DatagramChannel类的使用
DatagramChannel类是针对面向DatagramSocket的可选择通道。DatagramChannel 不是DatagramSocket的完整抽象,必须通过调用socket() 方法获得的关联DatagramSocket对象来完成套接字选项的绑定和操作。不可能为任意的已有DatagramSocket创建通道,也不可能指定与DatagramChannel关联的DatagramSocket所使用的DatagramSocketImpl对象。
通过调用此类的open()方法创建DatagramChannel。新创建的DatagramChannel已打开,但尚未连接。使用send()和receive()方法,不需要将DatagramChannel进行连接,但是每次send和receive操作时都要执行安全检查,会造成系统开销,要避免这种情况也可以通过调用DatagramChannel的connect() 方法来建立DatagramChannel连接。为了使用read()和write()方法,必须建立DatagramChannel连接,因为这些方法不接受或返回套接字地址。
一旦建立连接,在断开DatagramChannel的连接或将其关闭之前,该DatagramChannel保持连接状态。可通过调用DatagramChannel的isConnected()方法来确定它是否已连接。
多个并发线程可安全地使用DatagramChannel。尽管在任意给定时刻最多只能有一个线程进行读取和写入操作,但DatagramChannel支持并发读写。
使用DatagramChannel类实现UDP通信
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
DatagramChannel channel = DatagramChannel.open();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
//如果在两台物理计算机中进行实验,则要把localhost改成服务端的IP地址
channel.bind(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8888));
Selector selector = Selector.open();
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
boolean isRun = true;
while (isRun) {
selector.select();
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = it.next();
if (key.isReadable()) {
channel = (DatagramChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
channel.receive(byteBuffer);
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array(), 0, byteBuffer.position()));
}
it.remove();
}
channel.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
DatagramChannel channel = DatagramChannel.open();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
Selector selector = Selector.open();
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
