关于Env的源代码如下:
/** A class for environments, instances of which are passed as
* arguments to tree visitors. Environments refer to important ancestors
* of the subtree that's currently visited, such as the enclosing method,
* the enclosing class, or the enclosing toplevel node. They also contain
* a generic component, represented as a type parameter, to carry further
* information specific to individual passes.
*
* 一个类的环境,它的实例将被作为树访问者的参数进行传递。环境涉及到重要的子树的先祖,
* 子树是目前被访问过的。例如封闭的方法、封闭的类或者是封闭的顶层结点。它们也包含了
* 一个一般性的组件,被描述为类型参数,针对个别的传递携带更多的信息
*
*/
public class Env<A> implements Iterable<Env<A>> {
/** The next enclosing env.
*
* 下一个封闭的环境,和作用域是不同的。这个与语法树的组织嵌套是一样的
*/
public Env<A> next;
/** The env enclosing the current class.
*
* 参考文章:
*/
public Env<A> outer;
/** The tree with which this environment is associated.
*/
public JCTree tree;
/**
* The enclosing toplevel tree.封闭的顶层语法树,语法节点类型为JCCompilationUnit
*/
public JCCompilationUnit toplevel;
/** The next enclosing class definition.
*/
public JCClassDecl enclClass;
/** The next enclosing method definition.
*/
public JCMethodDecl enclMethod;
/** A generic field for further information.
*/
public A info;
// ...
}
主要通过三种途径来获取Env对象,如下:
(1)构造函数创建Env对象并返回
代码如下:
/** Create an outermost environment for a given (toplevel)tree,with a given info field.
*/
public Env(JCTree tree, A info) {
this.next = null;
this.outer = null;
this.tree = tree; // 初始化时就赋值
this.toplevel = null;
this.enclClass = null;
this.enclMethod = null;
this.info = info; // 初始化时就赋值
}
调用的地方如下图所示。
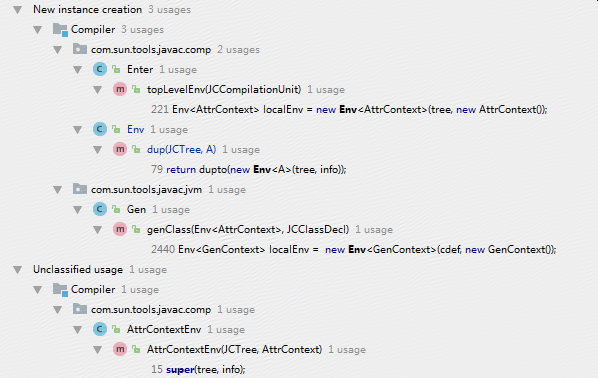
除去Env中的dup方法与子类通过super()进行调用后,剩下了两个主要的地方在调用。
(2)调用dupto()方法获取Env对象
/** Duplicate this environment into a given Environment,
* using its tree and info, and copying all other fields.
*/
public Env<A> dupto(Env<A> that) {
that.next = this;
that.outer = this.outer;
that.toplevel = this.toplevel;
that.enclClass = this.enclClass;
that.enclMethod = this.enclMethod;
return that;
}
被调用的地方如下图所示。
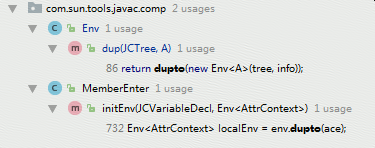
(3)调用dup()方法获取Env对象
/** Duplicate this environment, updating with given tree,
* and copying all other fields.
*/
public Env<A> dup(JCTree tree) { // 更新tree的信息
return dup(tree, this.info);
}
/** Duplicate this environment, updating with given tree and info,
* and copying all other fields.
