Sytemd 的介绍
一个服务经常关系到多个服务。在7版本中,PID1是systemd,新的init system.
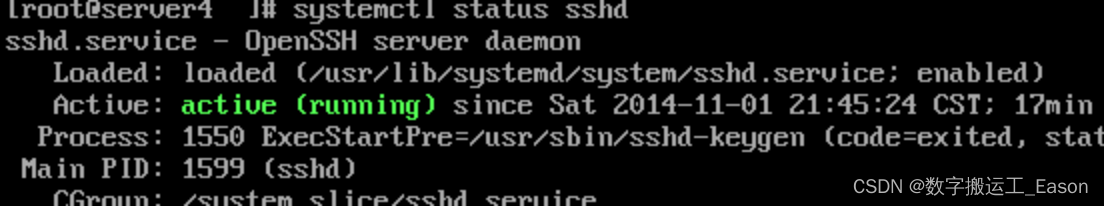
查看服务状态。
systemctl status service
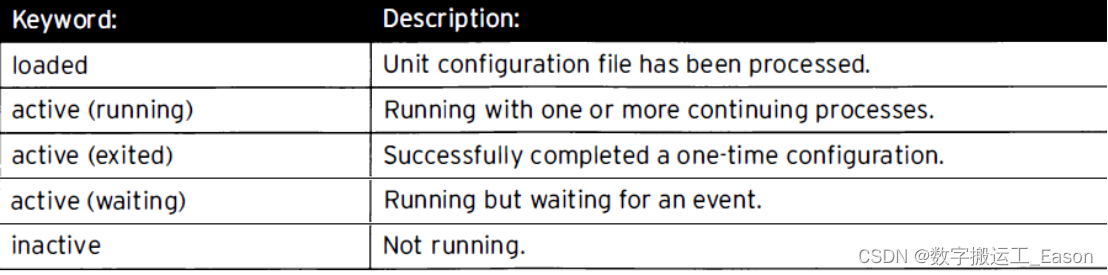

