目录
摘要 :组件通信与状态管理是 Vue.js 开发中的核心主题,直接关系到应用的架构合理性、可维护性及开发效率。本文深入剖析 Vue 组件通信的多种方式,包括父子组件通信、非父子组件通信,并深入讲解 Vuex 的核心机制与模块化开发。结合实际案例,如表单多组件协作、数据共享与缓存、实时数据监控面板等,详细展示不同场景下的应用实现,并辅以 Mermaid 数据流图梳理交互流程。同时,总结开发中的注意事项与性能优化策略,助力开发者构建高效、稳定的 Vue 应用。
一、Vue 组件通信方式详解
(一)父子组件通信
1. 父组件向子组件传递数据
使用场景 :适用于父组件向子组件提供配置参数、初始数据等场景。
代码示例 :
// 父组件
<div id="app">
<child-component :user-info="parentUser"></child-component>
</div>
// 子组件
Vue.component('child-component', {
props: ['userInfo'],
template: '<div>子组件收到的用户名:{{ userInfo.name }}</div>'
});
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
parentUser: { name: '张三', age: 25 }
}
});2. 子组件向父组件传递数据
使用场景 :子组件触发事件(如表单提交、按钮点击),并携带数据反馈给父组件,便于父组件统筹管理关键业务逻辑与数据状态。
代码示例 :
// 子组件
Vue.component('child-component', {
template: `
<button @click="notifyParent">点击向父组件传值</button>
`,
methods: {
notifyParent() {
this.$emit('custom-event', '子组件的数据');
}
}
});
// 父组件
<div id="app">
<child-component @custom-event="handleChildData"></child-component>
</div>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
methods: {
handleChildData(data) {
console.log('父组件收到的数据:', data);
}
}
});(二)非父子组件通信
1. 使用全局事件总线
使用场景 :适用于中等复杂度的项目,当多个组件需要相互通信但又不存在直接父子关系时,可创建一个中央事件中心来协调通信。
代码示例 :
// 创建事件总线
const EventBus = new Vue();
// 组件 A - 发送消息
Vue.component('component-a', {
template: '<button @click="sendMessage">发送消息</button>',
methods: {
sendMessage() {
EventBus.$emit('message-event', '组件 A 的数据');
}
}
});
// 组件 B - 接收消息
Vue.component('component-b', {
created() {
EventBus.$on('message-event', (data) => {
console.log('组件 B 收到的数据:', data);
});
}
});
new Vue({ el: '#app' });2. 使用 Vuex
使用场景 :对于大型复杂应用,尤其是存在多层组件嵌套、多个视图依赖同一份数据、需要考虑数据持久化或严格遵循单一数据源原则的场景,Vuex 是更合适的选择。
代码示例 :
// store.js
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex);
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++;
}
},
actions: {
incrementAction({ commit }) {
commit('increment');
}
},
getters: {
doubleCount: state => state.count * 2
}
});
// 组件中使用
<div id="app">
<p>当前计数:{{ count }}</p>
<p>计数翻倍:{{ doubleCount }}</p>
<button @click="incrementCount">增加计数</button>
</div>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
computed: {
count() {
return this.$store.state.count;
},
doubleCount() {
return this.$store.getters.doubleCount;
}
},
methods: {
incrementCount() {
this.$store.commit('increment');
// 或通过 action 提交
// this.$store.dispatch('incrementAction');
}
}
});二、Vue 状态管理之 Vuex 深入剖析
(一)Vuex 核心概念
-
