没错,如题所见,在发版前代码落地评审的时候,因为写了一个BeanUtils.copyProperties,架构师说要给我打个D绩效,但是最后因为加班时间长并且完成了一个临时插入进来的大需求。直属领导给我打了个A绩效,最后惊险地逃过了D绩效,至此就有了这篇文章。
文章目录
在我们的项目开发过程中中少不了使BeanUtils.copyProperties(org.springframework.beans)去复制类,但是由于 BeanUtils.copyProperties 需要通过反射来访问对象的属性,因此它的性能相对较低。我们可以看看他和其他的工具的性能对比:
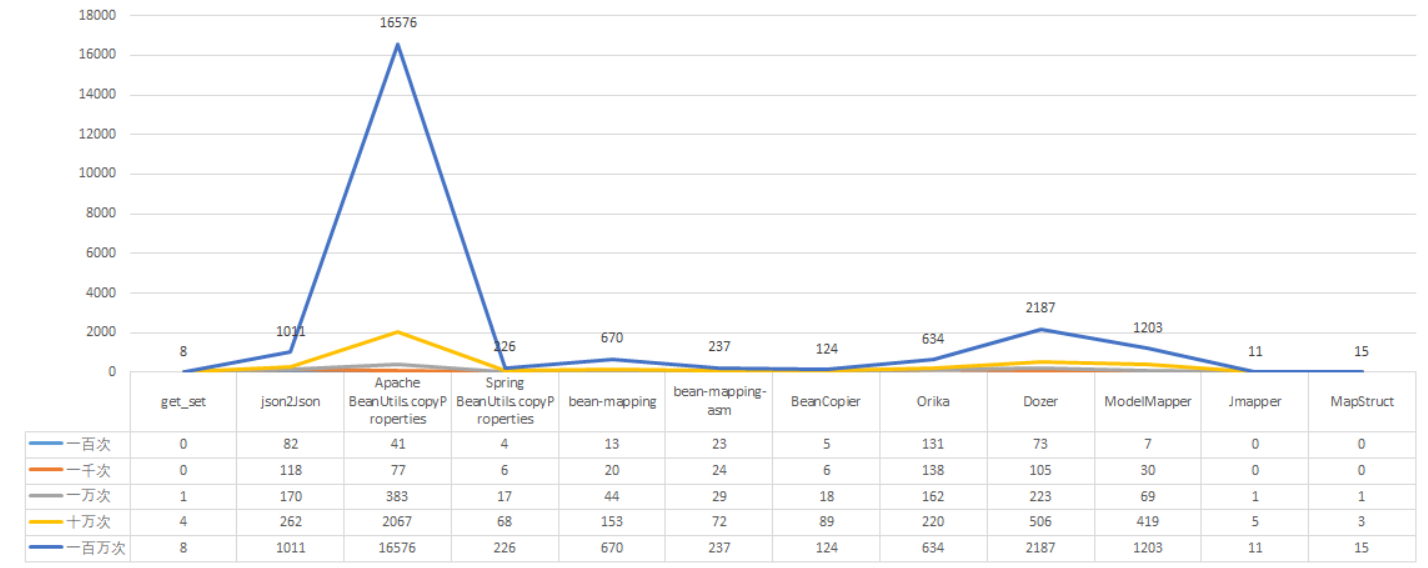
而我们上面举的例子就是spring(第四列),可以看到随着复制的复制的增加,消耗的时间明显高于直接getset方法。但是我们看最后一列的 MapStruct的表现,他的性能直接逼近getset方法。但是如果在企业开发中没有明确的开发规范或者性能瓶颈,作者还是觉得选用BeanUtils.copyProperties 方法就挺好了,因为够用,而且学习成本低,效率也提升微乎其微(相比于MapStruct)。但是如果你的企业要求必须使用MapStruct,那么就另当别论。
所以什么是MapStruct?
上面我们也说了他的性能很好,比BeanUtils.copyProperties 方法快那么多,为什么呢,因为MapStruct的实现原理和他不一样,MapStruct直接在编译期间就处理好了。甚至直接媲美getset方法,因为他的本质就是编译期间运行直接生成了getset方法。
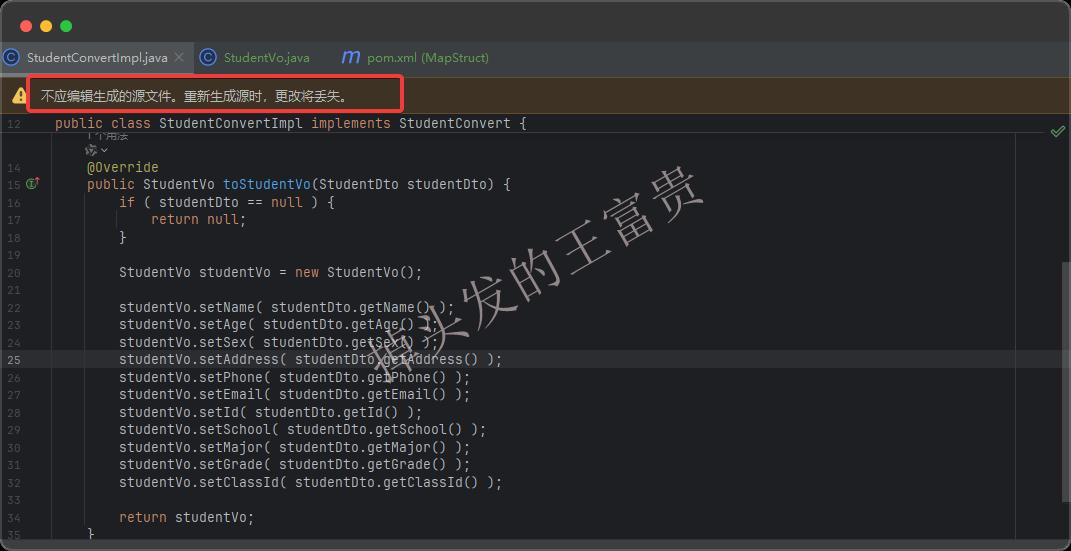
使用MapStruct
基础用法
作者使用的环境为JDK23,所以咱们的MapStruct的版本选择为最新的 1.6.3 版本:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mapstruct/mapstruct-processor -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct-processor</artifactId>
<version>1.6.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mapstruct/mapstruct -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct</artifactId>
<version>1.6.3</version>
</dependency>
编写源类和目标类,MapStruct 作为 Java 编译过程的一部分工作,通过注解处理器(annotation processor)机制,在编译期自动生成类型安全的映射代码。属性的读取是通过无参数的 getter 方法完成的,而属性的写入则是通过 setter 方法实现的。如果这些方法不存在,MapStruct 将无法正确地访问或修改对象的属性。
StudentDto(源类)
package com.masiyi.mapstruct.service.dto;
/**
* @Author: masiyi
* @Date: 2025/3/5
* @Describe:
*/
public class StudentDto {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String sex;
