWithLogits(sparse=True, reduction='mean')
# 实例化模型
model = train.Model(network, loss_fn, opt, metrics={"Accuracy": Accuracy()})
def forward_fn(inputs, targets):
logits = network(inputs)
loss = loss_fn(logits, targets)
return loss
grad_fn = mindspore.ops.value_and_grad(forward_fn, None, opt.parameters)
def train_step(inputs, targets):
loss, grads = grad_fn(inputs, targets)
opt(grads)
return loss
# 创建迭代器
data_loader_train = dataset_train.create_tuple_iterator(num_epochs=num_epochs)
# 最佳模型保存路径
best_ckpt_dir = "./BestCheckpoint"
best_ckpt_path = "./BestCheckpoint/resnet50-best.ckpt"
import os
import time
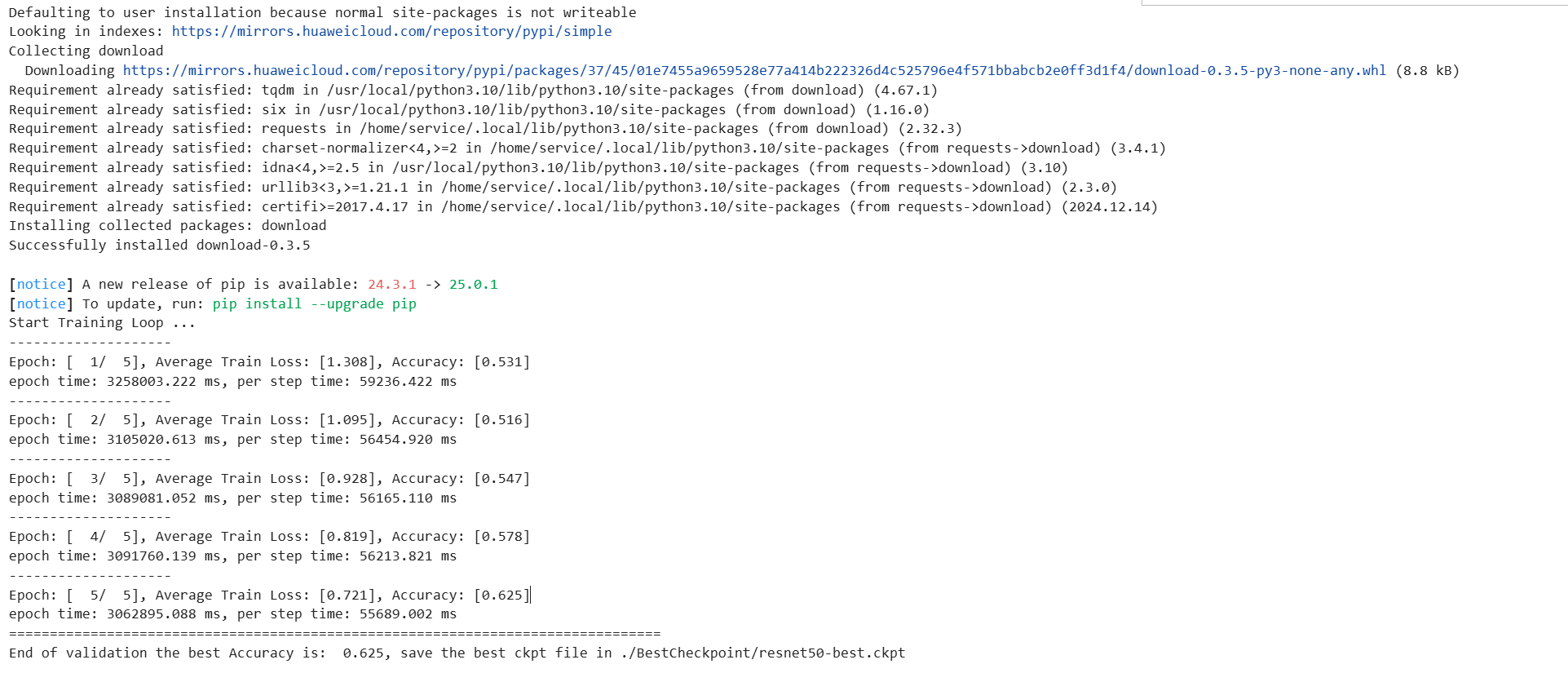
# 开始循环训练
print("Start Training Loop ...")
