五、Math类
Math类是java.lang包中的一个工具类,提供了许多用于执行基本数学运算的静态方法。这个类不需要实例化,所有方法都是静态的,可以直接通过类名调用。
(1)主要功能
1. 基本数学运算
abs(x)- 返回绝对值max(a, b)- 返回两个值中的较大值min(a, b)- 返回两个值中的较小值addExact(x, y)- 精确加法(溢出时抛出异常)multiplyExact(x, y)- 精确乘法(溢出时抛出异常)
int a = -5;
int b = 10;
System.out.println(Math.abs(a)); // 输出5
System.out.println(Math.max(a, b)); // 输出10
System.out.println(Math.addExact(100, 200)); // 输出300
2. 指数和对数函数
exp(x)- 返回e的x次幂log(x)- 返回自然对数(底为e)log10(x)- 返回底为10的对数pow(a, b)- 返回a的b次幂sqrt(x)- 返回平方根
System.out.println(Math.pow(2, 3)); // 输出8.0
System.out.println(Math.sqrt(25)); // 输出5.0
System.out.println(Math.sqrt(-25)); // 输出NaN
System.out.println(Math.log10(100)); // 输出2.0
3. 三角函数
sin(x)- 正弦函数cos(x)- 余弦函数tan(x)- 正切函数asin(x)- 反正弦函数acos(x)- 反余弦函数atan(x)- 反正切函数atan2(y, x)- 从直角坐标(x,y)转换到极坐标(r,θ)的角度θ
double angle = Math.PI / 4; // 45度
System.out.println(Math.sin(angle)); // 输出约0.7071
System.out.println(Math.toDegrees(Math.atan(1))); // 输出45.0
4. 舍入运算
ceil(x)- 向上取整,返回≥该参数的最小整数【返回值为double类型】floor(x)- 向下取整,返回≤该参数的最大整数round(x)- 四舍五入【返回值为long类型】rint(x)- 返回最接近的整数(双精度)
System.out.println(Math.ceil(3.2)); // 输出4.0
System.out.println(Math.floor(3.8)); // 输出3.0
System.out.println(Math.round(3.5)); // 输出4
System.out.println(Math.round(-3.5)); // 输出-3
5. 随机数
random()- 返回[0.0, 1.0)之间的随机双精度数
double rand = Math.random(); // 0.0到1.0之间的随机数
int dice = (int)(Math.random() * 6) + 1; // 模拟掷骰子(1-6)
int num = (int)(Math.random() * (b - a + 1)) + a; // (a-b)
6. 其他实用方法
-
copySign(x, y)- 返回带有第二个参数符号的第一个参数 -
nextAfter(x, y)- 返回与x相邻的浮点数(方向为y)System.out.println(Math.nextAfter(3.14, 5)); // 输出3.1400000000000006 System.out.println(Math.nextAfter(3.14, -5)); // 输出3.1399999999999997 -
scalb(x, y)- 返回x × 2^y -
hypot(x, y)- 返回sqrt(x² + y²)
(2)重要常量
Math类还定义了两个常用的数学常量:
Math.PI- π的近似值(3.141592653589793)Math.E- e的近似值(2.718281828459045)
double circleArea = Math.PI * Math.pow(radius, 2);
(3)注意事项
- 大多数方法都有针对不同基本类型(double, float, int, long)的重载版本
- 三角函数的参数以弧度为单位,不是角度