private String address;
private String phone;
private String email;
private String id;
private String school;
private String major;
private String grade;
private String classId;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getSchool() {
return school;
}
public void setSchool(String school) {
this.school = school;
}
public String getMajor() {
return major;
}
public void setMajor(String major) {
this.major = major;
}
public String getGrade() {
return grade;
}
public void setGrade(String grade) {
this.grade = grade;
}
public String getClassId() {
return classId;
}
public void setClassId(String classId) {
this.classId = classId;
}
}
目标类(StudentVo)
package com.masiyi.mapstruct.controller.vo;
/**
* @Author: masiyi
* @Date: 2025/3/5
* @Describe:
*/
public class StudentVo {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String sex;
private String address;
private String phone;
private String email;
private String id;
private String school;
private String major;
private String grade;
private String classId;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getSchool() {
return school;
}
public void setSchool(String school) {
this.school = school;
}
public String getMajor() {
return major;
}
public void setMajor(String major) {
this.major = major;
}
public String getGrade() {
return grade;
}
public void setGrade(String grade) {
this.grade = grade;
}
public String getClassId() {
return classId;
}
public void setClassId(String classId) {
this.classId = classId;
}
}
编写了这两个类的目的就是模仿我们平时在开发过程中需要复制的类,例如将DTO转换为VO返回给前端。
编写转换接口
package com.masiyi.mapstruct;
