10.23 linux任务计划cron (固定时间执行命令或者脚本)
crontab -u、-e、-l、-r
格式:分 时 日 月 周 user command
文件/var/spool/cron/username 分范围0-59,时范围0-23,日范围1-31,月范围1-12,周1-7
可用格式1-5表示一个范围1到5
可用格式1,2,3表示1或者2或者3
可用格式*/2表示被2整除的数字,比如小时,那就是每隔2小时
要保证服务是启动状态 systemctl start crond.service
任务计划配置文件
[root
@test ~]# cat /etc/crontab
SHELL=/bin/bash
PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin (环境变量,命令路径)
MAILTO=root (发送邮件给指定用户)
# For details see man 4 crontabs
# Example of job definition:
# .---------------- minute (0 - 59)
# | .------------- hour (0 - 23)
# | | .---------- day of month (1 - 31)
# | | | .------- month (1 - 12) OR jan,feb,mar,apr ...
# | | | | .---- day of week (0 - 6) (Sunday=0 or 7) OR sun,mon,tue,wed,thu,fri,sat
# | | | | |
# * * * * * user-name command to be executed
*号五个位置
1.minute (0 - 59) 时间的分钟
2.hour (0 - 23) 时间的小时
3.day of month (1 - 31) 日期
4.month (1 - 12) OR jan,feb,mar,apr ... 月份(数字或者简写)
5.day of week (0 - 6) (Sunday=0 or 7) OR sun,mon,tue,wed,thu,fri,sat 星期(数字或者简写) 周日为0 则(0 - 6) 周日为7 则(1-7)
user-name 在root用户下不需要写用户默认root
command to be executed执行命令
定义用户计划
[root
@test ~]# crontab -e
任务计划:
每天凌晨三点执行指定脚本
*表示任意
0 3 * * * /bin/bash /usr/local/sbin/123.sh
每天凌晨三点执行指定脚本,并且把正确错误的输出追加到指定到日志中
0 3 * * * /bin/bash /usr/local/sbin/123.sh >>/tmp/123.log 2>>/tmp/123.log
每个月1-10号凌晨三点执行指定脚本,并且把正确错误的输出追加到指定到日志中
0 3 1-10 * * /bin/bash /usr/local/sbin/123.sh >/tmp/123.log 2>/tmp/123.log
双月1-10号凌晨三点执行指定脚本,并且把正确错误的输出追加到指定到日志中
0 3 1-10 */2 * /bin/bash /usr/local/sbin/123.sh >/tmp/123.log 2>/tmp/123.log
双月1-10号并且周二周五凌晨三点执行指定脚本,并且把正确错误的输出追加到指定到日志中
0 3 1-10 */2 2,5 /bin/bash /usr/local/sbin/123.sh >/tmp/123.log 2>/tmp/123.log
注:没有定义年份,因为是用星期去定义,因为每年指定日期的星期是不一样的
启动任务计划
[root
@test ~]# systemctl start crond
是否启动:
[root@test ~]# ps aux |grep crond
root 1239 0.0 0.0 126284 1620 ? Ss 10月26 0:01 /usr/sbin/crond -n