State :存储应用的全局状态数据,所有组件都可从中读取数据。
-
Getter :状态的派生属性,类似于 Vuex 中的计算属性,可用于处理 state 数据或返回部分 state。
-
Mutation :更新 state 的唯一方式,采用常量作为事件类型,确保状态变更可追踪、可调试。
-
Action :处理应用中的异步操作,最终会调用 mutation 来更新状态。
(二)Vuex 模块化开发
-
模块划分依据 :按功能、业务领域或数据类型等维度对应用状态进行模块化拆分,使代码结构更清晰、可维护性更高。
-
代码示例 :
// store/modules/user.js
const userModule = {
namespaced: true, // 开启命名空间
state: {
name: '',
age: 0
},
mutations: {
setUser(state, payload) {
state.name = payload.name;
state.age = payload.age;
}
},
actions: {
fetchUser({ commit }) {
// 异步获取用户数据
setTimeout(() => {
commit('setUser', { name: '张三', age: 25 });
}, 1000);
}
},
getters: {
userStatus: state => `用户名:${state.name},年龄:${state.age}`
}
};
// store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
import userModule from './modules/user';
Vue.use(Vuex);
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
user: userModule
}
});
// 组件中使用
<div id="app">
<p>用户状态:{{ userStatus }}</p>
<button @click="fetchUserData">获取用户数据</button>
</div>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
computed: {
userStatus() {
return this.$store.getters['user/userStatus'];
}
},
methods: {
fetchUserData() {
this.$store.dispatch('user/fetchUser');
}
}
});三、Vue 组件通信与状态管理应用场景
(一)表单多组件协作
-
场景描述 :一个复杂的表单往往由多个子组件构成,如输入框、下拉选择框、日期选择器等,这些子组件需要将各自收集到的数据汇总到父组件,由父组件统一处理提交逻辑。
-
代码示例 :
// 父组件
<div id="app">
<form @submit.prevent="submitForm">
<input-component v-model="formData.username"></input-component>
<select-component v-model="formData.gender"></select-component>
<date-picker-component v-model="formData.birthdate"></date-picker-component>
<button type="submit">提交</button>
</form>
</div>
// input-component
Vue.component('input-component', {
props: ['value'],
template: `
<input type="text" :value="value" @input="$emit('input', $event.target.value)">
`
});
// select-component
Vue.component('select-component', {
props: ['value'],
template: `
<select :value="value" @change="$emit('input', $event.target.value)">
<option value="male">男</option>
<option value="female">女</option>
</select>
`
});
// date-picker-component
Vue.component('date-picker-component', {
props: ['value'],
template: `
<input type="date" :value="value" @input="$emit('input', $event.target.value)">
`
});
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
formData: {
username: '',
gender: '',
birthdate: ''
}
},
methods: {
submitForm() {
console.log('表单数据:', this.formData);
// 表单提交逻辑
}
}
});(二)数据共享与缓存
-