import com.masiyi.mapstruct.controller.vo.StudentVo;
import com.masiyi.mapstruct.service.dto.StudentDto;
import org.mapstruct.Mapper;
import org.mapstruct.factory.Mappers;
/**
* @Author: masiyi
* @Date: 2025/3/5
* @Describe:
*/
@Mapper
public interface StudentConvert {
StudentConvert INSTANCE = Mappers.getMapper(StudentConvert.class);
StudentVo toStudentVo(StudentDto studentDto);
}
注意这里的 @Mapper 注解是mapstruct的注解,而非mybatis的注解。定义静态实例 INSTANCE,通过 Mappers.getMapper(StudentConvert.class) 获取 StudentConvert 接口的实现。这点大家一定要这么写,至于类名随便取,但是还是建议以 Convert 结尾,规范一点。
toStudentVo 方法,接收 StudentDto 对象作为参数,并返回 StudentVo 对象,用于将 StudentDto 转换为 StudentVo。这里的方法名不重要,入参和出参才重要,甚至我们方法名字叫test都行
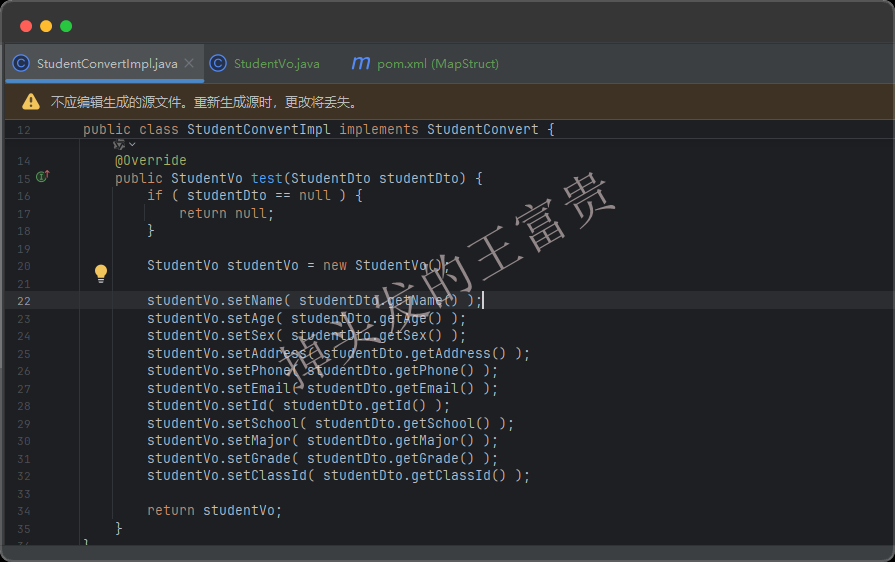
编写测试接口
package com.masiyi.mapstruct.controller;
import com.masiyi.mapstruct.StudentConvert;
import com.masiyi.mapstruct.controller.vo.StudentVo;
import com.masiyi.mapstruct.service.dto.StudentDto;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Author: masiyi
* @Date: 2025/3/5
* @Describe:
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/student")
public class StudentController {
@GetMapping(value = "/getStudent")
public StudentVo getStudent() {
StudentDto studentDto = new StudentDto();
studentDto.setName("masiyi");
studentDto.setAge(18);
studentDto.setSex("男");
studentDto.setPhone("12345678901");
studentDto.setEmail("masiyi@163.com");
studentDto.setId("12345678901");
studentDto.setMajor("计算机科学与技术");
studentDto.setGrade("2021");
studentDto.setClassId("2021级计算机科学与技术1班");
studentDto.setAddress("深圳");