- 对于精确计算(如金融计算),应考虑使用
BigDecimal类 - 从Java 8开始,新增了一些精确计算方法(如
addExact),在溢出时会抛出异常
六、Arrays类
java.util.Arrays类是Java集合框架中的一个工具类,提供了大量静态方法来操作数组(排序、搜索、比较、填充等)。这些方法大大简化了数组操作,提高了开发效率。
(1)主要功能
1. 数组排序
-
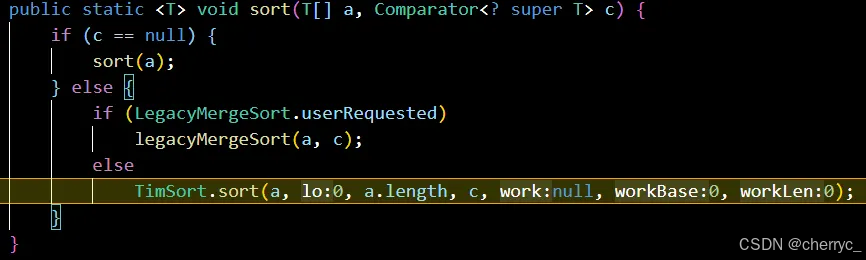
sort(array)- 对整个数组进行升序排序,会直接影响到实参

-
T[] a:要排序的对象数组(不能是基本类型数组,如int[],必须是Integer[]等包装类型)。 -
Comparator<? super T> c:自定义的比较器,用于定义排序规则。<? super T>表示比较器可以接受T或其父类型,提供更大的灵活性。 -
可以通过传入Comparator接口的匿名内部类,实现compare方法,进而实现定制排序【对于基本类型数组(如
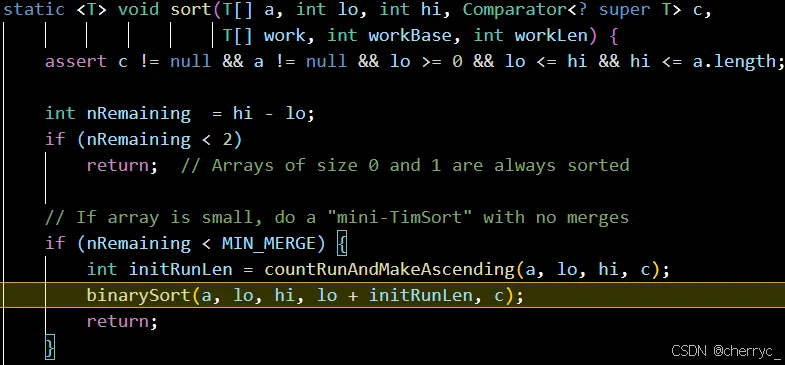
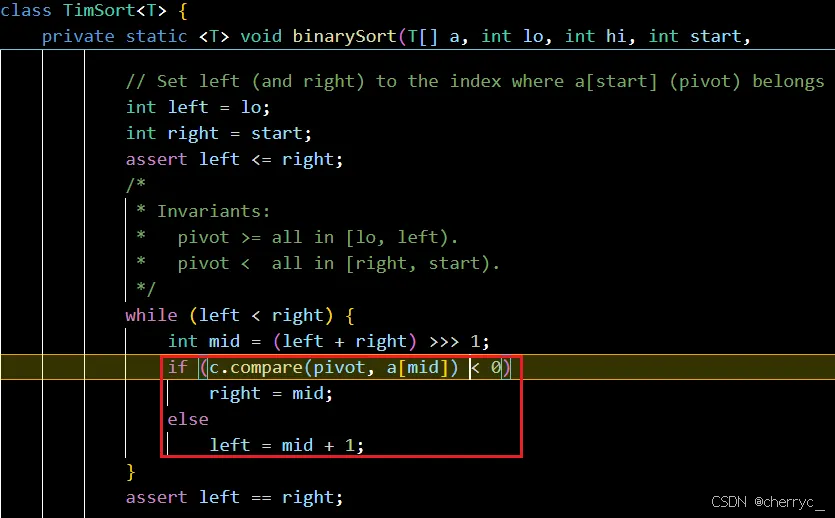
int[])不能使用自定义比较器,比较器只能用于对象数组(如Integer[])】【底层使用二叉树/二分插入排序,核心思想是对已排序部分使用二分查找快速定位插入位置,减少比较次数】
- 在排序过程中多次调用
Comparator.compare()方法【接口编程+动态绑定+匿名内部类】,根据当前要排序的值和已排序好的元素的中间值的比较关系,决定元素的相对位置
Arrays.sort()对对象数组的排序主要基于 TimSort(一种优化的归并排序算法),其特点是:- 稳定排序:相等元素的相对顺序不会改变。
- 时间复杂度:平均和最坏情况下都是 O(n log n)。
- 空间复杂度:需要 O(n) 的额外空间(归并排序的特性)。
比较规则:
- 如果
compare(a, b) < 0,则a排在b前面。 - 如果
compare(a, b) > 0,则a排在b后面。 - 如果
compare(a, b) == 0,则a和b的顺序保持不变(稳定排序)。
import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Comparator; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer[] num = {3, 1, 0, 4, -3}; // 改为 Integer[] Arrays.sort(num, new Comparator<Integer>() { // 使用 Comparator @Override public int compare(Integer a, Integer b) { return b - a; // 降序排序 } }); // Arrays.sort(num, (a, b) -> b - a); // 使用 lambda 表达式 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num)); } }// 冒泡排序 + 比较器 import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Comparator; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] num = {3, 1, 0, 4, -3}; bubble(num, new Comparator<Object>() { @Override public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) { int a = (Integer) o1; int b = (Integer) o2; return a - b; } }); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num)); } public static void bubble (int[] arr, Comparator c) { int temp; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - i - 1; j++) { if (c.compare(arr[j], arr[j + 1]) < 0) { temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j + 1]; arr[j + 1] = temp; } } } } } -