int keyCount = selector.select();
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = it.next();
if (key.isWritable()) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap("我来自客户端!".getBytes());
//如果在两台物理计算机中进行实验,则要把localhost改成客户端的IP地址
channel.send(byteBuffer, new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8888));
channel.close();
}
}
System.out.println("client end!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
我来自客户端!
连接操作
public abstract DatagramChannel connect(SocketAddress remote)方法的作用是连接此通道的套接字。
服务端与上面一致,客户端如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
DatagramChannel channel = DatagramChannel.open();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
channel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8888));
Selector selector = Selector.open();
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
int keyCount = selector.select();
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = it.next();
if (key.isWritable()) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap("我来自客户端!".getBytes());
channel.write(byteBuffer);
channel.close();
}
}
System.out.println("client end!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
我来自客户端!
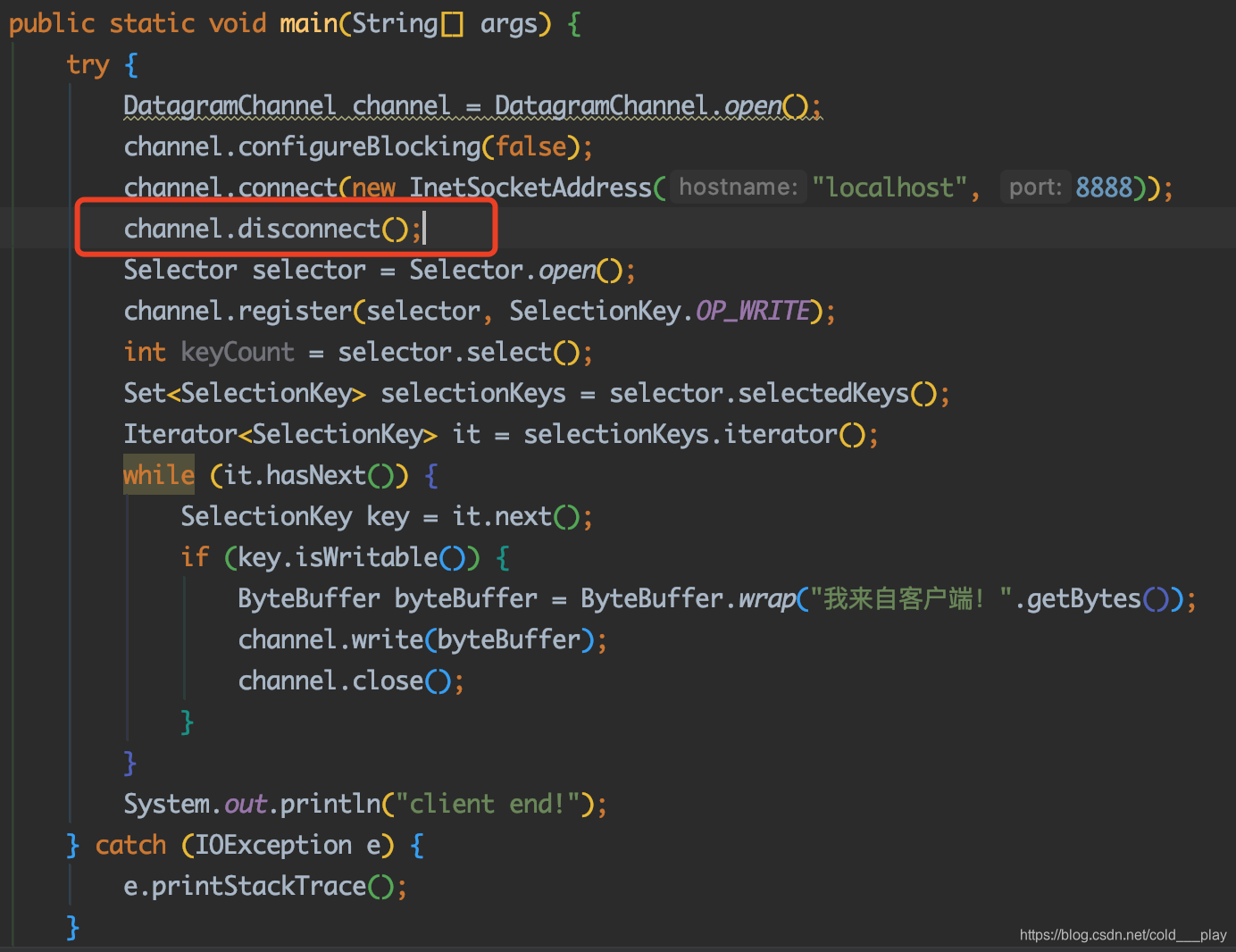
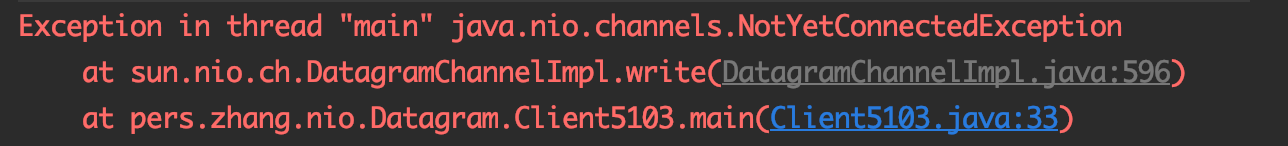
断开连接
public abstract DatagramChannel disconnect()方法的作用是断开此通道套接字的连接。





 本文深入探讨了DatagramChannel类的使用方法,包括如何创建、配置和使用该类进行UDP通信。文章详细介绍了DatagramChannel的特性,如并发读写支持、连接和断开连接的操作,并提供了具体的代码示例。
本文深入探讨了DatagramChannel类的使用方法,包括如何创建、配置和使用该类进行UDP通信。文章详细介绍了DatagramChannel的特性,如并发读写支持、连接和断开连接的操作,并提供了具体的代码示例。
















 942
942

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