StudentVo studentVo = StudentConvert.INSTANCE.toStudentVo(studentDto);
return studentVo;
}
}
这里我们只new了一个dto对象,但是我们的接口返回的是vo对象,而我们调用接口看看效果,已经完全把dto的每个属性都复制到了vo对象里面了:
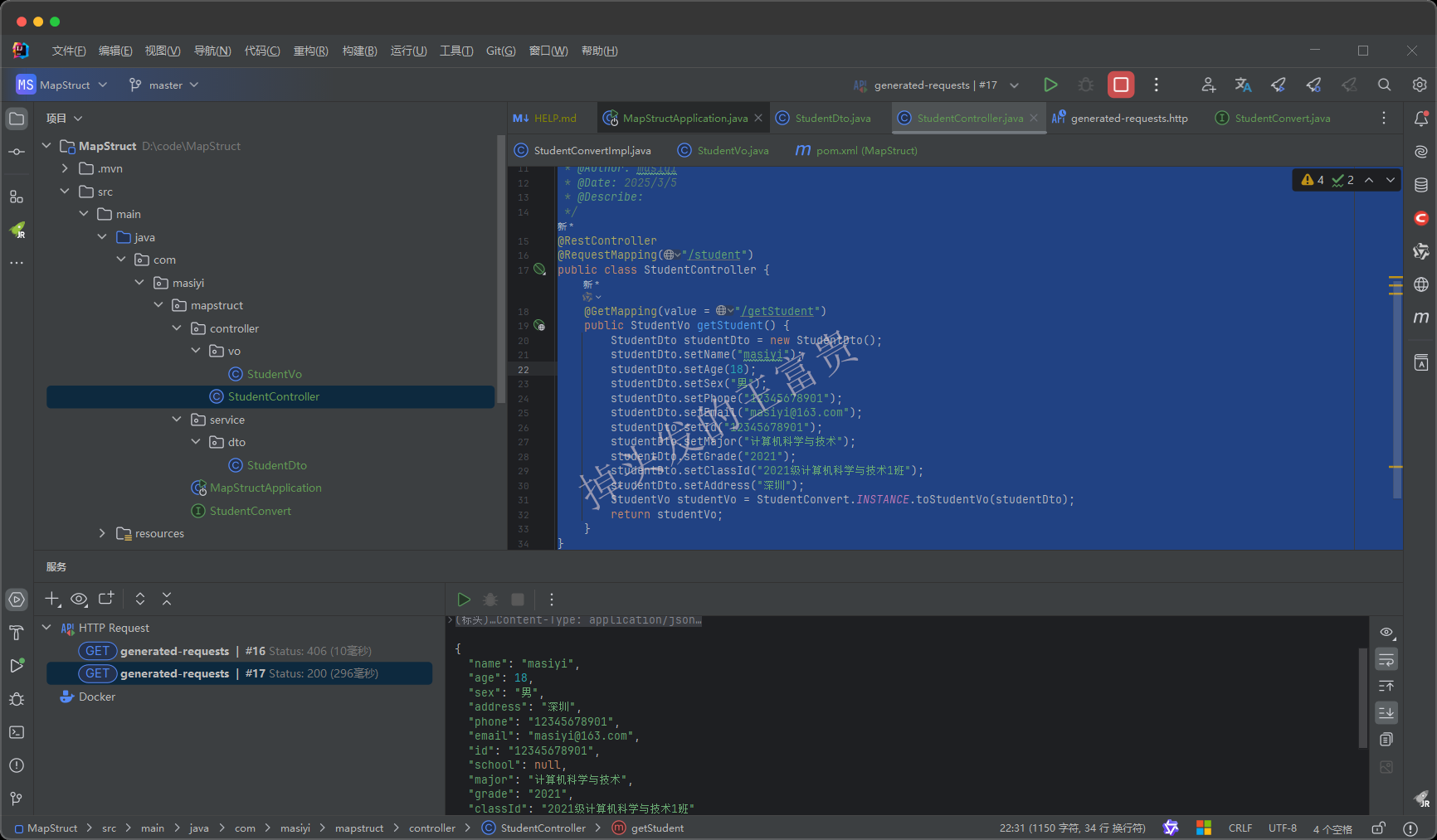
到这里,我们已经90%地替代了BeanUtils.copyProperties的功能了。相信也是90%的满足了大家日常开发过程中需要copy对象的场景了吧。接下来我们查看一些更高级的用法。
高阶用法
虽说上面的写法已经满足了90%的场景,但是我们难免会接触那剩下的10%的场景。所以下面我们来了解一下MapStruct还有哪些看家本事。
复制List
我们在StudentConvert接口里面添加以下方法
List<StudentVo> toStudentVoList(List<StudentDto> studentDto);
而我们写一个测试接口测试一下也是没有问题的:
@GetMapping(value = "/getStudents")
public List<StudentVo> getStudents() {
StudentDto studentDto = new StudentDto();
studentDto.setName("masiyi");
studentDto.setAge(18);
studentDto.setSex("男");
studentDto.setPhone("12345678901");
studentDto.setEmail("masiyi@163.com");
studentDto.setId("12345678901");
studentDto.setMajor("计算机科学与技术");
studentDto.setGrade("2021");
studentDto.setClassId("2021级计算机科学与技术1班");
studentDto.setAddress("深圳");
StudentDto studentDto2 = new StudentDto();
studentDto2.setName("wangfugui");
studentDto2.setAge(24);
studentDto2.setSex("男");
studentDto2.setPhone("23556546");
List<StudentDto> studentDtos = new ArrayList<>();
studentDtos.add(studentDto);
studentDtos.add(studentDto2);
List<StudentVo> studentVoList = StudentConvert.INSTANCE.toStudentVoList(studentDtos);
return studentVoList;
}
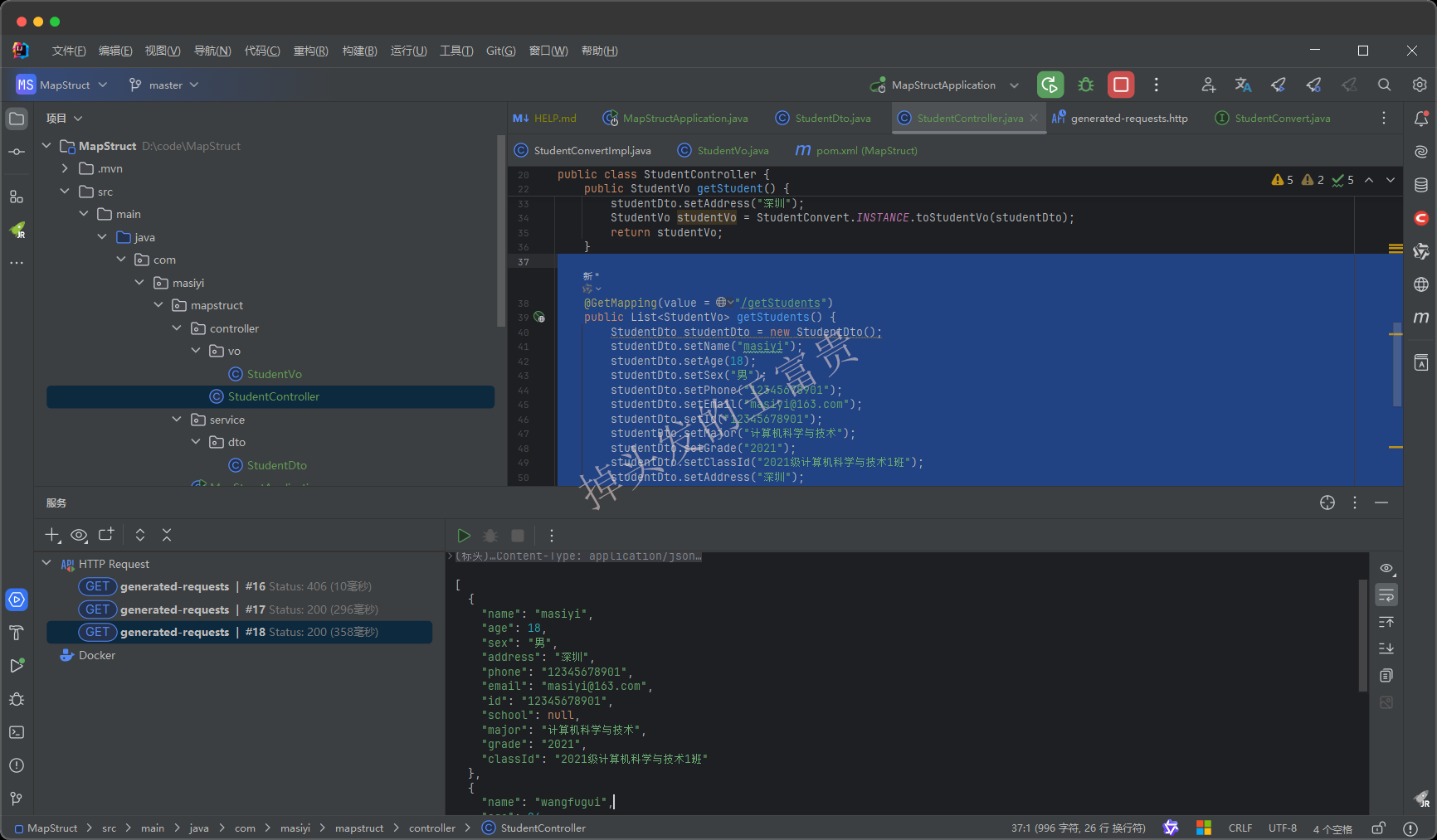
而这里有意思的是当我们查看编译出来的代码的时候,我们发现MapStruct的toStudentVoList方法居然里面调用了我们编写的toStudentVo方法!!
真有你的,MapStruct!!
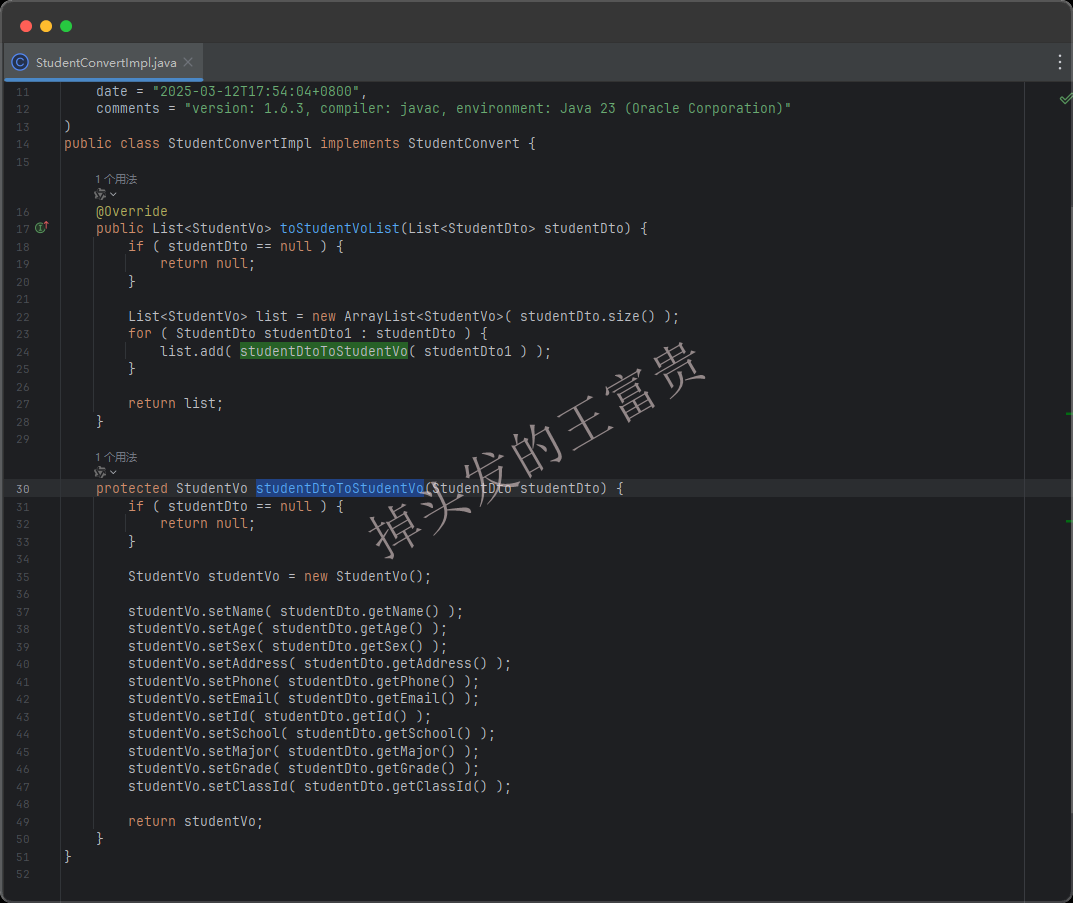
那我们吧toStudentVo注释掉会怎么样呢?我们可以看到的是他根据我们的入参和出参自动生成了一个studentDtoToStudentVo方法,然后在for循环里面调用这个方法,真够“智能”的!!