-
sort(array, fromIndex, toIndex)- 对数组指定范围排序 -
parallelSort(array)- 并行排序(Java 8+)
int[] numbers = {5, 2, 9, 1, 5};
Arrays.sort(numbers); // [1, 2, 5, 5, 9]
String[] names = {"John", "Alice", "Bob"};
Arrays.sort(names, 0, 2); // 只排序前两个元素
-
💻例题:

import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Comparator; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Book[] books = new Book[4]; books[0] = new Book("红楼梦", 100); books[1] = new Book("金瓶梅", 90); books[2] = new Book("青年文摘", 5); books[3] = new Book("JAVA", 300); // 按价格排序 Arrays.sort(books, new Comparator<Book>() { @Override public int compare(Book b1, Book b2) { double diff = b1.price - b2.price; if (diff > 0) { return 1; } else if (diff < 0) { return -1; } else { return 0; } } }); // 按书名长度排序 // Arrays.sort(books, new Comparator<Book>() { // @Override // public int compare(Book b1, Book b2) { // return b1.name.length() - b2.name.length(); // } // }); for (int i = 0; i < books.length; i++) { System.out.println(books[i].toString()); } } } class Book { String name; double price; public Book(String name, double price) { this.name = name; this.price = price; } @Override public String toString() { String output = name + ": " + price; return output; } }
2. 数组搜索
binarySearch(array, key)- 二分查找(数组必须已升序排序,不排序不会报错,但会返回错误的值),找不到就返回-(应该在的位置+1)binarySearch(array, fromIndex, toIndex, key)- 在指定范围二分查找
int[] sorted = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
int index = Arrays.binarySearch(sorted, 5); // 返回2
int index = Arrays.binarySearch(sorted, 2); // 返回-2
3. 数组比较
equals(array1, array2)- 比较两个数组内容是否相同deepEquals(array1, array2)- 深度比较(适用于多维数组)
int[] a = {1, 2, 3};
int[] b = {1, 2, 3};
boolean isEqual = Arrays.equals(a, b); // true
4. 数组填充
-
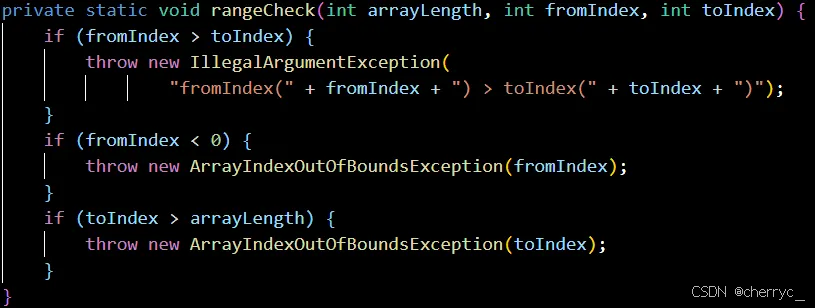
fill(array, value)- 用指定值填充整个数组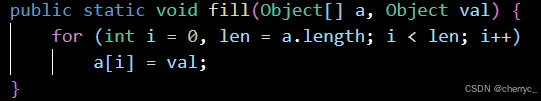