*/
public Env<A> dup(JCTree tree, A info) { // 更新tree与info的信息
return dupto(new Env<A>(tree, info));
}
如上两个dup()方法都将调用dupto()方法来获取Env对象。
第一个方法的调用地方如下图所示。
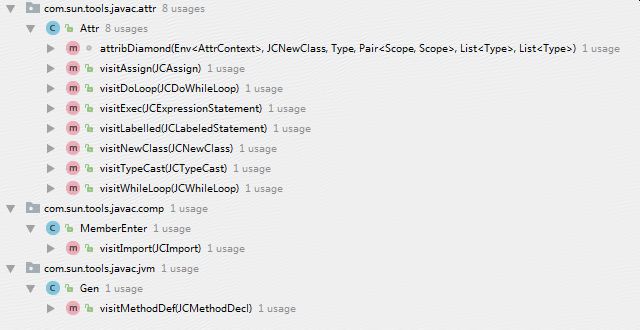
第二个方法的调用地方如下图所示。
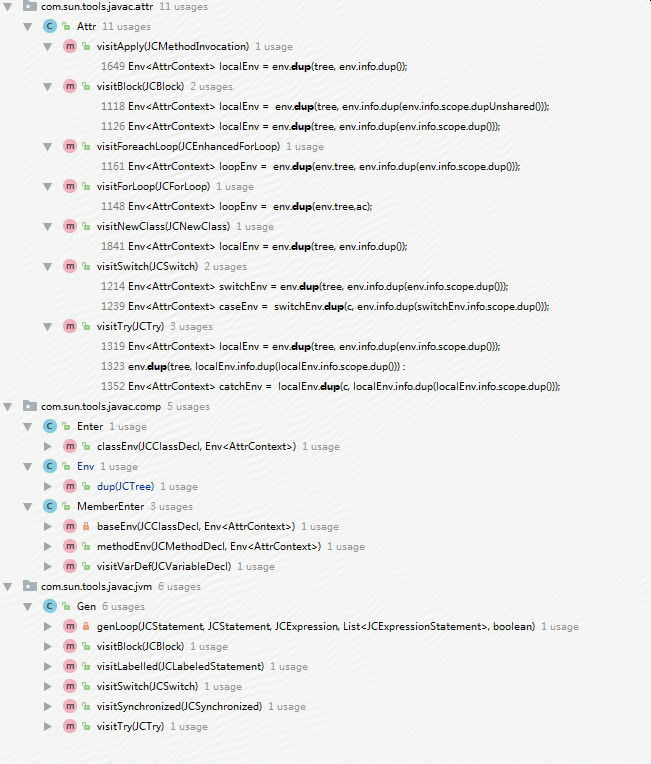
下面来介绍各个属性。
1、info属性:
参考文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/extjs4/p/9285113.html
2、outer属性:
class A {
static class B { // 只有在toplevel类中可用static,所有的内部类不可以使用static关键字
int b = 2;
public void methodB(){
class C {
Object c = new Object(){
int c = b;
};
{
class D{
public void t() {
int c = b;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
对于匿名内部类的int c = b语句来说,其outer是JCNewClass(JCNewClass属于类C)。类C的outer为类B的JCBlock。类B的outer为类A。
对于方法t中的int c = b语句来说,语句属于类D,类D的外层为JCBlock(JCBlock{classD{...}},而JCBlock(JCBlock{classD{...}}的outer为methodB的Block。
3、enclClass属性:
一个编译单元JCCompilationUnit的Env下的enclClass属性为:
/** Create a fresh environment for toplevels.
* @param tree The toplevel tree.
*/
public Env<AttrContext> topLevelEnv(JCCompilationUnit tree) {
// 初始化namedImportScope属性
tree.namedImportScope = new ImportScope(tree.packge);
tree.starImportScope = new StarImportScope(tree.packge);
Env<AttrContext> localEnv = new Env<AttrContext>(tree, new AttrContext());
localEnv.toplevel = tree;
// predefClassDef:A dummy class to serve as enclosingClass
// for toplevel environments.