root 23771 0.0 0.0 112724 976 pts/0 S+ 10:42 0:00 grep --color=auto crond
启动状态
[root@test ~]# systemctl status crond.service
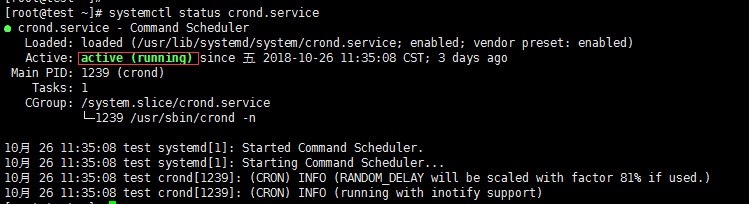
注:任务计划中很多任务没有执行,原因出在脚本中命令没有用绝对路径,也有可能脚本中命令没有在任务计划的PATH变量定义的路径范围中
解决方案一,脚本中命令写绝对路径 解决方案二将路径加入到任务计划的PATH的中
规矩:每个任务计划都要写输出日志

备份任务计划
将/tmp/目录下大于100天的文件删除
* 1 2 * * /usr/bin/find /tmp/ -type f -mtime +100 |xargs rm -f
查看任务计划
[root@test ~]# crontab -l
* 1 2 * * /usr/bin/find /tmp/ -type f -mtime +100 |xargs rm -f
每个用户的任务计划所在位置(用户名字命名文件)(
直接备份目录就可以
)
[root@test ~]# ls /var/spool/cron/
root
10.24 chkconfig工具(系统服务管理centos6及之前版本使用 SysV机制,centos7兼容 )
查看使用chkconfig服务有哪些
[root@test ~]# chkconfig --list
注:该输出结果只显示 SysV 服务,并不包含原生 systemd 服务。SysV 配置数据可能被原生 systemd 配置覆盖。
要列出 systemd 服务,请执行 'systemctl list-unit-files'。
查看在具体 target 启用的服务请执行
'systemctl list-dependencies [target]'。
netconsole 0:关 1:关 2:关 3:关 4:关 5:关 6:关
network 0:关 1:关 2:开 3:开 4:开 5:开 6:关
注:centos6及之前版本使用 SysV机制 centos7使用systemd机制
[root@test ~]# top
服务启动脚本位置(chkconfig管理)
[root@test ~]# ls /etc/init.d/
functions netconsole network README
设置0-6级别开机启动还是关闭
network 0:关 1:关 2:开 3:开 4:开 5:开 6:关
[root@test ~]# chkconfig network off
[root@test ~]# chkconfig --list
注:该输出结果只显示 SysV 服务,并不包含
原生 systemd 服务。SysV 配置数据
可能被原生 systemd 配置覆盖。
要列出 systemd 服务,请执行 'systemctl list-unit-files'。
查看在具体 target 启用的服务请执行
'systemctl list-dependencies [target]'。
netconsole 0:关 1:关 2:关 3:关 4:关 5:关 6:关
network 0:关 1:关 2:关 3:关 4:关 5:关 6:关
[root@test ~]# chkconfig network on
[root@test ~]# chkconfig --list
注:该输出结果只显示 SysV 服务,并不包含
原生 systemd 服务。SysV 配置数据
可能被原生 systemd 配置覆盖。
要列出 systemd 服务,请执行 'systemctl list-unit-files'。
查看在具体 target 启用的服务请执行
'systemctl list-dependencies [target]'。
netconsole 0:关 1:关 2:关 3:关 4:关 5:关 6:关
network 0:关 1:关 2:开 3:开 4:开 5:开 6:关
centos6及之前版本有7个级别
0级别关机
1级别单用户
2级别多用户模式不带图形无NFS服务(网络文件系统)
3级别多用户模式不带图形
4级别保留级别
5级别多用户带图形
6级别重启
centos7更改级别配置文件(系统默认已经不使用这个机制)
