执行AsyncTask
onPreExecute()///首先执行这个方法,它在UI线程中 可以执行一些异步操作 比如初始化一些东西
doInBackground(Object... arg0) //异步后台执行 ,执行完毕可以返回出去一个结果object对象
onPostExecute(Object result) //可以拿到执行中的进度 当然进度须要在doInBackground中手动调用publishProgress()方法返回
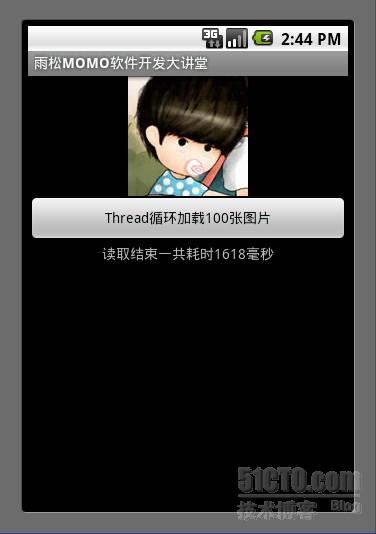
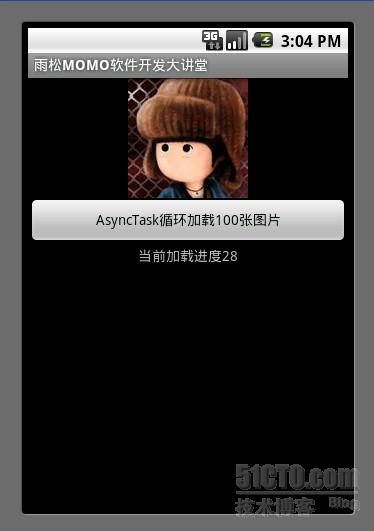
通过例子可以清楚的看到计算出读取100张图片的时间,执行的效率上来说AsyncTask 没有Thread效率块,但是AsyncTask 比Thread更规整,它可是时时的拿到异步线程中进度以及最后的结果集,可以让我们的代码更佳规范。这里说一下 Thread能做到的事AsyncTask 都可以做到 但是AsyncTask 能做到的事Thread 不一定能做到就算勉强做到也很麻烦 。我给大家的建议是如果处理大量的异步操作就用AsyncTask 如果少部分的则使用Thread
doInBackground(Object... arg0) //异步后台执行 ,执行完毕可以返回出去一个结果object对象
onPostExecute(Object result) //可以拿到执行中的进度 当然进度须要在doInBackground中手动调用publishProgress()方法返回
通过例子可以清楚的看到计算出读取100张图片的时间,执行的效率上来说AsyncTask 没有Thread效率块,但是AsyncTask 比Thread更规整,它可是时时的拿到异步线程中进度以及最后的结果集,可以让我们的代码更佳规范。这里说一下 Thread能做到的事AsyncTask 都可以做到 但是AsyncTask 能做到的事Thread 不一定能做到就算勉强做到也很麻烦 。我给大家的建议是如果处理大量的异步操作就用AsyncTask 如果少部分的则使用Thread
- import java.io.InputStream;
- import java.util.Timer;
- import java.util.TimerTask;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.content.Context;
- import android.graphics.Bitmap;
- import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
- import android.os.AsyncTask;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.view.View;
- import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
- import android.widget.Button;
- import android.widget.TextView;
- public class AsyncTaskActivity extends Activity {
- /**执行Timer进度**/
- public final static int LOAD_PROGRESS = 0;
- /**关闭Timer进度**/
- public final static int CLOSE_PROGRESS = 1;
- /** 开始StartAsync按钮 **/
- Button mButton0 = null;
- /** 显示内容 **/
- TextView mTextView = null;
- Context mContext = null;
- /**Timer对象**/
- Timer mTimer = null;
- /**TimerTask对象**/
- TimerTask mTimerTask = null;
- /**记录TimerID**/
- int mTimerID = 0;
- @Override
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- setContentView(R.layout.async);
- mContext = this;
- /** 拿到button 与 TextView 对象 **/
- mButton0 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button0);
- mTextView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView0);
- //开始
- mButton0.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
- @Override
- public void onClick(View arg0) {
- //开始执行StartAsync
- StartAsync();
- }
- });
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- }
- public void StartAsync() {
- new AsyncTask<Object, Object, Object>() {
- @Override
- protected void onPreExecute() {
- //首先执行这个方法,它在UI线程中 可以执行一些异步操作
- mTextView.setText("开始加载进度");
- super.onPreExecute();
- }
- @Override
- protected Object doInBackground(Object... arg0) {
- //异步后台执行 ,执行完毕可以返回出去一个结果object对象
- //得到开始加载的时间
- Long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
- // 这里循环加载图片100遍
- ReadBitMap(mContext, R.drawable.bg);
- //执行这个方法会异步调用onProgressUpdate方法,可以用来更新UI
- publishProgress(i);
- }
- //得到结束加载的时间
- Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- //将读取时间返回
- return endTime - startTime;
- }
- @Override
- protected void onPostExecute(Object result) {
- //doInBackground之行结束以后在这里可以接收到返回的结果对象
- mTextView.setText("读取100张图片一共耗时" + result+ "毫秒");
- super.onPostExecute(result);
- }
- @Override
- protected void onProgressUpdate(Object... values) {
