从事与显示系统有关的工作时,常接触一些术语和概念,并涉及到像素时钟与点时钟的计算,现总结如下:
1.Dotclock 与 Pixclock
Display Parameters
Sometimes, configuring the properties associated with your display panel might be the only driver changes that you need to make to enable video on your device, so let’s start learning about video drivers by looking at common display parameters. We will assume that the associated driver conforms to the frame buffer interface, and use the fbset utility to obtain display characteristics:
$ fbset
mode "1024x768-60"
# D: 65.003 MHz, H: 48.365 kHz, V: 60.006 Hz
geometry 1024 768 1024 768 8
timings 15384 168 16 30 2 136 6
hsync high
vsync high
rgba 8/0,8/0,8/0,0/0
endmode
The D: value in the output stands for the dotclock, which is the speed at which the video hardware draws pixels on the display. The value of 65.003MHz in the preceding output means that it’ll take (1/65.003*1000000) or about 15,384 picoseconds for the video controller to draw a single pixel. This duration is called the pixclock and is shown as the first numeric parameter in the line starting with timings. The numbers against “geometry” announce that the visible and virtual resolutions are 1024x768 (SVGA) and that the bits required to store information pertaining to a pixel is 8.
The H: value specifies the horizontal scan rate, which is the number of horizontal display lines scanned by the video hardware in one second. This is the inverse of the pixclock times the X-resolution. The V: value is the rate at which the entire display is refreshed. This is the inverse of the pixclock times the visible X-resolution times the visible Y-resolution, which is around 60Hz in this example. In other words, the LCD is refreshed 60 times in a second.
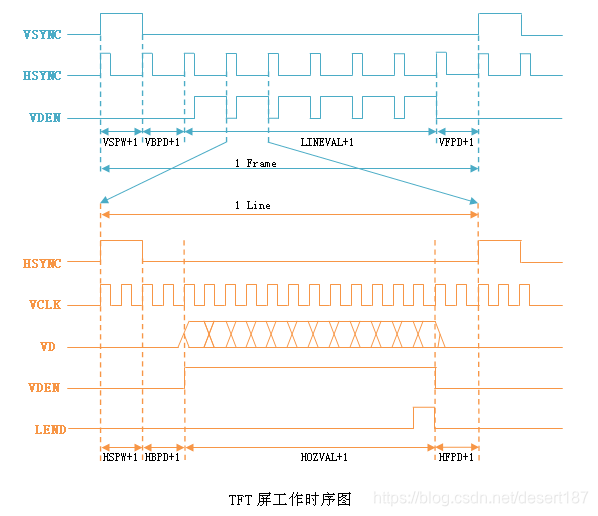
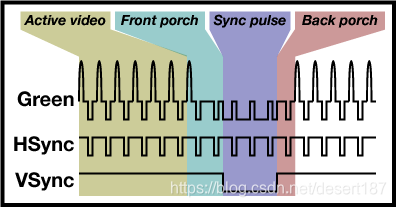
Video controllers issue a horizontal sync (HSYNC) pulse at the end of each line and a vertical sync (VSYNC) pulse after each display frame. The durations of HSYNC (in terms of pixels) and VSYNC (in terms of pixel lines) are shown as the last two parameters in the line starting with “timings.” The larger your display, the bigger the likely values of HSYNC and VSYNC. The four numbers before the HSYNC duration in the timings line announce the length of the right display margin (or horizontal front porch), left margin (or horizontal back porch), lower margin (or vertical front porch), and upper margin (or vertical back porch), respectively. Documentation/fb/framebuffer.txt and the man page of fb.modes pictorially show these parameters.
To tie these parameters together, let’s calculate the pixclock value for a given refresh rate, which is 60.006Hz in our example:
dotclock = (X-resolution + left margin + right margin
+ HSYNC length) * (Y-resolution + upper margin
+ lower margin + VSYNC length) * refresh rate