best_acc = 0
# 训练循环中,数据通过迭代器被加载,模型在每个epoch中更新权重,并计算训练损失。
# 在每个epoch结束时,模型在验证集上评估准确率,并保存具有最高准确率的模型检查点。
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
losses = []
network.set_train()
epoch_start = time.time()
# 为每轮训练读入数据
for i, (images, labels) in enumerate(data_loader_train):
labels = labels.astype(ms.int32)
loss = train_step(images, labels)
losses.append(loss)
# 每个epoch结束后,验证准确率
acc = model.eval(dataset_val)['Accuracy']
epoch_end = time.time()
epoch_seconds = (epoch_end - epoch_start) * 1000
step_seconds = epoch_seconds/step_size_train
print("-" * 20)
print("Epoch: [%3d/%3d], Average Train Loss: [%5.3f], Accuracy: [%5.3f]" % (
epoch+1, num_epochs, sum(losses)/len(losses), acc
))
print("epoch time: %5.3f ms, per step time: %5.3f ms" % (
epoch_seconds, step_seconds
))
if acc > best_acc:
best_acc = acc
if not os.path.exists(best_ckpt_dir):
os.mkdir(best_ckpt_dir)
ms.save_checkpoint(network, best_ckpt_path)
print("=" * 80)
print(f"End of validation the best Accuracy is: {best_acc: 5.3f}, "
f"save the best ckpt file in {best_ckpt_path}", flush=True)
注释:定义模型训练的步骤,包括前向传播、反向传播、优化器和损失函数的设置,以及模型的训练和评估过程,保存最佳模型检查点。
分析:训练过程是模型学习数据特征的关键阶段,评估阶段用于监控模型的泛化能力,保存最佳模型可以用于后续的预测和部署。
模型评估
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import mindspore as ms
def visualize_model(best_ckpt_path, val_ds):
net = resnet50()
# 全连接层输入层的大小
in_channels = net.fc.in_channels
# 输出通道数大小为分类数4
head = nn.Dense(in_channels, 4)
# 重置全连接层
net.fc = head
# 平均池化层kernel size为7
avg_pool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=7)
# 重置平均池化层
net.avg_pool = avg_pool
# 加载模型参数
param_dict = ms.load_checkpoint(best_ckpt_path)
ms.load_param_into_net(net, param_dict)
model = train.Model(net)
# 加载验证集的数据进行验证
data = next(val_ds.create_dict_iterator())
images = data["image"].asnumpy()
labels = data["label"].asnumpy()
#print(labels)
class_name = {
0: "basal_cell_carcinoma",
1: "melanoma",
2: "nevus",
3: "pigmented_benign_keratosis"
}
# 预测图像类别
data_pre=ms.Tensor(data["image"])
output = model.predict(data_pre)