场景描述 :在应用中,某些数据(如用户信息、配置参数)需要在多个页面或组件间共享,并且希望在页面刷新后仍能保留这些数据,此时可结合 Vuex 与本地存储技术实现数据共享与持久化缓存。
-
代码示例 :
// store.js
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex);
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
userInfo: JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('userInfo')) || null
},
mutations: {
setUserInfo(state, payload) {
state.userInfo = payload;
localStorage.setItem('userInfo', JSON.stringify(payload));
},
clearUserInfo(state) {
state.userInfo = null;
localStorage.removeItem('userInfo');
}
}
});
// 登录组件
<div id="app">
<div v-if="!userInfo">
<input v-model="username" placeholder="用户名">
<input v-model="password" type="password" placeholder="密码">
<button @click="login">登录</button>
</div>
<div v-else>
<p>欢迎,{{ userInfo.name }}</p>
<button @click="logout">退出登录</button>
</div>
</div>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
username: '',
password: ''
},
computed: {
userInfo() {
return this.$store.state.userInfo;
}
},
methods: {
login() {
// 模拟登录请求
if (this.username && this.password) {
this.$store.commit('setUserInfo', { name: this.username, privileges: 'user' });
}
},
logout() {
this.$store.commit('clearUserInfo');
}
}
});(三)实时数据监控面板
-
场景描述 :构建一个用于展示实时数据指标(如服务器负载、在线用户数、交易数据等)的监控面板,数据需从后端实时推送,多个组件共同展示不同维度的数据信息,且界面需具备自动刷新和数据异常告警功能。
-
代码示例 :
// 主应用
<div id="app">
<server-load-chart :load-data="serverLoad"></server-load-chart>
<online-users-display :users="onlineUsers"></online-users-display>
<transaction-statistics :stats="transactionStats"></transaction-statistics>
<data-alerts :alerts="dataAlerts"></data-alerts>
</div>
// server-load-chart
Vue.component('server-load-chart', {
props: ['loadData'],
template: `
<div>
<h3>服务器负载</h3>
<div class="chart" v-if="loadData.length > 0">
<!-- 这里可使用图表库渲染图表 -->
<pre>{{ loadData }}</pre>
</div>
<p v-else>暂无数据</p>
</div>
`
});
// online-users-display
Vue.component('online-users-display', {
props: ['users'],
template: `
<div>
<h3>在线用户</h3>
<p>当前在线用户数:{{ users.count }}</p>
<p>活跃度:{{ users.activity }}</p>
</div>
`
});
// transaction-statistics
Vue.component('transaction-statistics', {
props: ['stats'],
template: `
<div>
<h3>交易统计</h3>
<p>今日交易额:¥{{ stats.amount }}</p>
<p>交易笔数:{{ stats.count }}</p>
</div>
`
});
// data-alerts
Vue.component('data-alerts', {
props: ['alerts'],
template: `
<div>
<h3>数据告警</h3>
<ul>
<li v-for="(alert, index) in alerts" :key="index" :class="{ 'alert-danger': alert.level === 'high' }">