其他集合转换
那么List能够转换,同理其他的集合也是没问题的:
/**
* map 转 map
*/
Map<String,StudentVo> toStudentVoMap(Map<String,StudentDto> studentDto);
/**
* set转set
*/
Set<StudentVo> toStudentVoSet(Set<StudentDto> studentDto);
/**
* set转list
*/
List<StudentVo> toStudentVoList(Set<StudentDto> studentDto);
/**
* list转set
*/
Set<StudentVo> toStudentVoSet(List<StudentDto> studentDto);
编译出来的是这样的,方法内部都调用了toStudentVo方法
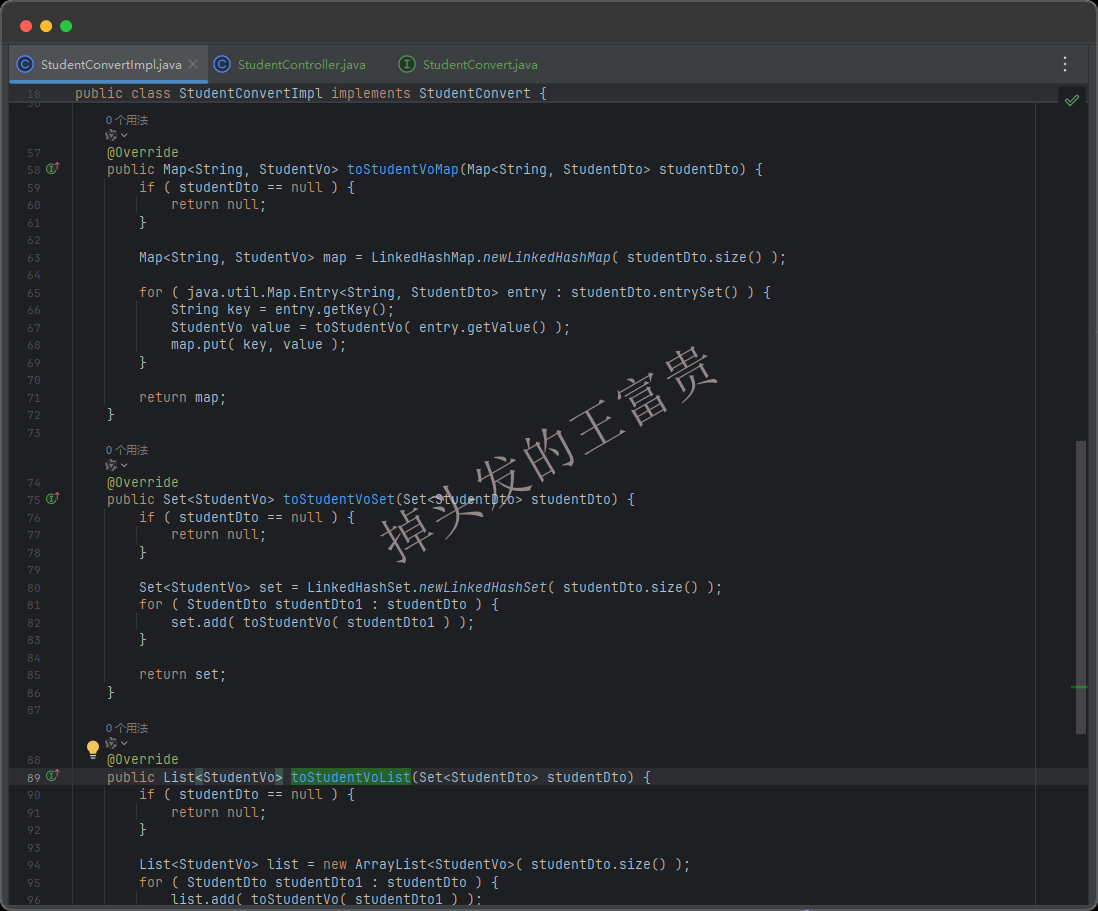
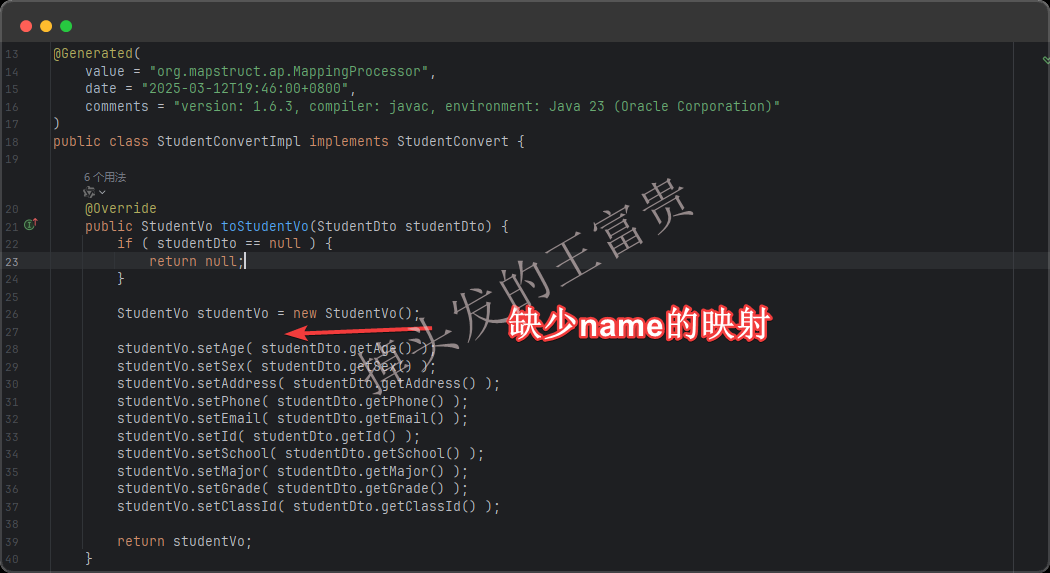
单独字段映射
截止目前不知道大家有没有发现一个问题,就是你的源类和目标类的每个字段都是一样的才能copy过来,但是我们现在有个这样的需求:dto里面的name为学生的名称,但是vo里面需要返回给前端学生的名称叫做studentName。这样直接复制肯定是找不到对应的字段的:
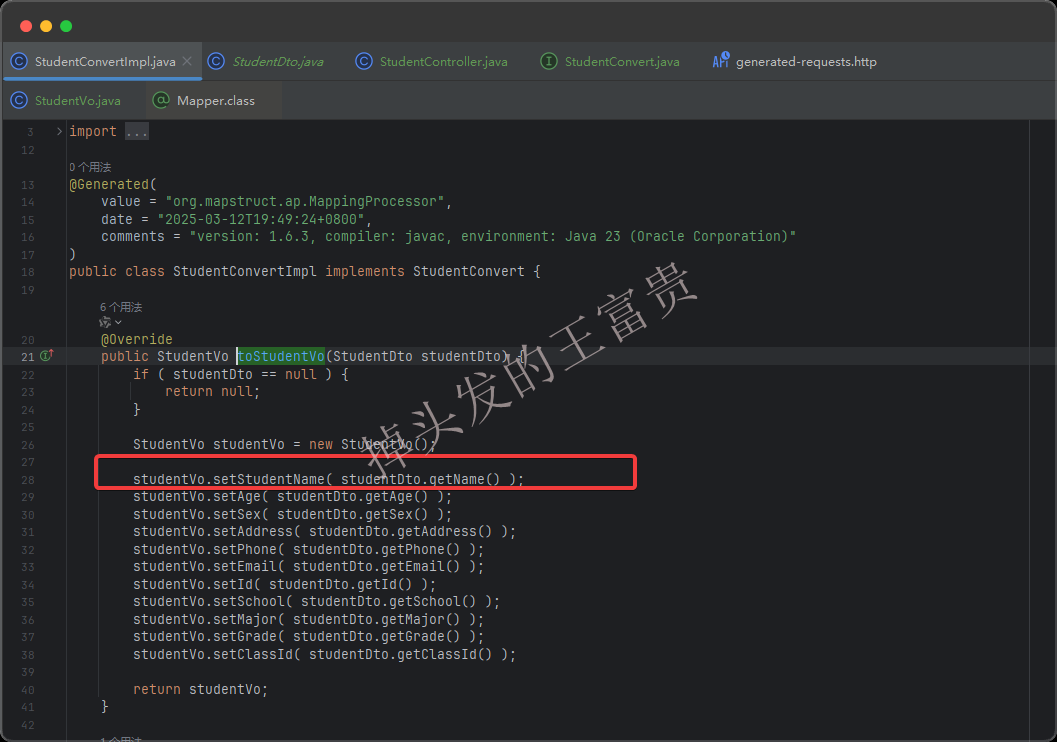
这个时候我们可以在 toStudentVo方法上面加上@Mapping 注解来手动指定name映射到vo的 studentName
package com.masiyi.mapstruct;
import com.masiyi.mapstruct.controller.vo.StudentVo;
import com.masiyi.mapstruct.service.dto.StudentDto;
import org.mapstruct.Mapper;
import org.mapstruct.Mapping;
import org.mapstruct.factory.Mappers;
/**
* @Author: masiyi
* @Date: 2025/3/5
* @Describe:
*/
@Mapper
public interface StudentConvert {
StudentConvert INSTANCE = Mappers.getMapper(StudentConvert.class);
@Mapping(source = "name", target = "studentName")
StudentVo toStudentVo(StudentDto studentDto);
}
之后再看我们编译出来的类,就没问题啦:
自定义方法
有时候我们需要把两个字段的映射做一些自定义的方法,例如把object类型的id字段转换为String类型的id,我们平常是这么写的:
@Mapping(source = "id", target = "id")
但是因为类型不匹配,这个时候就会报错:
java: Can't map property "Object id" to "String id". Consider to declare/implement a mapping method: "String map(Object value)".