[root@test ~]# vim /etc/inittab
指定某一个级别开启或者关闭
[root@test ~]# chkconfig --level 3 network off
[root@test ~]# chkconfig --list
注:该输出结果只显示 SysV 服务,并不包含
原生 systemd 服务。SysV 配置数据
可能被原生 systemd 配置覆盖。
要列出 systemd 服务,请执行 'systemctl list-unit-files'。
查看在具体 target 启用的服务请执行
'systemctl list-dependencies [target]'。
netconsole 0:关 1:关 2:关 3:关 4:关 5:关 6:关
network 0:关 1:关 2:开 3:关 4:开 5:开 6:关
设置多个级别同时启动或者关闭
[root@test ~]# chkconfig --level 35 network off
[root@test ~]# chkconfig --list
注:该输出结果只显示 SysV 服务,并不包含
原生 systemd 服务。SysV 配置数据
可能被原生 systemd 配置覆盖。
要列出 systemd 服务,请执行 'systemctl list-unit-files'。
查看在具体 target 启用的服务请执行
'systemctl list-dependencies [target]'。
netconsole 0:关 1:关 2:关 3:关 4:关 5:关 6:关
network 0:关 1:关 2:开 3:关 4:开 5:关 6:关
脚本加入到服务列表中
首先把脚本放在
/etc/init.d/中
其次如何被识别
shell脚本#! /bin/bash
# chkconfig: 2345 10 90 运行级别2345 启动顺序:第十位启动 关闭顺序90位关闭
自我描述
# description: Activates/Deactivates all network interfaces configured to \
# start at boot time.
[root@test init.d]# chkconfig --add 123
[root@test init.d]# chkconfig --list
注:该输出结果只显示 SysV 服务,并不包含
原生 systemd 服务。SysV 配置数据
可能被原生 systemd 配置覆盖。
要列出 systemd 服务,请执行 'systemctl list-unit-files'。
查看在具体 target 启用的服务请执行
'systemctl list-dependencies [target]'。
123 0:关 1:关 2:关 3:关 4:关 5:关 6:关
netconsole 0:关 1:关 2:关 3:关 4:关 5:关 6:关
network 0:关 1:关 2:开 3:开 4:开 5:开 6:关
删除服务
[root@test init.d]# chkconfig --del 123
10.25 systemd管理服务
systemctl list-units --all --type=service
几个常用的服务相关的命令
systemctl enable crond.service //让服务开机启动
systemctl disable crond //不让开机启动
systemctl status crond //查看状态
systemctl stop crond //停止服务
systemctl start crond //启动服务
systemctl restart crond //重启服务
systemctl is-enabled crond //检查服务是否开机启动
查看所有服务
[root@test init.d]# systemctl list-units --all --type=service(mount、path、scope、target、socket 、slice 等等类型可以选择 )
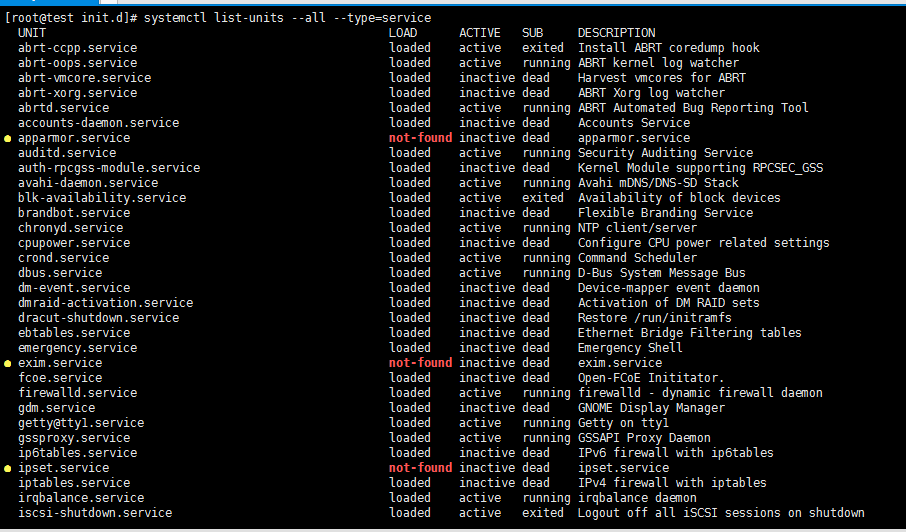
LOAD = Reflects whether the unit definition was properly loaded.
ACTIVE = The high-level unit activation state, i.e. generalization of SUB.激活状态
SUB = The low-level unit activation state, values depend on unit type.
To show all installed unit files use
'systemctl list-unit-files'.(要看全部使用这个命令,但是整理太乱)
只查看激活状态
[root@test init.d]# systemctl list-units --type=service
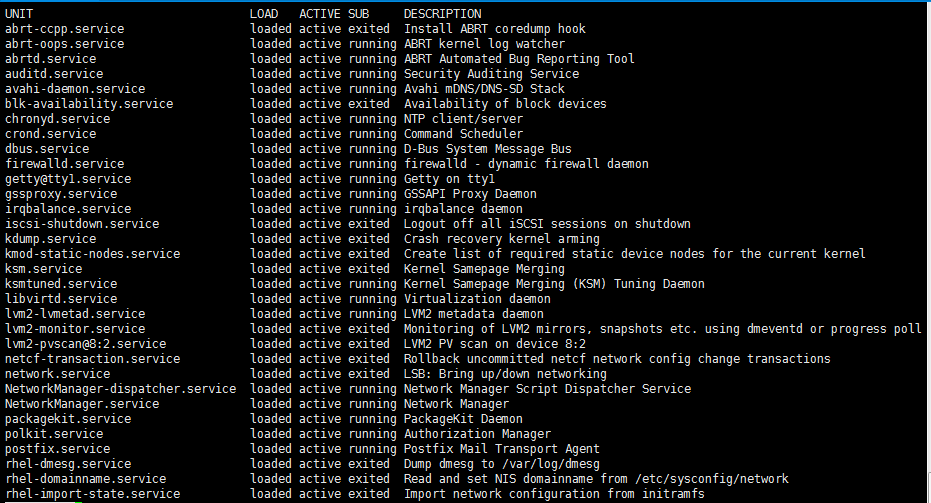
服务开机启动
[root@test ~]# systemctl enable crond.service
不让开机启动
[root@test ~]# systemctl disable crond.service
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/crond.service.