- //时时拿到当前的进度更新UI
- mTextView.setText("当前加载进度" + values[0]);
- super.onProgressUpdate(values);
- }
- }.execute();//可以理解为执行 这个AsyncTask
- }
- /**
- * 读取本地资源的图片
- *
- * @param context
- * @param resId
- * @return
- */
- public Bitmap ReadBitMap(Context context, int resId) {
- BitmapFactory.Options opt = new BitmapFactory.Options();
- opt.inPreferredConfig = Bitmap.Config.RGB_565;
- opt.inPurgeable = true;
- opt.inInputShareable = true;
- // 获取资源图片
- InputStream is = context.getResources().openRawResource(resId);
- return BitmapFactory.decodeStream(is, null, opt);
- }
- }
- import java.io.InputStream;
-
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.content.Context;
- import android.graphics.Bitmap;
- import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.os.Handler;
- import android.os.Looper;
- import android.os.Message;
- import android.view.View;
- import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
- import android.widget.Button;
- import android.widget.Toast;
-
- public class LooperActivity extends Activity {
- /** 发送消息按钮 **/
- Button mButton = null;
- /** 加载图片前的时间 **/
- Long mLoadStatr = 0L;
- /** 加载图片后的时间 **/
- Long mLoadEnd = 0L;
-
- Context mContext = null;
-
- private Handler handler = new Handler() {
- public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
- new Thread() {
- @Override
- public void run() {
-
- //如果handler不指定looper的话
- //默认为mainlooper来进行消息循环,
- //而当前是在一个新的线程中它没有默认的looper
- //所以我们须要手动调用prepare()拿到他的loop
- //可以理解为在Thread创建Looper的消息队列
- Looper.prepare();
-
-
- Toast.makeText(LooperActivity.this, "收到消息",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
-
-
- //在这里执行这个消息循环如果没有这句
- //就好比只创建了Looper的消息队列而
- //没有执行这个队列那么上面Toast的内容是不会显示出来的
- Looper.loop();
-
-
-
-
- //如果没有 Looper.prepare(); 与 Looper.loop();
- //会抛出异常Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()
- //原因是我们新起的线程中是没有默认的looper所以须要手动调用prepare()拿到他的loop
-
- }
- }.start();
- }
- };
-
- @Override
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- setContentView(R.layout.loop);
- mContext = this;
-
- /** 拿到button 与 TextView 对象 **/
- mButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button0);
- mButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
- @Override
- public void onClick(View arg0) {
- new Thread() {
- @Override
- public void run() {
-
- //发送一条空的消息
- //空消息中必需带一个what字段
- //用于在handler中接收
- //这里暂时我先写成0
- handler.sendEmptyMessage(0);
-
- }
- }.start();
- }
- });
-
-
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- }
- /**
- * 读取本地资源的图片
- *
- * @param context
- * @param resId
- * @return
- */
- public Bitmap ReadBitMap(Context context, int resId) {
- BitmapFactory.Options opt = new BitmapFactory.Options();
- opt.inPreferredConfig = Bitmap.Config.RGB_565;
- opt.inPurgeable = true;
- opt.inInputShareable = true;
- // 获取资源图片
- InputStream is = context.getResources().openRawResource(resId);
- return BitmapFactory.decodeStream(is, null, opt);
- }
- }





 本文深入探讨了游戏及软件开发中多线程的重要性,并通过具体示例介绍了Thread与Handler、TimerTask与Handler以及AsyncTask等多线程技术的应用。此外还讲解了如何利用Looper管理线程的消息队列。
本文深入探讨了游戏及软件开发中多线程的重要性,并通过具体示例介绍了Thread与Handler、TimerTask与Handler以及AsyncTask等多线程技术的应用。此外还讲解了如何利用Looper管理线程的消息队列。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