# print(output)
pred = np.argmax(output.asnumpy(), axis=1)
# 显示图像及图像的预测值
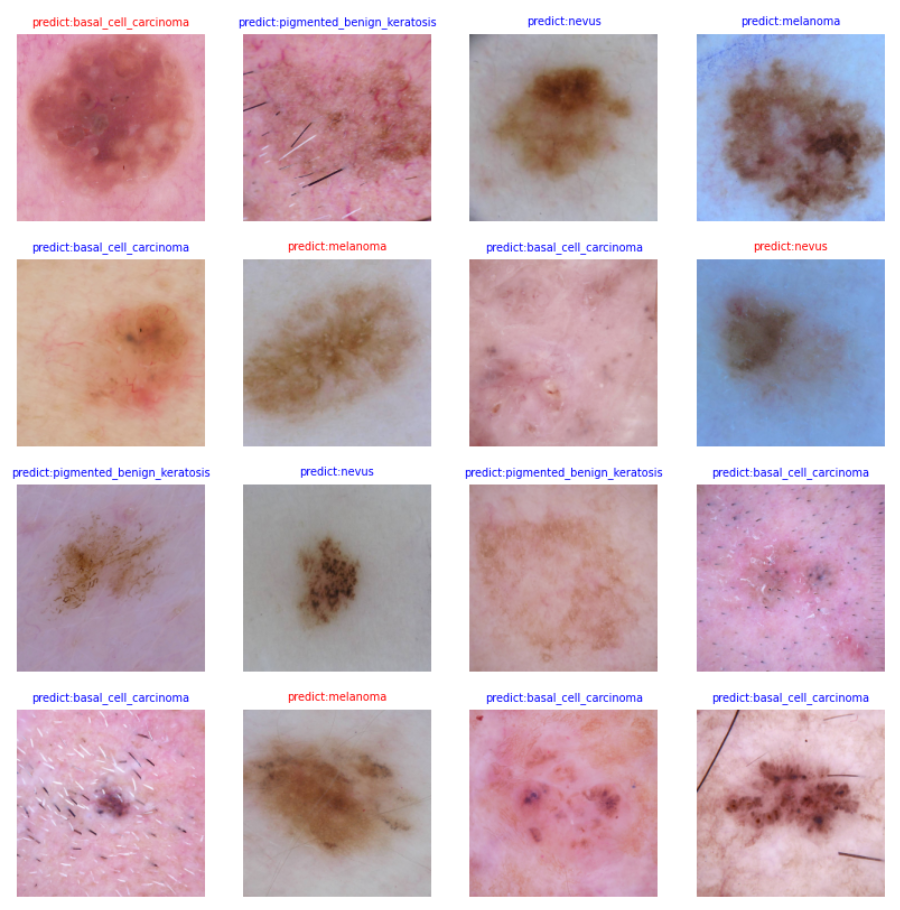
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
for i in range(16):
plt.subplot(4, 4, i + 1)
# 若预测正确,显示为蓝色;若预测错误,显示为红色
color = 'blue' if pred[i] == labels[i] else 'red'
plt.title('predict:{}'.format(class_name[pred[i]]), color=color,fontsize=7)
picture_show = np.transpose(images[i], (1, 2, 0))
mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
std = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
picture_show = std * picture_show + mean
picture_show = np.clip(picture_show, 0, 1)
plt.imshow(picture_show)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
visualize_model('BestCheckpoint/resnet50-best.ckpt', dataset_val)
从验证数据集中提取了一批次的数据,使用模型进行预测,并根据预测结果将图像及其预测标签以蓝色(正确)或红色(错误)显示。
使用matplotlib库绘制了一个包含四个子图的图像,每个子图展示了一张图像及其预测结果。
推理使用
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import mindspore as ms
from mindspore import nn
from mindspore.train.serialization import load_checkpoint, load_param_into_net
import mindspore.numpy as mnp
def preprocess_image(image_path):
# 使用PIL加载图像
from PIL import Image
image = Image.open(image_path)
# 转换图像为RGB模式
image = image.convert('RGB')
# 调整图像大小以匹配模型输入
image = image.resize((224, 224)) # 假设模型输入大小为224x224
# 将图像转换为numpy数组
image_array = np.array(image)
# 归一化图像数组
image_array = image_array / 255.0
image_array = np.transpose(image_array, (2, 0, 1))
# 扩展维度以匹配模型输入,例如 (1, 3, 224, 224)
image_array = np.expand_dims(image_array, axis=0)
return image_array.astype(np.float32) # 确保数据类型为float32
def visualize_prediction(image_path, best_ckpt_path):
net = resnet50()
# 全连接层输入层的大小
in_channels = net.fc.in_channels
# 输出通道数大小为分类数4
head = nn.Dense(in_channels, 4)
# 重置全连接层
net.fc = head
# 平均池化层kernel size为7
avg_pool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=7)
# 重置平均池化层
net.avg_pool = avg_pool
# 加载模型参数
param_dict = ms.load_checkpoint(best_ckpt_path)
ms.load_param_into_net(net, param_dict)
model = train.Model(net)
# 预处理图像
image = preprocess_image(image_path)
