How Many Answers Are Wrong HDU - 3038
TT and FF are ... friends. Uh... very very good friends -________-b
FF is a bad boy, he is always wooing TT to play the following game with him. This is a very humdrum game. To begin with, TT should write down a sequence of integers-_-!!(bored).
Then, FF can choose a continuous subsequence from it(for example the subsequence from the third to the fifth integer inclusively). After that, FF will ask TT what the sum of the subsequence he chose is. The next, TT will answer FF's question. Then, FF can redo this process. In the end, FF must work out the entire sequence of integers.
Boring~~Boring~~a very very boring game!!! TT doesn't want to play with FF at all. To punish FF, she often tells FF the wrong answers on purpose.
The bad boy is not a fool man. FF detects some answers are incompatible. Of course, these contradictions make it difficult to calculate the sequence.
However, TT is a nice and lovely girl. She doesn't have the heart to be hard on FF. To save time, she guarantees that the answers are all right if there is no logical mistakes indeed.
What's more, if FF finds an answer to be wrong, he will ignore it when judging next answers.
But there will be so many questions that poor FF can't make sure whether the current answer is right or wrong in a moment. So he decides to write a program to help him with this matter. The program will receive a series of questions from FF together with the answers FF has received from TT. The aim of this program is to find how many answers are wrong. Only by ignoring the wrong answers can FF work out the entire sequence of integers. Poor FF has no time to do this job. And now he is asking for your help~(Why asking trouble for himself~~Bad boy)
Input
Line 1: Two integers, N and M (1 <= N <= 200000, 1 <= M <= 40000). Means TT wrote N integers and FF asked her M questions.
Line 2..M+1: Line i+1 contains three integer: Ai, Bi and Si. Means TT answered FF that the sum from Ai to Bi is Si. It's guaranteed that 0 < Ai <= Bi <= N.
You can assume that any sum of subsequence is fit in 32-bit integer.
Output
A single line with a integer denotes how many answers are wrong.
Sample Input
10 5 1 10 100 7 10 28 1 3 32 4 6 41 6 6 1
Sample Output
1
题意:有编号为1-n的n个序列,给m个查询:x y s,每个查询表示区间[x,y]的和为s
问有多少个有矛盾的询问
题解(转自https://dilthey.cnblogs.com/):
经典的带权并查集问题;
我们设sum[x]是这n个数的前缀和数组,那么就可以把所有的 a+…+b = s 都变成 sum[b] - sum[a-1] = s;
那么我们就可以利用带权并查集进行进行建树,照例par[x]代表了节点x的父亲节点,而val[x]代表了sum[x] - sum[par[x]];
首先是find()函数,我们在原来最基础的并查集find函数中,是有一种类似于把x的父亲节点par[x]变成par[par[x]]这样的,将节点沿着树枝往上移动的操作,
那么相应的,我们每次做将par[x]变成par[par[x]]这样的操作时,val[x]也要修改为val[x]+val[par[x]];
其次,我们对于每次查询的结果a,b,s,令 t1 = find(a),t2 = find(b),那么对应的s,val[a],val[b],val[t2]就可以如下图的向量所示:
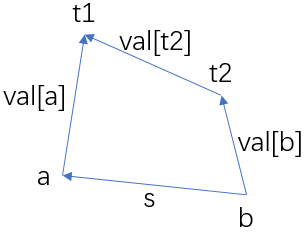
向量的方向相当重要(因为这个WA了两发= =):对于任何的从x指向y的向量都代表了sum[x] - sum[y];
那么很显然的有:
①若a,b还不是一个集合内,那么就要unite他们,即令par[t2]=t1;
那么同时,根据向量的加减法,val[t2]也要跟随着par[t2]的变动,转变成sum[t2] - sum[t1];所以根据向量加减的规则就有val[t2] = - val[b] + s + val[a];
②若a,b已经是一个集合内的,那么就要判断是否有矛盾;
显然此时t1=t2,那么如果s是正确的话,就应该有 - val[b] + s = val[a],否则,s就是一个与前面产生矛盾的、有错误的查询结果;
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
#define N 200010
#define nmax 6
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
int fa[N],sum[N]; //sum[x]表示从x到它的根(fa[x])的区间的和
int fin(int x)
{
if(fa[x]==x)
return x;
int t=fa[x];
fa[x]=fin(fa[x]);
/*因为sum[x]表示从x到它的根(fa[x])的区间的和,所以,当x的根发生改变时,
例如x的根原本是t=fa[x],即sum[x]原本表示[x,t]这段区间和,这里的x不一定比t大,现在x的根要指向fy,那么sum[x]要表示[x,fy]的区间和,则现在的sum[x]=sum[x]+sum[t];
sum[x]+=sum[t];
return fa[x];
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF)
{
int x,y,s;
int ans=0;
memset(sum,0,sizeof(sum));
for(int i=0; i<=n; i++)
fa[i]=i;
for(int i=0; i<m; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&s);
x--;
int fx=fin(x);
int fy=fin(y);
if(fx!=fy)
{
fa[fy]=fx;
sum[fy]=-sum[y]+s+sum[x];
/*(1)
fa[fx]=fy;
sum[fx]=-sum[x]+s+sum[y];
*/
}
else if(sum[y]!=sum[x]+s)
ans++;
/*(2)
对应(1)处的if语句
else if(sum[x]!=sum[y]+s)
ans++;
*/
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}







 本文介绍了一道经典算法题目HDU-3038的解决方案,通过使用带权并查集来解决一系列连续子序列求和的矛盾查询问题,详细解释了算法思路及实现细节。
本文介绍了一道经典算法题目HDU-3038的解决方案,通过使用带权并查集来解决一系列连续子序列求和的矛盾查询问题,详细解释了算法思路及实现细节。
















 150
150

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








