一. 委托
面向接口编程,应该是每个人都十分熟悉的编程方式了,主要是用类实现接口中的方法,用接口来对外进行展示,外界只用关注接口就行,内部如何实现的并不用去关心。委托其实也是类似于面向接口一样的编程方式,在C#中有委托专门的语法特性,主要是针对方法的调用,我们不用关注该方法内部是如何实现的,只需要调用这个委托就行,也就是说委托把类似的方法通过一个实例进行传递,我们在其它地方也可以进行调用。
二.代码展示
//创建委托
namespace DelegateConsoleApp2.Way.Delegate
{
//进行委托链的测试
public delegate int DelegateTestOne(int a,int b);
//进行lambad表达式测试
public delegate void DelegateTestTwo();
//进行委托实景测试
public delegate bool Compare(int left, int right);
}
//设定计算方法
namespace DelegateConsoleApp2.Way.Unstatic
{
class WayTwo
{
public int Add(int a, int b)
{
Console.WriteLine("Add");
return a + b;
}
public int Divide(int a, int b)
{
Console.WriteLine("Divide");
return a / b;
}
public int subtract(int a, int b)
{
return a - b;
}
public int multiply(int a, int b)
{
Console.WriteLine("multiply");
return a * b;
}
public int GetAdd(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
public void Calculate(DelegateTestOne ex, int a, int b)
{
Console.WriteLine((ex(a, b)+a*b) + "\n");
}
}
}
//测试回调函数
namespace DelegateConsoleApp2.Way.Unstatic
{
public class WayThree
{
public void Calculate(DelegateTestOne ex, int a, int b)
{
Console.WriteLine((ex(a, b) + a * b) + "\n");
}
}
}
namespace DelegateConsoleApp2.Way.Unstatic
{
//排序方法
public class SortDemo
{
public class SortWay
{
private int[] items;//数组属性
public int[] Items//创建set,get进行对外可视
{
set { items = value; }
get { return items; }
}
// 比大
public bool Greater(int left, int right)
{
return left > right;
}
// 比小
public bool Less(int left, int right)
{
return !Greater(left, right);
}
/// <summary>
/// 利用委托的形式进行传递,因此可以只用这一种方法进行降序与升序的操作。
/// 以委托传递的参数进行判定用Greater或Less
/// </summary>
/// <param name="compare"></param>
public void Sort(Compare compare)
{
for (int i = 0; i < items.Length - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < items.Length; j++)
{
if (compare(items[i], items[j]))
{
int tmp = items[i];
items[i] = items[j];
items[j] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
namespace DelegateConsoleApp2
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//进行委托链的测试
WayTwo wayTwo = new WayTwo();//创建WayTwo这个类
DelegateTestOne delegateTestOne = new DelegateTestOne(wayTwo.Add);//把wayTwo.Add作为参数传递给委托
delegateTestOne += new DelegateTestOne(wayTwo.multiply);//委托链的添加
delegateTestOne += new DelegateTestOne(wayTwo.Divide);
Console.WriteLine(delegateTestOne(10,5));//在执行delegateTestOne委托时,delegateTestOne已经把里面的所有方法都已经执行一遍了,不过返回的还是最后一个方法的值。
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");//分割
WayThree wayThree = new WayThree();//创建WayThree 对象进行回调函数的测试
wayThree.Calculate(wayTwo.Add,2,4);//此处没有直接调用wayTwo.Add的方法,而是通过Calculate来进行调用其参数进行使用
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
string[] str = {"12","34","32","11","63","54","31"};//创建一个字符串数组,用来排序使用
SortWay way = new SortWay();//创建一个排序方法的对象
way.Items = GetStrings(str);//对SortWay对象中的Items属性赋值
// 使用降序排列
way.Sort(new Compare(way.Less));
ConsoleWay(way);
Console.WriteLine("Hello World");
// 使用升序排列
way.Sort(new Compare(way.Greater));
ConsoleWay(way);
Console.WriteLine("Hello World");
//进行lamda表达式编写
DelegateTestTwo delegateTestTwo = () => { Console.WriteLine("很棒吧!"); };
delegateTestTwo();
Console.ReadKey();
}
private static void ConsoleWay(SortWay sortWay)
{
for (int i = 0; i < sortWay.Items.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(sortWay.Items[i]);
}
}
private static int[] GetStrings(string[] str)
{
int[] items = new int[str.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < str.Length; i++)
items[i] = int.Parse(str[i]);
return items;
}
}
}
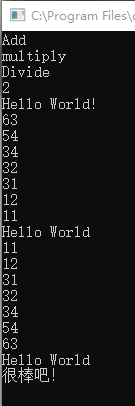
上述代码中,我们可以看到,类似的方法是SortDemo中的Sort,WayTwo中的Calculate,这些方法产生的结果不一致主要还是内部调用的其它方法有不同,所以用委托的方式进行方法的传递,使得这些类似的方法可以公用同一个方法,只是参数不一样,这样就不用进行多余的if else/swich等判断了,另外委托也可以直接进行方法的编写,尤其是可以使用lamda表达式的形式,lamda表达式主要是针对匿名函数进行方法的编写,刚好委托可以直接运用此方法进行编写,而不依赖其它的方法,不过这种方法最好是就在一个地方使用,因为委托的意义本来就是要增加系统的伸缩性。
另外上述的例子中,涉及到了回调函数,其实回调函数就是本身函数没有直接使用,而是在特定的条件下由另一方进行调用,用于对该事件的响应。其实上述的调用基本都是属于回调函数,只是为了区分下,单独做了个回调函数的例子。







 本文深入探讨C#中的委托概念,展示了如何通过委托实现方法的传递与调用,增强代码的灵活性与复用性。同时,文章还介绍了回调函数的应用场景与实现方式,通过具体示例代码说明了委托链、匿名方法及Lambda表达式的使用。
本文深入探讨C#中的委托概念,展示了如何通过委托实现方法的传递与调用,增强代码的灵活性与复用性。同时,文章还介绍了回调函数的应用场景与实现方式,通过具体示例代码说明了委托链、匿名方法及Lambda表达式的使用。
















 2555
2555

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








