电源管理的目标
在给定的系统状态、配置和使用场景中,消耗尽可能少的功率
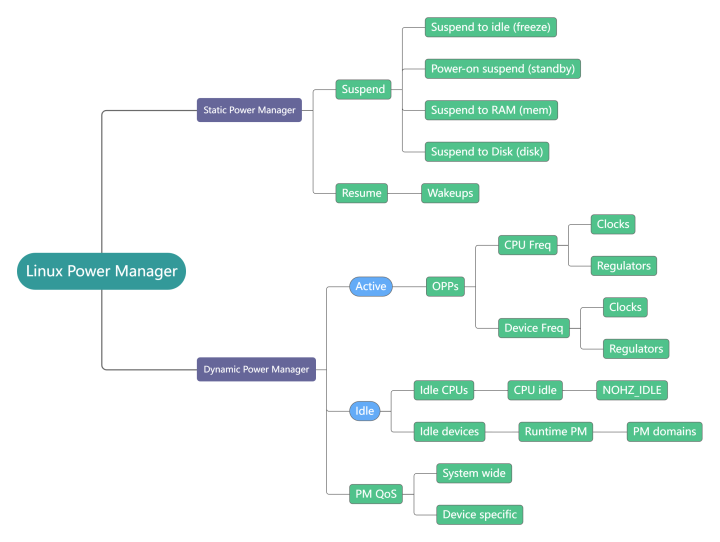
Linux 两种电源管理策略
Linux 内核支持两种主要的高级电源管理策略:
Static Power Management
用于设备处于 Inactive 状态。即长时间不使用设备时,比如:手机息屏后待机场景。
这种策略基整个系统的全局低功耗状态,在这种状态下用户空间代码无法执行并且整个系统活动显著减少,称为睡眠状态(包括:freeze,standby,mem,disk 5种状态)。 当用户空间请求时,内核将系统置于这些状态之一,并且系统停留在其中,直到从指定设备之一接收到特殊信号(比如 Alarm 或 Modem 硬件中断),触发转换到用户空间代码可以运行的工作状态。因为睡眠状态是全局的,并且整个系统都会受到状态变化的影响,所以这种策略也被称为 system-wide power management (系统范围的电源管理)。
Dynamic Power Management
用于设备处于 Active 或 Idle 状态。即正在使用设备运行某些程序或者处于短暂的 Inactive 时
这种策略也被称为 working-state power management (工作状态电源管理),在工作状态下,会根据需要调整系统的各个硬件组件的电源状态。因此,如果使用这种策略,系统的工作状态通常不对应于它的任何特定物理配置,而是可以被视为涵盖系统的一系列不同电源状态的元状态,其中各个组件它可以是 active活动的(使用中)或inactive非活动的(空闲)。如果它们处于活动状态,则它们必须处于允许它们处理数据并被软件访问的电源状态。反过来,如果它们处于非活动状态,理想情况下,它们应该处于可能无法访问的低功耗状态。
参考
[1] http://events17.linuxfoundation.org/sites/events/files/slides/Intro_Kernel_PM.pdf
[2] https://static.linaro.org/connect/yvr18/presentations/yvr18-221.pdf





 本文介绍了Linux内核支持的两种主要电源管理策略:静态电源管理和动态电源管理。静态电源管理适用于设备长时间不使用的情况,如手机待机;而动态电源管理则针对设备在活跃或短暂不活动的状态。
本文介绍了Linux内核支持的两种主要电源管理策略:静态电源管理和动态电源管理。静态电源管理适用于设备长时间不使用的情况,如手机待机;而动态电源管理则针对设备在活跃或短暂不活动的状态。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