查看状态
[root@test ~]# systemctl status crond
● crond.service - Command Scheduler
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/crond.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since 五 2018-10-26 11:35:08 CST; 3 days ago
Main PID: 1239 (crond)
CGroup: /system.slice/crond.service
└─1239 /usr/sbin/crond -n
10月 26 11:35:08 test systemd[1]: Started Command Scheduler.
10月 26 11:35:08 test systemd[1]: Starting Command Scheduler...
10月 26 11:35:08 test crond[1239]: (CRON) INFO (RANDOM_DELAY will be scaled with factor 81% if used.)
10月 26 11:35:08 test crond[1239]: (CRON) INFO (running with inotify support)
服务停止
[root@test ~]# systemctl stop crond
开启服务
[root@test ~]# systemctl start crond
服务重启
[root@test ~]# systemctl restart crond
检查是否开机启动
[root@test ~]# systemctl is-enabled crond
disabled
设置开机启动服务时可以查看到配置文件的信息(开启时才会有这个软链接)
[root@test ~]# systemctl enable crond
Created symlink from
/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/crond.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/crond.service.
[root@test ~]# ls -l /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/crond.service
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 37 10月 30 11:36 /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/crond.service ->
/usr/lib/systemd/system/crond.service(文件真正路径)
10.26 unit介绍
ls /usr/lib/systemd/system //系统所有unit,分为以下类型
service 系统服务
target 多个unit组成的组 (多个service或者多个unit组成的组,形成target)
device 硬件设备
mount 文件系统挂载点
automount 自动挂载点
path 文件或路径
scope 不是由
systemd启动的外部进程
slice 进程组
snapshot systemd快照
socket 进程间通信套接字
swap swap文件
timer 定时器
系统所有unit(unit)
[root@test ~]# ls /usr/lib/systemd/system
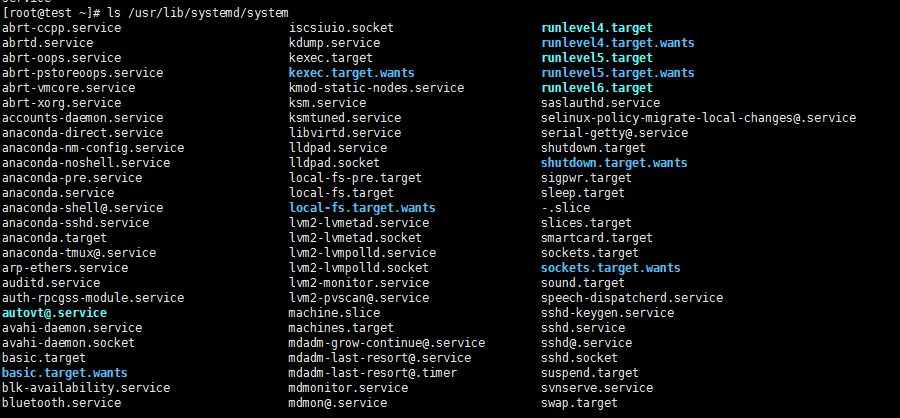