-
fill(array, fromIndex, toIndex, value)- 填充数组指定范围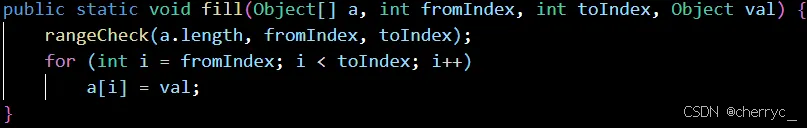
int[] arr = new int[5];
Arrays.fill(arr, 10); // [10, 10, 10, 10, 10]
Arrays.fill(arr, 1, 3, 20); // [10, 20, 20, 10, 10]
5. 数组转换
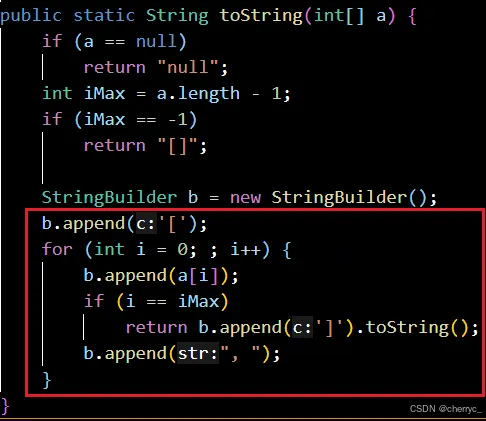
-
toString(array)- 返回数组的字符串表示
-
deepToString(array)- 返回多维数组的字符串表示 -
asList(T... a)- 将数组转换为固定大小的List【编译类型】,运行类型是java.util.Arrays$ArrayList- 接收可变参数
T,并且T必须是对象类型(如Integer、String)
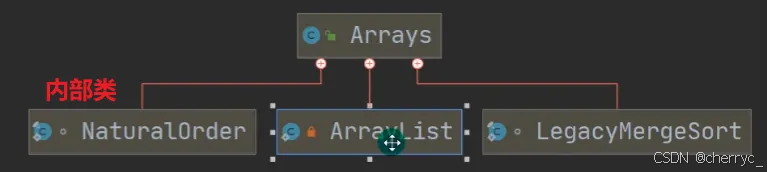
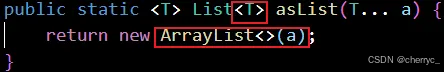
- 接收可变参数
int[] nums = {1, 2, 3};
// Integer integers = {1, 2, 3};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums)); // [1, 2, 3]
String[][] deepArray = {{"A", "B"}, {"C", "D"}};
System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(deepArray)); // [[A, B], [C, D]]
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c"); // [a, b, c]
6. 数组复制
copyOf(original, newLength)- 复制数组,可指定新长度;如果指定长度<0,抛出NegativeArraySizeException异常copyOfRange(original, from, to)- 复制数组指定范围
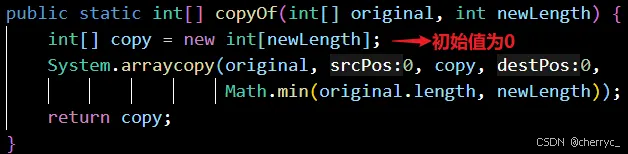
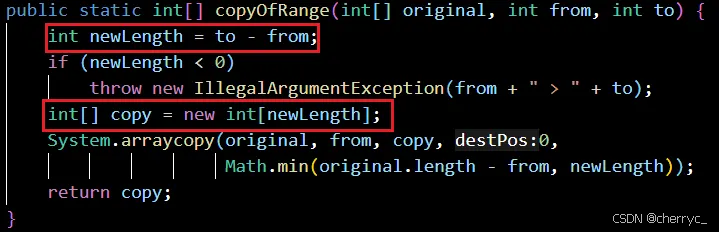
超出部分会填充该类型的默认值,int默认0,而对象类型(如Integer)默认值是null。
int[] original = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int[] copy = Arrays.copyOf(original, 3); // [1, 2, 3]
int[] copy = Arrays.copyOf(original, 6); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0]
int[] rangeCopy = Arrays.copyOfRange(original, 1, 4); // [2, 3, 4]
7. 数组流操作(Java 8+)
stream(array)- 将数组转换为流setAll(array, generator)- 使用生成函数设置所有元素parallelPrefix(array, op)- 并行累积操作
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
Arrays.stream(numbers).forEach(System.out::println);
Arrays.setAll(numbers, i -> i * 2); // [0, 2, 4, 6, 8]
8. 其他实用方法
hashCode(array)- 计算数组的哈希码deepHashCode(array)- 计算多维数组的哈希码mismatch(array1, array2)- 查找并返回第一个不匹配的索引(Java 9+)
int[] a = {1, 2, 3};
int[] b = {1, 2, 4};
int mismatch = Arrays.mismatch(a, b); // 返回2
(2)使用注意事项
