In the late 1700s', Gauss, a famous mathematician, found a special kind ofnumbers. These integers are all in the form: a + b![]() .The sum and multiplicationofthese integers can be naturally defined as the follows:
.The sum and multiplicationofthese integers can be naturally defined as the follows:
(a + b![]() ) + (c + d
) + (c + d![]() ) = (a + c) + (b + d )
) = (a + c) + (b + d )![]()
(a + b![]() ) * (c + d
) * (c + d![]() ) = (a * c = b * d * k) + (a * d + b * c)
) = (a * c = b * d * k) + (a * d + b * c)![]()
One can prove that the sum and multiplication of these integers constitute thestructure called ``imaginary quadratic field" in calculus.
In case k = 1, these are common complex numbers.
In case both a and b are integers, these numbers are called ``Gauss integers", andthis is the very case that interests people the most in quadratic algebra.
As we all know that every integer can be factorized into the multiplication ofseveral primes (Fundamental theoorem of arithmetic, or unique factorization theorem).
Primes are the integers that can only be divided by 1 and itself. We do have asimilar concept in the context ofGauss integer.
If a Gauss integer cannot bee factorized into the multiplication of other Gaussintegers (0, 1, -1 exclusive), we call it a ``Gauss Prime" or ``Non-divisible".
Please note that 0, 1 and - 1 are not regarded as gauss primes but ![]() is.
is.
However, unique factorization theorem doesn't apply to arbitrary k. For examplein the case k = 5, 6 can be factorized in two different ways:6 = 2 * 3, 6 = (1 + ![]() ) * (1 -
) * (1 - ![]() ).
).
Thanks to the advance of mathematics in the past 200 years, one can prove thatthere are only 9 integers can be used as k, such that the unique factorization theoremsatisfies. These integers are k = { 1, 2, 3, 7, 1 1, 19, 43, 67, 163}.
Input
The first line of the input is an integer n (1 < n < 100), followed by n lines. Each line is a single case and contains two integers, a and b (0![]() a
a![]() 10000, 0 < b
10000, 0 < b![]() 10000).
10000).
Output
To make this problem not too complicated, we just suppose that k is 2.
For every case of the input, judge whether a + b![]() is a gauss prime.
is a gauss prime.
Output the answer `Yes' or `No' in a single line.
Sample Explanation
Please notes that (5, 1) is not a gauss prime because (5, 1) = (1, -1) * (1, 2).
Sample Input
2 5 1 3 4
Sample Output
No Yes
高斯整数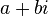 是素数当且仅当:
是素数当且仅当:
- a、b中有一个是零,另一个是形为
 或其相反数
或其相反数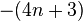 的素数;
的素数; - 或a、b均不为零,而
 为素数。
为素数。
证明 点击打开链接
这里是a+b√-2,因为素数不一定是高斯素数,当a=0或b=0时,素数也有可能分解成(a+b√-2)*(a-b√-2)(素数如果能分解,只能是这种形式),费马定理不能用了,就暴力看有没有b=x*x+2*y*y。
如果a,b都不为零,就判断(a+b√-2)*(a-b√-2)=a*a+2*b*b是不是素数。如果是就不能分解,不是就能分解。
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<algorithm>
#define eps 1e-9
#define MAXN 30010
#define MAXM 110
#define MOD 999983
typedef long long LL;
using namespace std;
int T,K;
int is_prime(int x){
for(int i=2;i*i<=x;i++) if(x%i==0) return 0;
return 1;
}
int check(int a,int b){
if(!a){
if(!is_prime(b)) return 1;
int sq=sqrt(b)+0.5;
for(int i=0;i<=sq;i++){
double t=sqrt((b-i*i)/2.0);
if(floor(t)==ceil(t)) return 1;
}
return 0;
}
if(is_prime(a*a+2*b*b)) return 0;
return 1;
}
int main(){
freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
int a,b;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
if(!check(a,b)) printf("Yes\n");
else printf("No\n");
}
return 0;
}





 该博客探讨了高斯素数的概念,即在形式为a + b√-2的高斯整数中,当a和b满足特定条件时,它们是否为素数。文章指出,在k = 2的情况下,需要判断a + b是否为高斯素数,并提供了判断方法。通过检查a和b的特定组合,可以确定高斯整数是否为素数。
该博客探讨了高斯素数的概念,即在形式为a + b√-2的高斯整数中,当a和b满足特定条件时,它们是否为素数。文章指出,在k = 2的情况下,需要判断a + b是否为高斯素数,并提供了判断方法。通过检查a和b的特定组合,可以确定高斯整数是否为素数。
















 1067
1067