target 多个unit组成的组(7个target)与centos6及之前版本 7个级别对应
target就是多个service或者多个unit组成的组,形成target
[root@test ~]# ls -l /usr/lib/systemd/system/runlevel*
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 15 10月 9 12:53 /usr/lib/systemd/system/runlevel0.target -> poweroff.target关机
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 13 10月 9 12:53 /usr/lib/systemd/system/runlevel1.target -> rescue.target救援模式
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 17 10月 9 12:53 /usr/lib/systemd/system/runlevel2.target -> multi-user.target
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 17 10月 9 12:53 /usr/lib/systemd/system/runlevel3.target -> multi-user.target
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 17 10月 9 12:53 /usr/lib/systemd/system/runlevel4.target -> multi-user.target
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 16 10月 9 12:53 /usr/lib/systemd/system/runlevel5.target -> graphical.target图形化
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 13 10月 9 12:53 /usr/lib/systemd/system/runlevel6.target -> reboot.target重启
unit相关的命令
systemctl list-units //列出正在运行的unit
systemctl list-units --all //列出所有,包括失败的或者inactive的
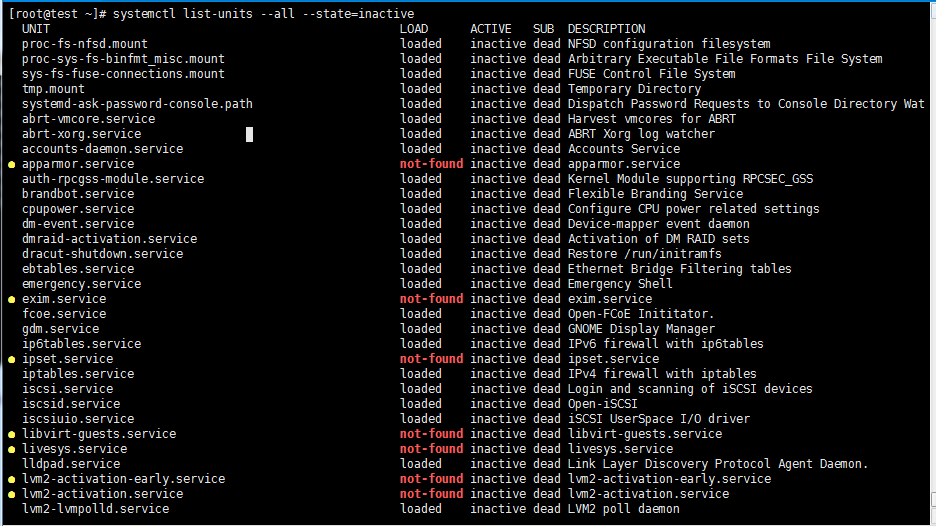
systemctl list-units --all --state=inactive //列出inactive的unit
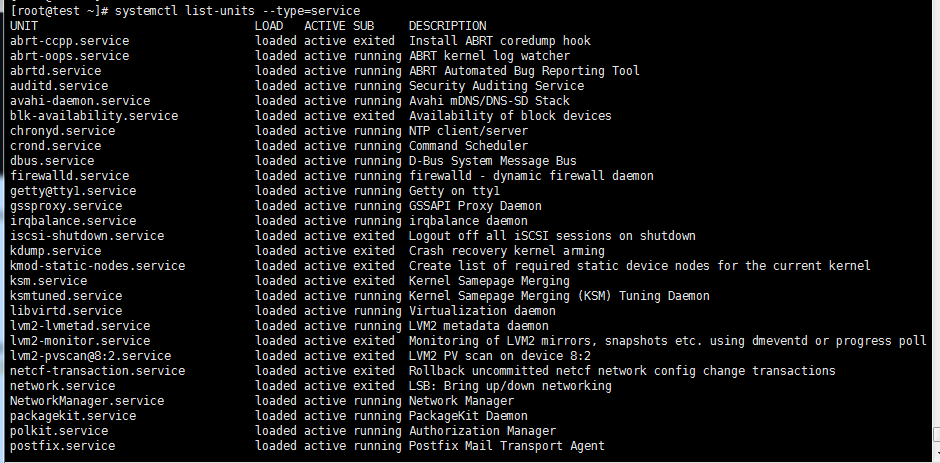
systemctl list-units --type=service//列出状态为active的service
systemctl is-active crond.service //查看某个服务是否为active
列出正在运行的unit
[root@test ~]# systemctl list-units
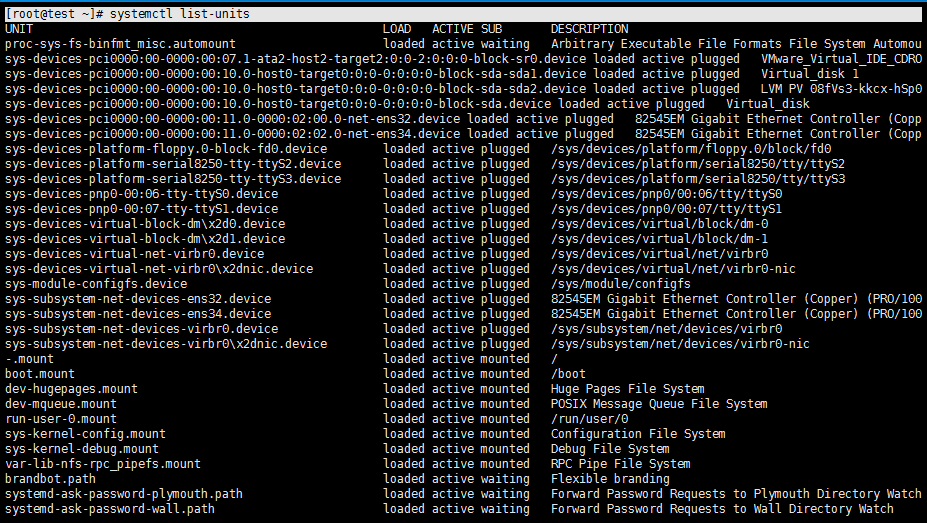
列出所有,包括失败的或者inactive的
[root@test ~]# systemctl list-units -all
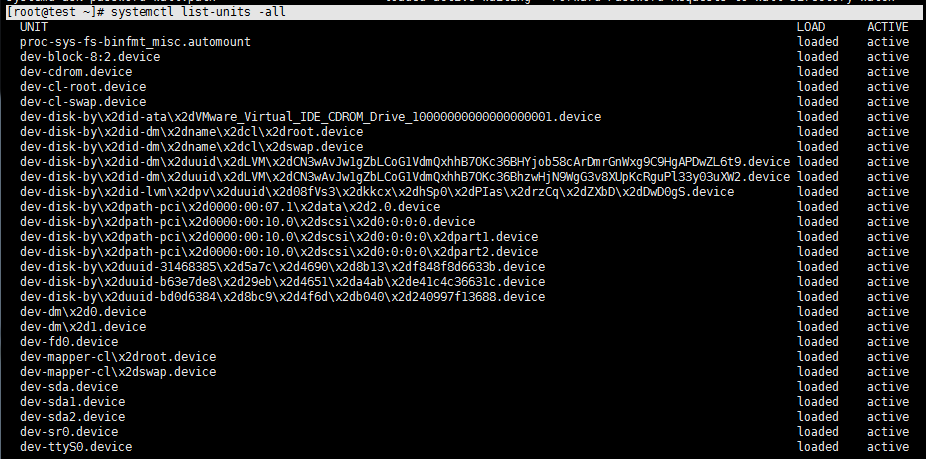
列出inactive的unit
[root@test ~]# systemctl list-units --all --state=inactive
列出状态为active的service