这个时候我们可以自定义一个java的转换方法,类似这样:
@Named("objectIdToString")
default String objectIdToString(Object value) {
if (value == null) {
return null;
}
return value.toString();
}
然后我们在@Mapping里面这样写:
@Mapping(source = "id", target = "id", qualifiedByName = "objectIdToString")
这样我们的source字段到target 字段编译之后就会调用我们的objectIdToString方法了
学习BeanUtils.copyProperties
用过BeanUtils.copyProperties的都知道,我们需要先new一个目标类,就像这样:
//studentDto 已存在
StudentDto studentDto = ...;
StudentVo studentVo = new StudentVo();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(studentDto,studentVo)
这样复制完成之后studentVo 里面的字段就有值了。但是上面我们的mapstruct 都是直接返回的是一个StudentVo。那么万能的mapstruct也是可以这么写滴:
package com.masiyi.mapstruct;
import com.masiyi.mapstruct.controller.vo.StudentVo;
import com.masiyi.mapstruct.service.dto.StudentDto;
import org.mapstruct.Mapper;
import org.mapstruct.MappingTarget;
import org.mapstruct.factory.Mappers;
/**
* @Author: masiyi
* @Date: 2025/3/5
* @Describe:
*/
@Mapper
public interface StudentConvert {
StudentConvert INSTANCE = Mappers.getMapper(StudentConvert.class);
void copyStudentVo(StudentDto studentDto, @MappingTarget StudentVo studentVo);
}
然后我们只需要和 BeanUtils.copyProperties一样的写法即可:
//studentDto 已存在
StudentDto studentDto = ...;
StudentVo studentVo = new StudentVo();
StudentConvert.INSTANCE.copyStudentVo(studentDto, studentVo);
这样复制完成之后studentVo 里面的字段也有值啦。
复用规则
就像上面我们有这样的一个方法:
@Mapping(source = "name", target="studentName")
StudentVo toStudentVo(StudentDto studentDto);
我们需要把studentName 映射到vo的name上面,那么我们现在需要写一个方法将vo转换为dto,我们可以这样写:
@Mapping(source = "studentName", target="name")
StudentDto toStudentDto(StudentVo studentVo);
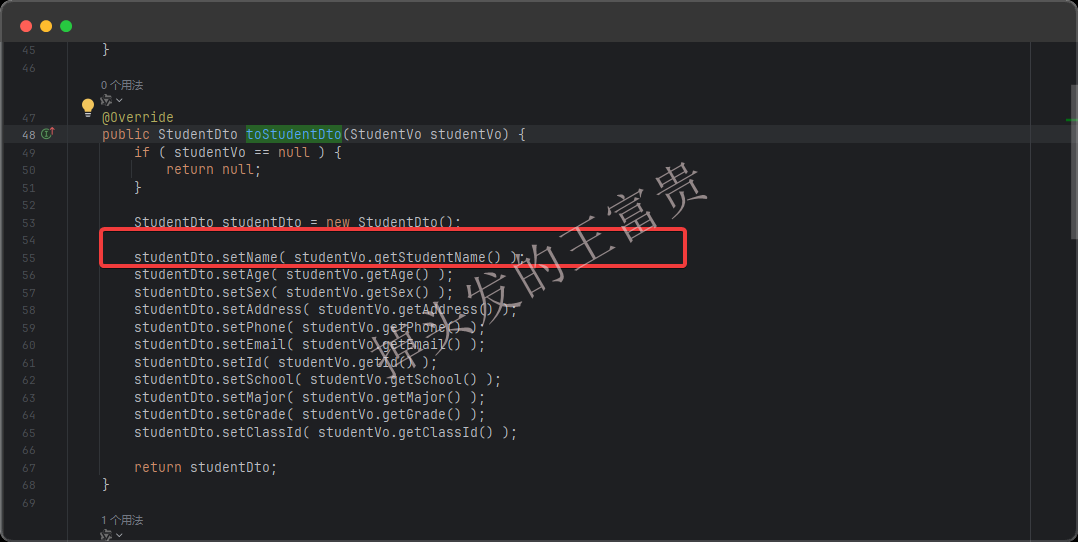
这样写看似没问题,但是如果字段非常多呢,是不是要同时维护两套逻辑,所以这个时候我们可以直接使用 @InheritInverseConfiguration复用 toStudentVo方法的规则:
@InheritInverseConfiguration(name = "toStudentVo")
StudentDto toStudentDto(StudentVo studentVo);
这样就没问题啦:
但是需要注意的是只能引用入参和出参与当前方法刚刚反过来的方法名称,就是不能这么写(实测name复制不了):
package com.masiyi.mapstruct;
import com.masiyi.mapstruct.controller.vo.StudentVo;
import com.masiyi.mapstruct.service.dto.StudentDto;
import org.mapstruct.InheritInverseConfiguration;
import org.mapstruct.Mapper;
import org.mapstruct.Mapping;
import org.mapstruct.factory.Mappers;
/**
* @Author: masiyi
* @Date: 2025/3/5
* @Describe:
*/
@Mapper
public interface StudentConvert {
StudentConvert INSTANCE = Mappers.getMapper(StudentConvert.class);
@Mapping(source = "name", target="studentName")
StudentVo toStudentVo(StudentDto studentDto);
@InheritInverseConfiguration(name = "toStudentVo")
StudentVo toStudentVo2(StudentDto studentDto);
}
多类组合
现在我们再加一个Dto类,例如StudentDto里面classId对应的class(班级):
package com.masiyi.mapstruct.service.dto;
/**
* @Author: masiyi
* @Date: 2025/3/16
* @Describe: 班级dto
*/
public class ClassDto {
private String id;
private String name;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
但是我们的vo还是原来的那个类,只不过多加了一个班级名称:className
package com.masiyi.mapstruct.controller.vo;
/**
* @Author: masiyi
* @Date: 2025/3/5
* @Describe:
*/
public class StudentVo {
private String studentName;
private Integer age;
private String sex;
private String address;
private String phone;
private String email;
private String id;
private String school;
private String major;
private String grade;
private String classId;
private String className;
public String getClassName() {
return className;
}
public void setClassName(String className) {
this.className = className;
}
public String getStudentName() {
return studentName;
}
public void setStudentName(String studentName) {
this.studentName = studentName;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getSchool() {
return school;
}
public void setSchool(String school) {
this.school = school;
}
public String getMajor() {
return major;
}
public void setMajor(String major) {
this.major = major;
}
public String getGrade() {
return grade;
}
public void setGrade(String grade) {
this.grade = grade;
}
public String getClassId() {
return classId;
}
public void setClassId(String classId) {
this.classId = classId;
}
}
这样的情况我们应该怎么将StudentDto和ClassDto同时映射到StudentVo上面去呢?
