Architecture
Processor Architecture = Instruction Set + Programmer’s model
|
Architecture |
4T |
5TE |
6 |
7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
core |
ARM7TDMI ARM922T Thumb instruction set |
ARM926EJ-S ARM946E-S ARM966E-S Improved ARM/Thumb Interworking DSP instructions Extensions: Jazelle (5TEJ) |
ARM1136JF-S ARM1176JZF-S ARM11 MPCore SIMD Instructions Unaligned data support Extensions: Thumb-2 (6T2) TrustZone (6Z) Multicore (6K) |
Cortex-A8/R4/M3/M1 Thumb-2 Extensions: v7A (applications) – NEON v7R (real time) – HW Divide V7M (microcontroller) – HW Divide and Thumb-2 only |
Development of the ARM Architecture
■ ARM Architecture profiles
Application profile (ARMv7-A e.g. Cortex-A8)
Real-time profile (ARMv7-R e.g. Cortex-R4)
Microcontroller profile (ARMv7-M e.g. Cortex-M3)
■ Implementations of the same architecture can be very different
ARM7TDMI - architecture v4T. Von Neuman core with 3 stage pipeline
ARM920T - architecture v4T. Harvard core with 5 stage pipeline and MMU
|
Architecture |
Cores designed by ARM Holdings |
Cores designed by 3rd parties |
|---|---|---|
|
ARMv1 |
ARM1 |
|
|
ARMv2 |
ARM2, ARM3 |
Amber |
|
ARMv3 |
ARM6, ARM7 |
|
|
ARMv4 |
ARM7TDMI, ARM8, ARM9TDMI |
StrongARM, FA526 |
|
ARMv5 |
ARM7EJ, ARM9E, ARM10E |
XScale, FA626TE, Feroceon, PJ1/Mohawk |
|
ARMv6 |
ARM11 |
|
|
ARMv6-M |
ARM Cortex-M0, ARM Cortex-M0+, ARM Cortex-M1 |
|
|
ARMv7-M |
ARM Cortex-M3 |
|
|
ARMv7E-M |
ARM Cortex-M4 |
|
|
ARMv7-R |
ARM Cortex-R4, ARM Cortex-R5, ARM Cortex-R7 |
|
|
ARMv7-A |
ARM Cortex-A5, ARM Cortex-A7, ARM Cortex-A8, |
|
|
ARMv8-A |
ARM Cortex-A53, ARM Cortex-A57[23] |
X-Gene, Denver, Apple A7 (Cyclone) |
Programmer’s Model
Processor Modes
Register Set
Data alignment
Exception Handling
Instruction Set
Thumb
Thumb-2 Instruction Set
Jazelle
Nomenclature
ARM{x}{y}{z}{T}{D}{M}{I}{E}{J}{F}{-S}
x—family
y—memory management/protection unit
ARMx1z (e.g. ARM710T) indicates cache& full MMU
ARMx2z (e.g. ARM720T) indicates cache,MMU & Process ID support
ARMx3z (e.g. ARM1136J-S) indicates physically mapped caches and MMU
ARMx4z (e.g. ARM740T) indicates cache and MPU
ARMx5z (e.g. ARM1156T2-S) indicates cache, MPU and error correcting memory
ARMx6z (e.g. ARM966E-S) indicates write buffer but no caches
ARMx7z (e.g. ARM1176JZ-S) indicates AXI bus, & physically mapped caches and MMU
z—cache
ARMxy6 (e.g. ARM946E-S) indicates TCMs(Tightly-Coupled Memory)
T—Thumb 16-bit decoder
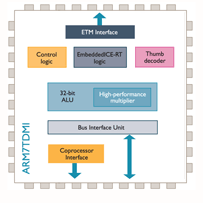
To improve compiled code-density, processors since the ARM7TDMI have featured Thumb instruction set, which have their own state. (The "T" in "TDMI" indicates the Thumb feature.) When in this state, the processor executes the Thumb instruction set, a compact 16-bit encoding for a subset of the ARM instruction set
D—JTAG debug
All modern ARM processors include hardware debugging facilities, allowing software debuggers to perform operations such as halting, stepping,and breakpointing of code starting from reset. These facilities are built using JTAG support,though some newer cores optionally support ARM's own two-wire "SWD" protocol
M—fast multiplier
I—EmbeddedICE macrocell
E—enhanced instructions
To improve the ARM architecture for digital signal processing and multimedia applications, DSP instructions were added to the set
J—Jazelle
Jazelle DBX (Direct Bytecode eXecution) is a technique that allows Java Bytecode to be executed directly in the ARM architecture as a third execution state (and instruction set) alongside the existing ARM and Thumb-mode
F—vector floating-point unit
VFP (Vector Floating Point) technology is an FPU coprocessor extension to the ARM architecture.
S—synthesizible version
the processor core is supplied as source code that can be compiled into a form easily used by EDA tools.
■ All ARM cores after the ARM7TDMI include the TDMI features even though they may not include those letters after the “ARM” label.
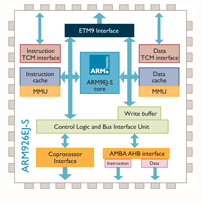
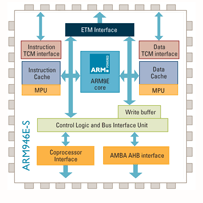
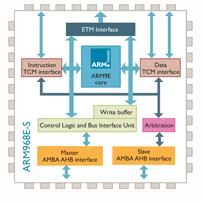
■ The processor family is a group of processor implementations that share the same hardware characteristics. For example, the A926EJ-S, A946E-S, and A968E-S all share the same family characteristics and belong to the ARM9 family.
■ SIMD Extensions for Multimedia
Single Instruction Multiple Data
■ Advanced SIMD (NEON)
The Advanced SIMD extension(aka NEON or"MPE" Media Processing Engine) is a combined 64- and 128-bit SIMD instruction set that provides standardized acceleration for media and signal processing applications
■ Security Extensions (TrustZone)
The Security Extensions is marketed as TrustZone Technology. It provides a low cost alternative to adding an additional dedicated security core to an SoC, by providing two virtual processors backed by hardware based access control.





 本文介绍了ARM架构的发展历程,包括从ARMv1到ARMv8-A的不同版本特性,并详细阐述了ARM处理器架构组成、指令集、程序员模型等核心概念。同时,文章还列举了多种ARM处理器型号及其特点。
本文介绍了ARM架构的发展历程,包括从ARMv1到ARMv8-A的不同版本特性,并详细阐述了ARM处理器架构组成、指令集、程序员模型等核心概念。同时,文章还列举了多种ARM处理器型号及其特点。
















 487
487

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