= (1024 + 168 + 16 + 136) * (768 + 30 + 2 + 6) * 60.006
= 65.003 MHz
pixclock = 1e12/dotclock
= 15384 picoseconds (which matches with the fbset output
above)
2.术语解析
- Left Margin:行切换,从同步到绘图之间的延迟,表示从水平同步信号开始到一行的有效数据开始之间的 VCLK 的个数,等同于 HBP(Horizontal Back Porch);
- Right Margin:行切换,从绘图到同步之间的延迟,表示一行的有效数据结束到下一个水平同步信号开始之间的 VCLK 的个数,等同于 HFP(Horizontal Front Porch, Horizontal Sync Offset);
- Upper Margin:帧切换,从同步到绘图之间的延迟,表示在一帧图像开始时,垂直同步信号以后的无效的行数,等同于 VBP(Vertical Back Porch);
- Lower Margin:帧切换,从绘图到同步之间的延迟,表示在一帧图像结束后,垂直同步信号以前的无效的行数,等同于 VFB(Vertical Front Porch, Vertical Sync Offset);
- HSYNC Len:水平同步的长度,表示水平同步信号的宽度,用 VCLK 计算,等同于 HSPW(Horizontal Sync Pulse Width, Horizontal Sync Pulse, XPULSE);
- VSYNC Len:垂直同步的长度,表示垂直同步脉冲的宽度,用行数计算,等同于 VSPW(Vertical Sync Pulse Width, Vertical Sync Pulse, YPULSE);
- HSYNC POL:水平脉冲极性;
- VSYNC POL:垂直脉冲极性。
可以用以下三张图来表示:
可以用以下两张图来表示:
+----------+---------------------------------------------+----------+-------+
| | ↑ | | |
| | |Upper Margin | | |
| | ↓ | | |
+----------###############################################----------+-------+
| # ↑ # | |
| # | # | |
| # | # | |
| # | # | |
| Left # | # Right | HSYNC |
| Margin # | X-Res # Margin | Len |
|<-------->#<---------------+--------------------------->#<-------->|<----->|
| # | # | |
| # | # | |
| # | # | |
| # |Y-Res # | |
| # | # | |
| # | # | |
| # | # | |
| # | # | |
| # | # | |
| # | # | |
| # | # | |
| # | # | |
| # ↓ # | |
+----------###############################################----------+-------+
| | ↑ | | |
| | |Lower Margin | | |
| | ↓ | | |
+----------+---------------------------------------------+----------+-------+
| | ↑ | | |
| | |VSYNC Len | | |
| | ↓ | | |
+----------+---------------------------------------------+----------+-------+
pixclock = 1e12/dotclock,其中 x1e12 是为了将时间单位统一为皮秒(picoseconds)。
- Horizontal Active:X Resolution;
- Horizontal Blanking Interval:HFP + HSPW + HBP;
- Vertical Active:Y Resolution;
- Vertical Blanking Interval:VFB + VSPW + VBP。
LCD提供的外部接口信号:
- VSYNC/VFRAME/STV:垂直同步信号(TFT)/帧同步信号(STN)/SEC TFT 信号;
- HSYNC/VLINE/CPV:水平同步信号(TFT)/行同步脉冲信号(STN)/SEC TFT 信号;
- VCLK/LCD_HCLK:象素时钟信号(TFT/STN)/SEC TFT 信号;
- VD[23:0]:LCD 像素数据输出端口(TFT/STN/SEC TFT);
- VDEN/VM/TP:数据使能信号(TFT)/LCD 驱动交流偏置信号(STN)/SEC TFT 信号;
- LEND/STH:行结束信号(TFT)/SEC TFT 信号;
- LCD_LPCOE:SEC TFT OE 信号;
- LCD_LPCREV:SEC TFT REV 信号;
- LCD_LPCREVB:SEC TFT REVB 信号。
3.DPI 的计算
sqrt(水平分分辨率^2+垂直分辨率^2)/屏幕尺寸
例如,5 英寸,分辨率为 1920x1080 的屏幕,其 DPI 为:
DPI=sqrt(1920^2+1080^2)/5





 本文深入解析了显示系统中的关键概念,如像素时钟(Dotclock)、点时钟(Pixclock)及其计算方法,详细阐述了左、右、上、下边距,水平与垂直同步信号的长度及极性等参数的含义。通过实例计算,帮助读者理解如何根据刷新率计算像素时钟值,以及DPI的计算公式。
本文深入解析了显示系统中的关键概念,如像素时钟(Dotclock)、点时钟(Pixclock)及其计算方法,详细阐述了左、右、上、下边距,水平与垂直同步信号的长度及极性等参数的含义。通过实例计算,帮助读者理解如何根据刷新率计算像素时钟值,以及DPI的计算公式。

















 1709
1709

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