localEnv.enclClass = predefClassDef;
// JCCompilationUnit的环境Scope中使用的是namedImportScope
localEnv.info.scope = tree.namedImportScope;
localEnv.info.lint = lint;
return localEnv;
}
是一个预先定义好的predefClassDef。
public Env<AttrContext> classEnv(JCClassDecl tree, Env<AttrContext> env) {
Scope sp = new Scope(tree.sym);
AttrContext ac = env.info.dup(sp);
Env<AttrContext> localEnv = env.dup(tree, ac);
localEnv.enclClass = tree;
localEnv.outer = env;
localEnv.info.isSelfCall = false;
localEnv.info.lint = null; // leave this to be filled in by Attr,
// when annotations have been processed
return localEnv;
}
被调用的截图如下:
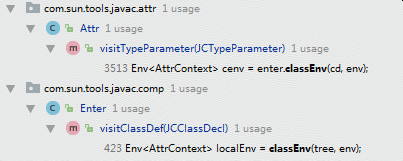
JCClassDecl语法节点的Env的属性enclClass为自己本身,而JCTypeParameter语法节点举例如下:
interface IA{}
interface IB{}
class CA{}
class CB{}
class TestC<T extends CA&IA&IB>{
public <B extends CB&IA&IB> void method(B b){}
}
则visitTypeParameter()方法的cd属性类型为JCClassDecl,分别为:
1、public abstract class T extends CA implements IA,IB{} 最终生成的Env如下截图。
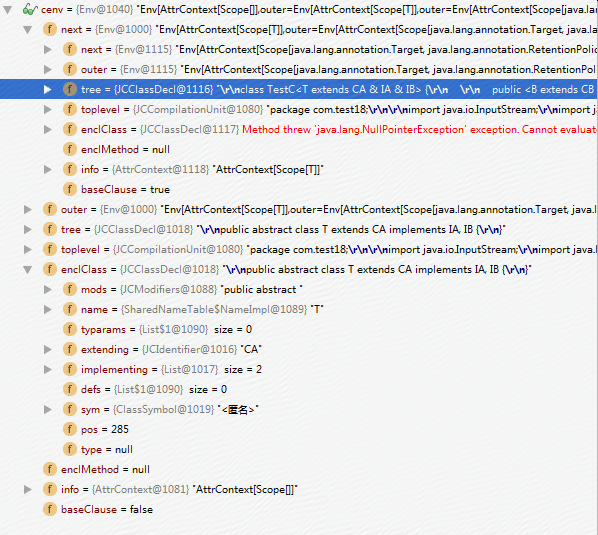
2、public abstract class B extends CB implements IA,IB{} 最终生成的Environment如下截图。
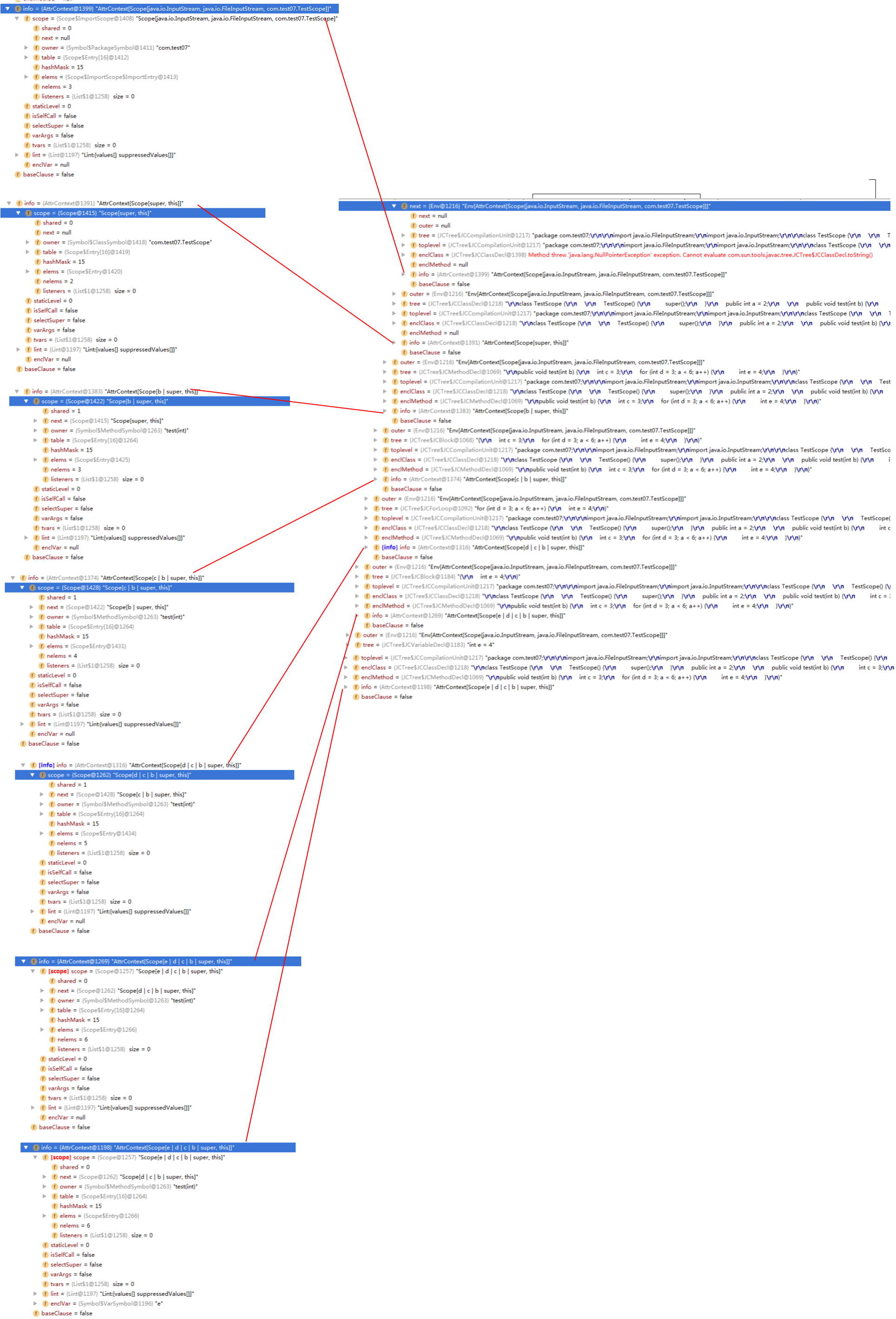
对于Scope属性举个例子,如下:
package com.test07;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
class TestScope {
public int a = 2;
public void test(int b) {
int c = 3;
for (int d = 3; a < 6; a++) {
int e = 4;
}
}
}
Scope如下截图。
在如上的例子中,JCVariableDecl节点及子结点的staticLevel都为1,而其父结节点及以上为0。再举个例子,如下:
public class Test3{
static{ // staticLevel = 1
// 在static块中不允许再有static出现,如
// static int a = 1;
// static class A{}
// class A{
