for循环在c++中的用法
Loops come into picture when we need to execute a particular action in a repeated manner.
当我们需要重复执行特定的动作时,就会出现循环。
C ++中的循环类型 (Types of loops in C++)

There are two broad categories of loops in C++ :
C ++中有两大类循环:
- Entry Controlled Loops 入口控制回路
- Exit Controlled Loops 退出控制循环
入口控制回路 (Entry Controlled Loops)
In entry controlled loops, the test expressions are tested beforehand i.e. they are tested before the execution of the preceding statements.
在条目控制的循环中,测试表达式是预先测试的,即它们是在执行前面的语句之前进行测试的。
There are two entry controlled loops:
有两个条目控制的循环:
- for Loop 循环
- while Loop while循环
对于循环 (For Loops)
The for loop is an iterative statement that executes for a given number of times based on the initialization expression.
for循环是一个迭代语句,该语句根据初始化表达式执行给定的次数。

Working of For Loops:
For循环的工作:
The for loops use a loop variable as a pointer to point to the particular instance of the loop being executed.
for循环使用循环变量作为指针来指向要执行的循环的特定实例。
- Initially, the loop variable is declared and initialized. 最初,循环变量被声明和初始化。
- Post which, the validity of the test expression in accordance with the particular program is done. 之后,根据特定程序完成测试表达式的有效性。
- Then, the loop variable is updated to a certain value. 然后,将循环变量更新为某个值。
The above steps are repeated until it meets the exit condition.
重复上述步骤,直到满足退出条件。
Note: In for loops, the number of iterations i.e. the number of times the loop will execute is known by definition.
注意:在for循环中,迭代次数(即循环执行的次数)在定义上是已知的。
Syntax:
句法:
for (initialization expression; Test expression; Update expression)
{
// body of the loop
}
Example:
例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for (int x = 0; x < 10; x++)
{
cout <<" "<< x;
}
return 0;
}
Output:
输出:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
While循环 (While Loops)
In while loops, the termination of the loop completely depends on the test expression because in this loop we do not specify the number of iterations.
在while循环中,循环的终止完全取决于测试表达式,因为在此循环中,我们不指定迭代次数。
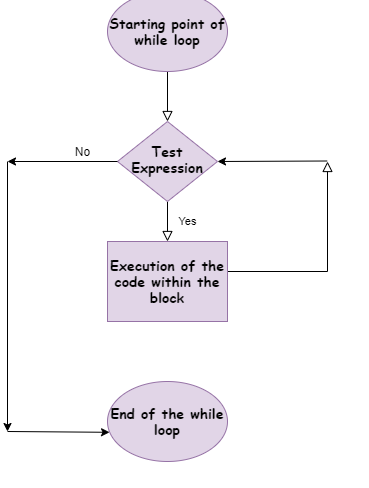
Syntax:
句法:
Initialization_expression;
while (Test_condition)
{
// statements
Update_expression;
}
Example:
例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{ int x = 0;
while(x<10)
{
cout<<" "<<x;
x++;
}
return 0;
}
Output:
输出:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
退出控制循环 (Exit Controlled Loops)
In exit controlled loops, the test expression is analyzed and evaluated at the end of the loop.
在出口控制的循环中,测试表达式在循环结束时进行分析和评估。
Thus, the loop will run and execute at-least-once irrespective of the test expression.
因此,无论测试表达式如何,循环都会至少运行一次并执行。
循环执行 (Do-while loop)
Do-while loops serve the same purpose as that of the while loops. But, in do-while loops, the test condition is evaluated at the end of the loop.
Do-while循环的功能与while循环的目的相同。 但是,在do-while循环中,测试条件在循环结束时进行评估。

As you must have understood from the illustration above, the loop will always execute first, check for the condition later.
正如您必须从上图理解的那样,循环将始终首先执行,然后再检查条件。
Syntax:
句法:
Initialization_Expression;
do
{
// statements
Update_Expression;
} while (Test_Expression);
Example:
例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x = 0;
do
{
cout <<" "<<x;
x++;
} while (x < 10);
return 0;
}
Output:
输出:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
循环控制语句 (Loop Control Statements)
The following loops statements are necessary to decide and control the flow of termination of the loop in the program:
以下循环语句对于确定和控制程序中循环终止的流程是必需的:
- break statement: As soon as the compiler encounters the break statement, the loop terminates on an immediate basis and the flow of control gets passed to the statement following the loop. break语句 :编译器遇到break语句时,循环立即终止,并且控制流在循环后传递给该语句。
- continue statement: As soon as the compiler encounters the continue statement at a particular instance of test-condition, it immediately leaves the current condition of the loop and restarts the loop. continue语句 :编译器在特定的test-condition实例上遇到Continue语句时,它将立即离开循环的当前条件并重新启动循环。
结论 (Conclusion)
Thus, in this article, we have understood the basic working of the C++ loops.
因此,在本文中,我们已经了解了C ++循环的基本工作。
参考资料 (References)
for循环在c++中的用法







 本文介绍了C++中的循环类型,包括for、while和do-while循环,详细讲解了for循环的工作原理和语法,强调了在for循环中迭代次数是已知的。同时提到了循环控制语句如break和continue在控制循环流程中的作用。
本文介绍了C++中的循环类型,包括for、while和do-while循环,详细讲解了for循环的工作原理和语法,强调了在for循环中迭代次数是已知的。同时提到了循环控制语句如break和continue在控制循环流程中的作用。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








