java.lang中的常用类:包装类,String,Object
一.Arrays类
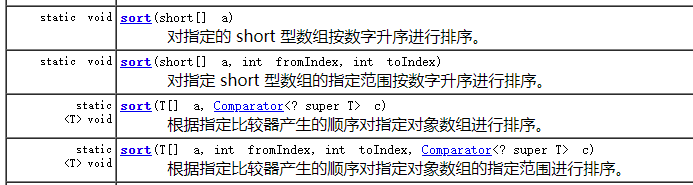
1.sort()
Arrays.sort(arr)
Arrays有多个重载的sort()方法,既可以按照自然顺序排序,也可以传入比较器参数定制顺序排序
2.index binarySearch(arr,key)
3.copyOf:拷贝数组
Arrays.copyOf(srcArray,newLength)
System.arrayCopy(srcArray,0,destArray,0,length)
(1)int[] copyOf(int[] original, int newLength) //original:原数组,newLength:新数组的长度
(2)底层采用 System.arraycopy() 实现,这是一个native方法。
void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,Object dest, int destPos,int length); //length:拷贝的长度
4.fill(arr,val)
将数组中的元素全部替换成同一个元素
5.List asList(arr)
可以将一个数组快速的转换成List
1 String[] str = {"a","b","c"};
2 List<String> listStr = Arrays.asList(str);
注意:
(1)返回的数组的视图,所以只能查看,修改,不能增删,对list的修改,会反映到数组
(2)只能传入引用类型数组,不能传入基本类型数组
(4)已知数组数据,如何快速获取一个可进行增删改查的列表List
List<String> listStr = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(str));
1 String[] str = {"a","b","c"};
2 List<String> listStr = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(str));
3 listStr.add("d");
4 System.out.println(listStr.size());//4
6.Arrays.toString(arr)
返回数组内容的字符串形式,打印的时候比较有用,就不用遍历了
二.Collections类:主要对List进行操作
1.Collections.sort(List) 对List排序
2.Collections.binarySearch(List) 对List二分查找
三.Integer类
1.valueOf(str)
2.parseInt(str)
四.Math类
常量:
Math.PI
Math.E
方法:
(1)Math.min() int,long,float,double
(2)Math.max()
(3)乘方:Math.pow(double,double) 返回:double
(4)开根号:Math.sqrt(double)
(5)绝对值:Math.abs()
(6)向下取整:Math.floor(),向上取整:Math.ceil(),四舍五入:Math.round()
(7)随机数:Math.random() //返回一个大于等于0.0且小于1.0的double值




 本文介绍了Java中常用的几个类:Arrays、Collections、Integer及Math。Arrays类提供了排序、搜索、拷贝和填充等功能;Collections主要用于List的操作,包括排序和二分查找;Integer类的valueOf和parseInt方法用于字符串转整数;Math类包含数学运算如平方、开根号、随机数等。了解这些基础类的方法,能有效提升Java编程效率。
本文介绍了Java中常用的几个类:Arrays、Collections、Integer及Math。Arrays类提供了排序、搜索、拷贝和填充等功能;Collections主要用于List的操作,包括排序和二分查找;Integer类的valueOf和parseInt方法用于字符串转整数;Math类包含数学运算如平方、开根号、随机数等。了解这些基础类的方法,能有效提升Java编程效率。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








