异步编程
同步行为就是代码按照顺序执行,JavaScript是单线程的,如果某个操作需要的时间很长(例如向服务器发送请求),那么可以通过异步编程等待当前任务响应,然后继续执行后续的代码。当等待的任务有响应,再通过某种方式通知被调用者。
在代码执行过程中,遇到同步任务执行栈执行,遇到异步任务进行等待,往消息队列中插入一条消息。当后续的同步任务执行完了,读取消息队列,把异步任务进入执行栈执行。异步任务是在后续同步任务执行完后再入栈的。
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i ++) {
setTimeout(function(){
console.log(i);
}, 0);
}
console.log(22);
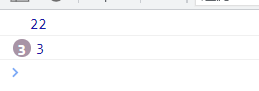
首先同步任务中for循环中i增加到了3,但是setTimeout表示console.log(i)这个函数是异步的,往消息队列中插入这个任务。继续执行console.log(22),现在同步任务执行完成,从消息队列中读取异步任务,现在才打印i=3.
回调函数解决
我们可以通过回调函数解决异步编程问题,回调函数指的是一个函数作为参数传递给另一个函数,当需要时另一个函数才调用它。
function a(x, y, callback) {
// 先干自己的事 等到需要回调函数再调用
const sum = x + y
// 现在调用回调函数
callback(sum)
}
function print(x) {
console.log(x)
}
a(2, 3, print)
promise
回调函数会出现回调地狱的问题,即回调中嵌套多层回调。promise可以解决回调地狱的问题,以更加清晰的逻辑写好异步编程。promise有3个状态,pending,resolved,rejected.
//基本模型
const p=new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
})
p.then(res=>{
}).catch((err)=>{
}).finally(()=>{
})
promise构造函数接受一个函数作为参数,该函数是同步的并且会被立即执行。它有两个参数,resolve表示promise成功的状态,reject表示promise失败的状态。
promise中的方法:
- then:异步操作成功时的回调函数
- catch:异步操作失败时的回调函数
- finally:无论成功失败都会执行的回调函数
如果异步操作成功resolve通知then执行成功的回调函数,如果失败reject通知catch执行失败的回调函数。
const p=new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
//这里是异步操作
setTimeout(()=>{
if(Math.random()<0.5){
resolve(true); //这里处理成功 传递给then方法
}else{
reject(false); //这里处理错误的 传递给catch方法
}
},2000)
})
p.then(res=>{
console.log(res); //成功的回调函数 成功就输出TRUE
}).catch(error=>{
console.log(error); //失败的回调函数 失败就输出false
}).finally(()=>{
console.log('the end') //最后一点会输出the end
})
async和await
async和await对promise进一步简化,可以用同步的方式写异步代码。
使用了asnyc之后标明这是一个异步函数,异步函数使用return返回值会被promise.resolve()包装成一个promise对象。
//async放在函数前面 函数返回的是一个promise对象 简化对promise对象的创建
async function test(){
console.log("简化promise写法");
return 22;
}
const a=test();
console.log(a); //这里返回是一个promise对象
// async相当于下面的写法
function test1() {
return new Promise(resolve=>{
console.log("原来写法");
resolve(22);
})
}
const b=test1();
console.log(b);
await会暂停异步函数中后面的代码,等到await右边的值可用再继续执行await下面的操作。
async function a(){
console.log(2);
const x=await 3;
console.log(x);
}
console.log(1);
a(); //在await的时候会暂停,退出了a,执行完下一句再返回执行console.log(x)
console.log("在await的时候退出了函数a");
// 1
// 2
// 在await的时候退出了函数a
// 3
await关键字要和async一起使用,原来异步函数返回的是一个promise对象,但是使用了await之后可以取到promise对象中的值。
async function test(){
console.log("简化promise写法");
return 22;
}
// await必须和async一起使用
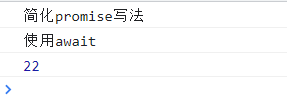
async function f() {
const result=await test();
console.log("使用await");
console.log(result);
}
f();
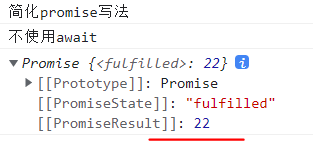
async function test(){
console.log("简化promise写法");
return 22;
}
// await必须和async一起使用
async function f() {
const result= test();
console.log("不使用await");
console.log(result);
}
f();





 文章详细介绍了JavaScript中的异步编程概念,包括同步任务和异步任务的执行流程,通过例子解释了回调函数的工作原理,以及如何使用Promise来避免回调地狱。最后,文章阐述了async和await如何简化异步代码,使得代码更接近同步风格。
文章详细介绍了JavaScript中的异步编程概念,包括同步任务和异步任务的执行流程,通过例子解释了回调函数的工作原理,以及如何使用Promise来避免回调地狱。最后,文章阐述了async和await如何简化异步代码,使得代码更接近同步风格。
















 1019
1019

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