// public static void m1(){}
// }
int a = 1; // staticLevel = 1
}
// 这个类的staticLevel为0,与一般类没有任何区别
static class Inner{ // staticLevel = 0
public static void m1(){ // staticLevel = 1
int b = 1; // staticLevel = 1
}
}
}
举个例子,如下:
interface I{
void m1();
}
public class Test3{
static void t(){}
static I a = new I(){
@Override
public void m1() {
t();
}
};
}
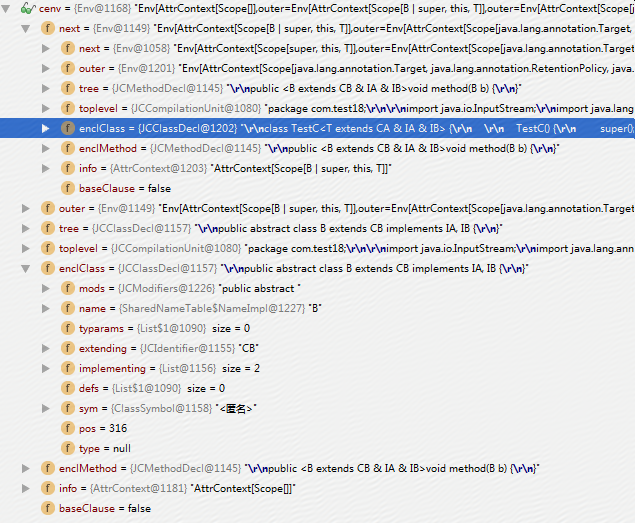
那么t()的环境Env的结构如下截图。
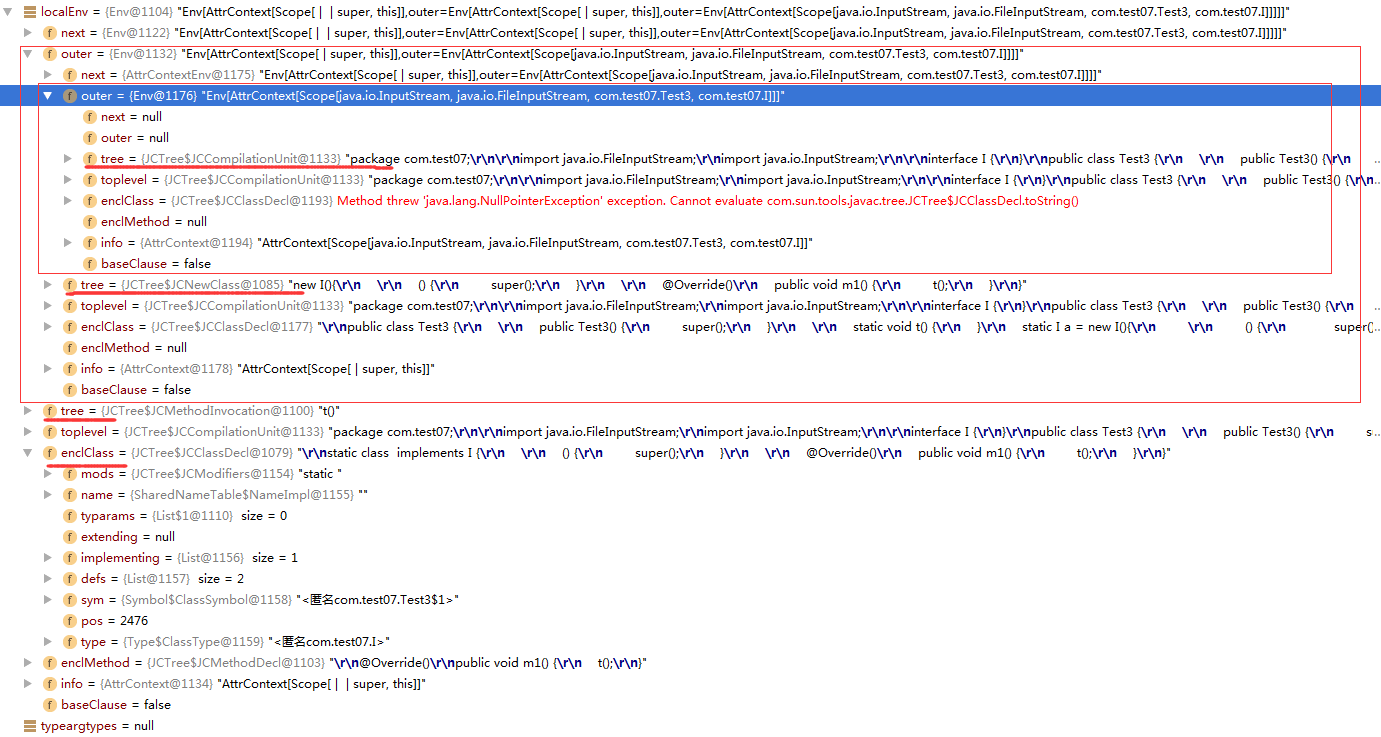
这是outer属性,而next属性和语法树的组织结构是严格一致的,如下截图。





 本文深入解析Java编译器中的Env对象,探讨其构造、属性与应用场景,包括info、outer、enclClass等关键字段的作用,以及Env对象在不同语法节点间的传递机制。
本文深入解析Java编译器中的Env对象,探讨其构造、属性与应用场景,包括info、outer、enclClass等关键字段的作用,以及Env对象在不同语法节点间的传递机制。
















 7171
7171

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