{{ alert.message }} ({{ alert.time }})
</li>
</ul>
</div>
`
});
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
serverLoad: [],
onlineUsers: { count: 0, activity: 'low' },
transactionStats: { amount: 0, count: 0 },
dataAlerts: []
},
created() {
// 模拟实时数据推送
this.setupRealTimeData();
},
methods: {
setupRealTimeData() {
setInterval(() => {
// 更新服务器负载数据
this.serverLoad.push(Math.random() * 100);
if (this.serverLoad.length > 20) this.serverLoad.shift();
// 更新在线用户数据
const userCountChange = Math.floor(Math.random() * 10) - 5;
this.onlineUsers.count = Math.max(0, this.onlineUsers.count + userCountChange);
this.onlineUsers.activity = this.onlineUsers.count > 50 ? 'high' : 'low';
// 更新交易统计数据
const newTransactionCount = Math.floor(Math.random() * 5);
this.transactionStats.amount += newTransactionCount * (Math.random() * 100 + 10);
this.transactionStats.count += newTransactionCount;
// 模拟数据告警
if (this.serverLoad[this.serverLoad.length - 1] > 80) {
this.dataAlerts.unshift({
message: '服务器负载过高',
time: new Date().toLocaleTimeString(),
level: 'high'
});
}
if (this.dataAlerts.length > 5) this.dataAlerts.pop();
}, 3000);
}
}
});四、组件通信与状态管理注意事项
(一)通信方式选择原则
-
简单场景优先使用父子通信 :若组件间存在明确的父子层级关系,且通信需求较为简单(如数据单向传递、事件简单反馈),应首选 props 与自定义事件的组合方式,以保持组件结构清晰、语义明确。
-
复杂场景考虑全局事件总线或 Vuex :当项目中存在多个无直接关联的组件需要频繁交互,或状态管理逻辑较为复杂时,全局事件总线可作为轻量级解决方案;而对于大型项目,尤其是涉及用户权限管理、多页面数据共享、复杂业务流程等场景,Vuex 能提供更规范、更强大的状态管理能力,确保应用状态的可追溯性与稳定性。
(二)Vuex 使用规范
-
合理划分模块 :依据业务逻辑对 Vuex store 进行模块化拆分,每个模块专注于管理特定领域的状态,避免 store 内状态过于杂乱,降低维护难度。
-
遵循单一数据源原则 :确保应用中所有组件所需的数据最终都来源于 Vuex store,避免出现组件私有数据与全局状态混用导致的数据不一致问题。
-
严格管控状态变更 :仅允许通过 mutations 更新状态,且 mutation 的提交应具备明确的语义化类型名称,便于调试与追踪状态变化根源;对于异步操作,统一通过 actions 进行封装处理,确保异步流程的可靠性与可维护性。
(三)性能优化要点
-
避免过度使用全局状态 :并非所有数据都需存入 Vuex store,仅将应用中真正需要全局共享的关键数据纳入其中,其余组件私有数据应尽量在局部范围内管理,以减少不必要的状态同步开销与 store 的复杂度。
-
运用 Vue 的响应式优化手段 :在结合 Vuex 使用时,合理运用 Vue 的计算属性、
v-show与v-if的恰当场景选择、列表渲染优化技巧(如key的正确使用、避免在列表项中放置复杂组件等),提升整体应用性能。 -
关注 Vuex 的数据持久化策略 :在实现数据持久化存储时,需权衡存储频率、数据量大小与存储介质的读写性能,避免因过度频繁的本地存储操作引发应用卡顿或存储空间占用过多问题。
五、组件通信与状态管理数据流图
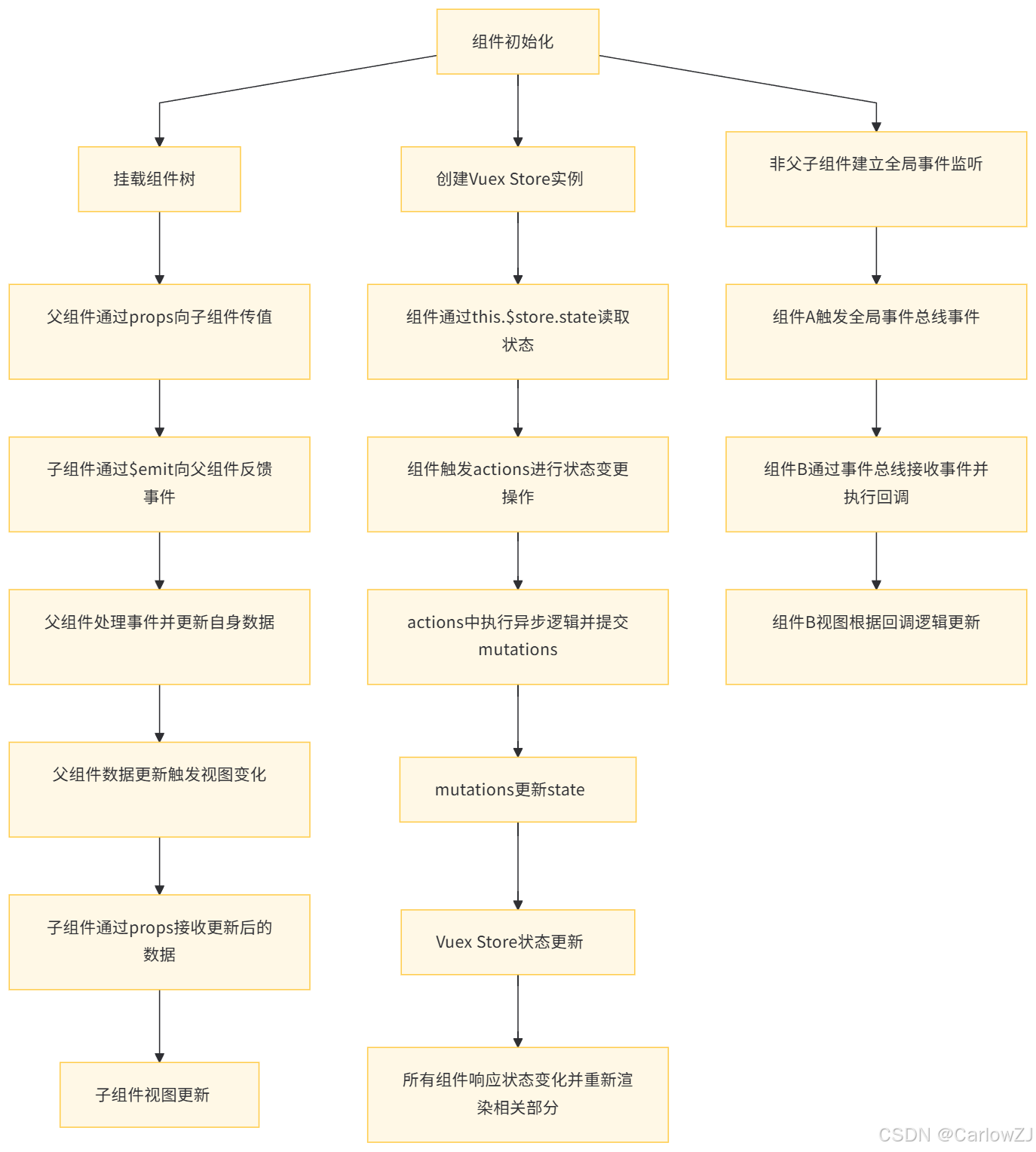
六、总结
Vue 组件通信与状态管理是构建现代化前端应用的基石,灵活掌握多样化的组件交互方式以及 Vuex 的精髓,在实际项目中合理规划应用架构,是每一名 Vue 开发者迈向高级阶段的必经之路。通过深入理解不同通信机制的适用场景、遵循规范化的开发原则、持续关注性能优化细节,我们能够打造出架构清晰、运行高效、维护便捷的 Vue 应用,从容应对各类复杂的业务需求挑战,在前端开发领域实现技术能力的不断进阶与突破。
引用 :
[1] Vue 官方文档 Introduction | Vue.js






















 3015
3015

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