systemctl list-units --type=service #查看active状态 -all将添加inactive单元。
systemctl list-units --type=service --all
systemctl list-units-files --type=service #查看 enable和disable单元设置。
system --falied --type=service #仅查看failed服务。
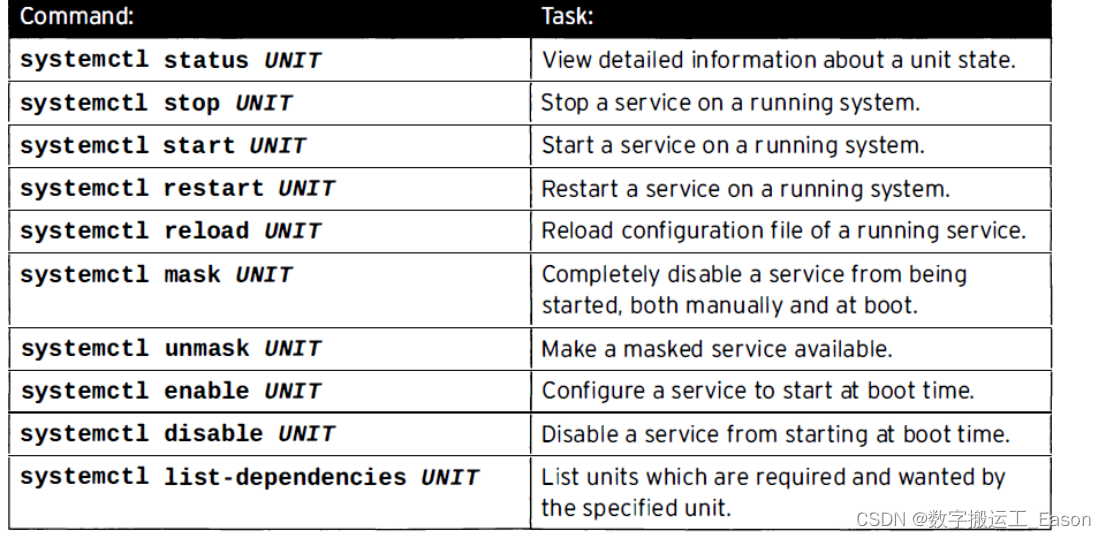
开启与停止系统守护进程。
systemctl stop sshd.service #停止sshd服务。
systemctl start sshd.service #开启sshd 服务。
Reload 与restart,reload重新加载服务,进程不会断掉,PID号不改变;restart关闭服务再开启,给予 新的PID号。
systemctl reload sshd.service
systemctl restart sshd.service
systemctl list--dependencies --type=service #查看服务的依赖服务。
Masking 服务。即便使用restart也不能开启。用于两个服务冲突,只能使用一个如:iptables,firewalld
systemct l mask iptables #禁止iptables
systemctl unmask iptables #解锁iptables
在开机的时候开启服务或者停止服务。
systemctl enable sshd #在开机的时候开启服务 类似于6版本的chkconfig on
systemctl disable sshd
控制BOOT进程
选择systemd target
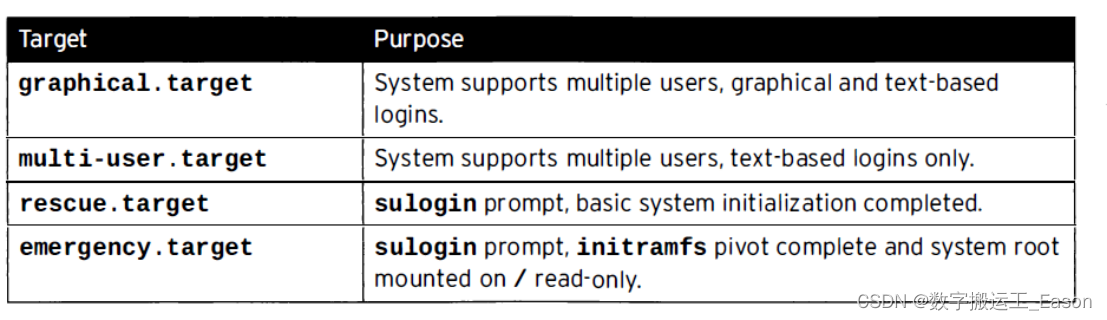
systemctl list-dependencies graphical.target | grep target #查看target的依赖关系
systemctl list-units --type=target --all #查看所有可用的target
systemctl list-unit--files --type=target --all #查看已经安装在磁盘的target
1.systemctl isolate multi-user.taget #临时切换到命令模式。
2.systemctl get-default #查看默认的target
systemctl set-default graphical.target #设置默认的target
3.systemd.unit=rescue.target #在开机的时候启动target,设置在linux 16行
诊断和修复 systemd boot
如果在开启服务的时候出现问题,可以使用#systemctl enable debug-shell.service
或者进入紧急和救援模式。
systemctl list-jobs systemd #产生一堆作业号码,用于排错。
请珍惜劳动成果,支持原创,欢迎点赞或者关注收藏,你每一次的点赞和收藏都是作者的动力,内容如有问题请私信随时联系作者,谢谢!





 本文介绍了Systemd的基础知识,包括如何查看服务状态、管理服务的启动与停止、服务的依赖关系以及开机启动服务。此外,还涉及了目标(target)的选择和切换,以及如何进行系统诊断和故障修复。内容涵盖systemctl命令的各种用法,是理解Systemd服务管理和Linux系统控制的重要参考。
本文介绍了Systemd的基础知识,包括如何查看服务状态、管理服务的启动与停止、服务的依赖关系以及开机启动服务。此外,还涉及了目标(target)的选择和切换,以及如何进行系统诊断和故障修复。内容涵盖systemctl命令的各种用法,是理解Systemd服务管理和Linux系统控制的重要参考。

















 1625
1625

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