data_pre = ms.Tensor(image)
print(data_pre.shape)
print(type(data_pre))
class_name = {
0: "basal_cell_carcinoma",
1: "melanoma",
2: "nevus",
3: "pigmented_benign_keratosis"
}
output = model.predict(data_pre)
print(output)
pred = np.argmax(output.asnumpy(), axis=1)
print(pred)
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
plt.subplot(1, 1, 1)
plt.title('predict:{}'.format(class_name[pred[0]]))
picture_show = image[0] # 已经是归一化后的图像
picture_show = np.transpose(picture_show, (1, 2, 0)) # 转换为(224, 224, 3)
plt.imshow(picture_show)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
# 调用函数,传入图片路径和模型检查点路径
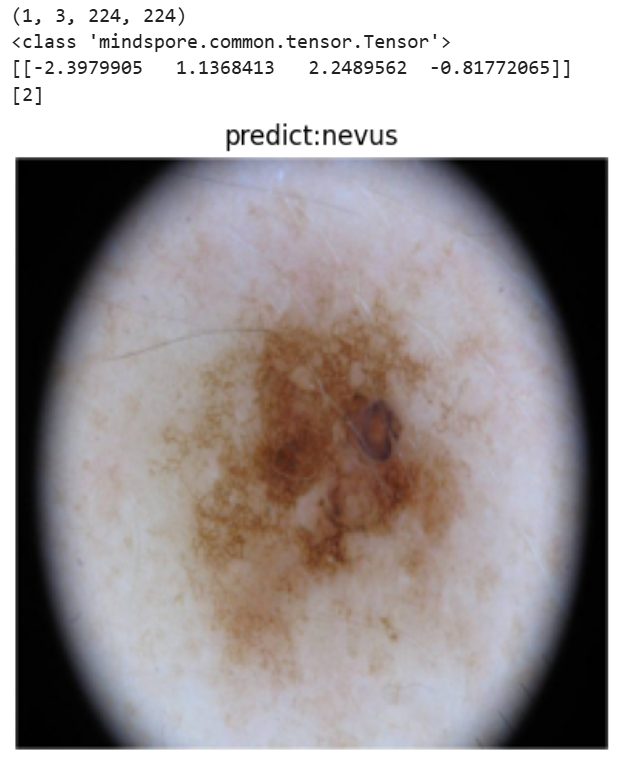
visualize_prediction('pifudata_Maker/images/val/2/ISIC_0000005.jpg','BestCheckpoint/resnet50-best.ckpt')
图像预处理与模型加载
-
定义了preprocess_image函数,用于将输入图像进行归一化处理并调整维度顺序,以适配模型的输入格式。
-
定义了visualize_prediction函数,加载预训练的ResNet50模型,并对模型的全连接层和平均池化层进行调整以适配皮肤肿瘤分类任务。
模型预测与结果可视化
-
使用预处理后的图像作为输入,通过模型进行预测,并获取预测结果。
-
将预测结果映射到对应的皮肤肿瘤类别名称,并通过matplotlib将图像及其预测类别进行可视化展示。
实际应用
- 通过调用visualize_prediction函数,对指定路径的图像进行预测和可视化,展示了如何将训练好的模型应用于实际的皮肤肿瘤分类任务中。
2.2 项目结果
模型构建与训练
- 成功构建了一个基于ResNet50的深度学习模型,用于皮肤肿瘤分类任务。
- 模型在训练集上进行了有效的学习,并在验证集上进行了性能评估。
分类准确率
-
模型在验证集上达到了一定的分类准确率,具体数值在训练过程中输出。
-
通过多个训练周期的迭代,准确率逐渐提升,最终在验证集上取得了最佳性能。
模型保存
- 训练过程中保存了最佳模型的检查点,便于后续的模型部署和预测。
可视化评估
-
通过可视化验证集中的图像,直观展示了模型对各类皮肤肿瘤的预测效果。
-
对比预测结果与真实标签,评估模型的分类准确性。
单张图像预测
-
实现了对单张皮肤肿瘤图像的预测功能,能够输出预测的肿瘤类型。
-
通过图像预处理和模型推理,展示了模型在实际应用中的效果。
2.3 项目意义
医学应用价值
-
皮肤肿瘤分类模型能够辅助医生进行皮肤肿瘤的早期筛查和诊断,提高诊断的准确性和效率。
-
对于医疗资源有限的地区,该模型可以作为一种初步的诊断工具,帮助患者及时发现潜在的皮肤肿瘤问题。
早期诊断与治疗
-
皮肤肿瘤的早期诊断对于治疗效果至关重要,尤其是对于恶性肿瘤如黑色素瘤。
-
该模型能够快速识别出疑似肿瘤区域,并提供分类建议,有助于患者尽早接受治疗。
医疗资源优化
-
减轻医生的工作负担,提高诊断效率,使医生能够将更多精力集中在复杂病例的处理上。
-
通过自动化诊断工具,可以在大规模人群中进行皮肤肿瘤的初步筛查,筛选出高风险患者进行进一步检查。
医学研究支持
-
为皮肤病学研究提供数据支持和分析手段,促进对皮肤肿瘤发病机制、特征和演变的研究。
-
帮助研究人员更系统地整理和分析大量皮肤肿瘤图像数据,推动相关领域的研究进展。
技术创新与推广
-
展示了深度学习技术在医学图像分类中的应用潜力,为其他医学领域的类似研究提供了参考和借鉴。
-
推动人工智能技术在医疗领域的应用和发展,提高医疗服务的质量和可及性。
2.4 运行结果

























 1145
1145

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