我们需要把入参的名字写到 source里面,target里面则对应vo里面的字段即可,就像这样:
@Mapping(source = "studentDto.name", target="studentName")
@Mapping(source = "classDto.name", target="className")
@Mapping(source = "classDto.id", target="classId")
@Mapping(source = "studentDto.id", target="id")
StudentVo convertStudentVo(StudentDto studentDto, ClassDto classDto);
但是有个注意的点,如果两个入参里面都有id的时候,需要告诉mapstruct 哪个id对应对应vo里面的id,否则就会报错,因为mapstruct 不知道要把哪个dto里面的id复制到vo里面的id:
@Mapping(source = "classDto.id", target="classId")
StudentVo convertStudentVo(StudentDto studentDto, ClassDto classDto);
java: Several possible source properties for target property "id".
同理,如果我们 source 里面找到两个name的话就会报这样的错, 因为mapstruct 不知道要把哪个name对应到vo的 studentName:
@Mapping(source = "name", target="studentName")
@Mapping(source = "classDto.name", target="className")
StudentVo convertStudentVo(StudentDto studentDto, ClassDto classDto);
java: Method has no source parameter named "name". Method source parameters are: "studentDto, classDto".
嵌套转换
现在我们的入参是这样的:一个班级Dto,一个学校dto,而出参就是一个班级Vo,类似:
package com.masiyi.mapstruct.controller.vo;
/**
* @Author: masiyi
* @Date: 2025/3/5
* @Describe:
*/
public class ClassVo {
private String id;
private String name;
private String type;
private SchoolVo schoolVo;
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public SchoolVo getSchoolVo() {
return schoolVo;
}
public void setSchoolVo(SchoolVo schoolVo) {
this.schoolVo = schoolVo;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
package com.masiyi.mapstruct.controller.vo;
/**
* @Author: masiyi
* @Date: 2025/3/16
* @Describe: 学校vo
*/
public class SchoolVo {
private String id;
private String name;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
dto是这样的(两个dto毫无关联):
package com.masiyi.mapstruct.service.dto;
/**
* @Author: masiyi
* @Date: 2025/3/16
* @Describe: 班级dto
*/
public class ClassDto {
private String id;
private String name;
private String type;
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
package com.masiyi.mapstruct.service.dto;
/**
* @Author: masiyi
* @Date: 2025/3/16
* @Describe: 学校dto
*/
public class SchoolDto {
private String id;
private String name;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
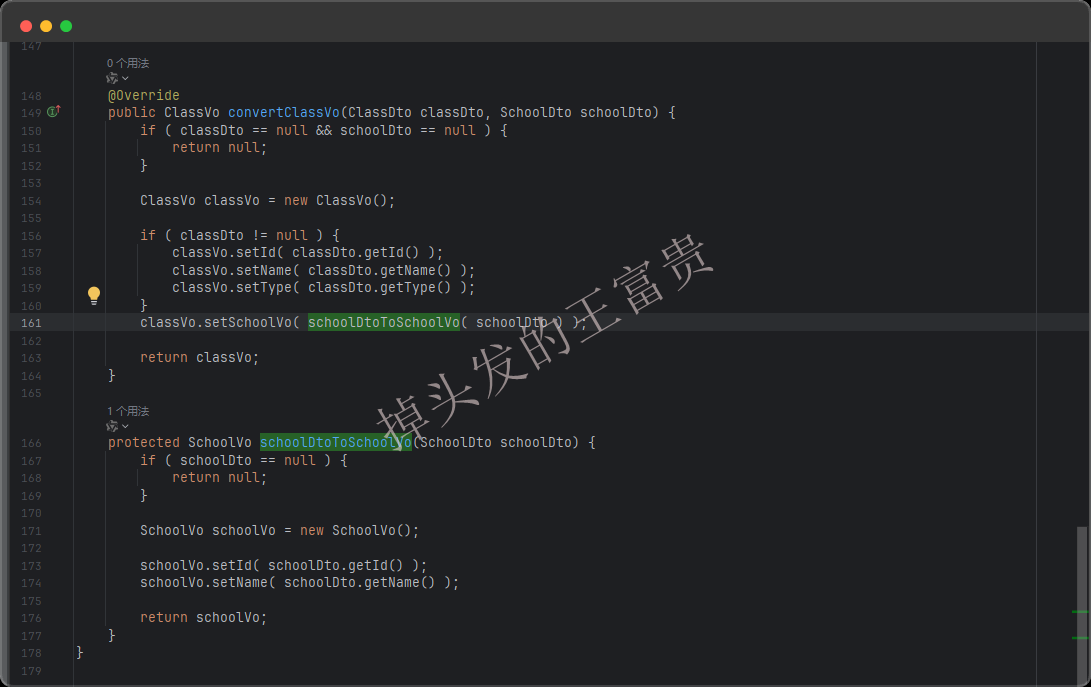
但是咱们可以传入两个dto入参返回嵌套完成的ClassVo出参:
@Mapping(source = "schoolDto", target="schoolVo")
@Mapping(source = "classDto.id", target="id")
@Mapping(source = "classDto.name", target="name")
ClassVo convertClassVo(ClassDto classDto, SchoolDto schoolDto);
而mapstruct可以编译成这样的代码:
入土用法
相信通过上面的用法大家都已经入手了MapStruct,上面的用法基本是博主认为能够覆盖公司项目中99%的开发了,博主公司就用到了最基本的基础用法,甚至高阶用法都没看到。。。
但是如果你想更深入了解MapStruct,篇幅原因这里不在赘述。博主这里可以把MapStruct最新用法的官网文档贴在这里,如果大家感兴趣的话可以去参考参考,谢谢大家观看!!
这篇博客的源码我会放在公众号:掉头发的王富贵 中,回复:MapStruct即可获取源代码。






















 1828
1828

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