[root@test ~]# systemctl list-units --type=service
查看某个服务是否为active
[root@test ~]# systemctl is-active crond.service
active
查看是否开机启动
[root@test ~]# systemctl is-enabled crond.service
enabled
10.27 target介绍
系统为了方便管理用target来管理unit
systemctl list-unit-files --type=target
systemctl list-dependencies multi-user.target //查看指定target下面有哪些unit
systemctl get-default //查看系统默认的target
systemctl set-default multi-user.target
一个service属于一种类型的unit
多个unit组成了一个target
一个target里面包含了多个service
查看service 属于哪个target
cat /usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd.service //
看[install]部分
[root@test ~]# cat /usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd.service
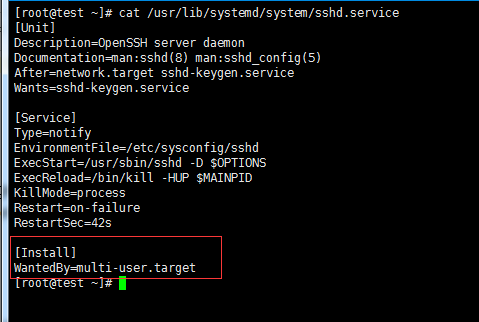
列出所有的target
[root@test ~]# systemctl list-unit-files --type=target
查看指定target下面有哪些unit(一个target是由若干个unit组成)
[root@test ~]# systemctl list-dependencies multi-user.target

查看系统默认的target (更改系统默认的target来决定运行级别)
[root@test ~]# systemctl get-default
multi-user.target
设置系统默认的运行级别
[root@test ~]# systemctl set-default multi-user.target
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/default.target.
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/default.target to /usr/lib/systemd/system/multi-user.target.
[root@test ~]# ls -l /etc/systemd/system/default.target
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 41 10月 30 12:15 /etc/systemd/system/default.target -> /usr/lib/systemd/system/multi-user.target







 本文详细介绍了Linux系统中任务计划的配置与管理,包括cron的使用方法、格式解析及常见命令。同时,深入探讨了服务管理工具chkconfig与systemd的使用技巧,帮助读者掌握系统服务的启动、停止、开机启动设置等操作。
本文详细介绍了Linux系统中任务计划的配置与管理,包括cron的使用方法、格式解析及常见命令。同时,深入探讨了服务管理工具chkconfig与systemd的使用技巧,帮助读者掌握系统服务的启动、停止、开机启动设置等操作。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