asList()返回的List大小固定,不能添加或删除元素binarySearch()要求数组必须已排序,否则结果不可预测parallelSort()对于大数据集性能更好,但小数组可能不如普通排序- Java 8引入的流式操作可以与Lambda表达式结合使用
- 对于对象数组,排序和搜索可以使用自定义比较器
七、System类
System类位于java.lang包中,提供了与系统相关的属性和方法。这个类不能被实例化,所有成员都是静态的,可以直接通过类名调用。
(1)主要功能
- 标准输入、输出和错误输出流
- 访问系统属性和环境变量
- 加载文件和库的方法
- 快速复制数组的方法
- 获取当前时间的方法
- 系统退出方法
- 标准流:
public static final InputStream in- 标准输入流public static final PrintStream out- 标准输出流public static final PrintStream err- 标准错误输出流
- 系统属性:
- 可以通过
System.getProperty()方法获取各种系统属性
- 可以通过
(2)常用方法
1. 数组复制
适合底层调用
public static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length)
示例:
int[] src = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int[] dest = new int[5];
System.arraycopy(src, 0, dest, 0, src.length);
2. 获取当前时间
public static long currentTimeMillis() // 返回当前时间(毫秒),距离1970-1-1的毫秒数
public static long nanoTime() // 返回当前时间(纳秒)
示例:
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 执行一些操作
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时:" + (end - start) + "毫秒");
3. 系统属性相关
public static String getProperty(String key) // 获取指定系统属性
public static Properties getProperties() // 获取所有系统属性
public static String setProperty(String key, String value) // 设置系统属性
常用系统属性:
java.version- Java运行时环境版本java.home- Java安装目录os.name- 操作系统名称user.name- 用户账户名称user.home- 用户主目录user.dir- 用户当前工作目录
示例:
System.out.println("Java版本: " + System.getProperty("java.version"));
System.out.println("操作系统: " + System.getProperty("os.name"));
4. 环境变量
public static String getenv(String name) // 获取指定环境变量
public static Map<String,String> getenv() // 获取所有环境变量
示例:
System.out.println("PATH: " + System.getenv("PATH"));
5. 系统退出
public static void exit(int status) // 终止当前运行的Java虚拟机
示例:
if (errorOccurred) {
System.err.println("发生严重错误,程序将退出");
System.exit(1);
}
6. 垃圾回收
public static void gc() // 运行垃圾回收器
示例:
// 建议JVM进行垃圾回收
System.gc();
(3)实际应用场景
- 性能测量:使用
currentTimeMillis()或nanoTime()测量代码执行时间 - 日志记录:使用
out和err流输出不同级别的日志 - 系统信息收集:获取系统属性用于适配不同环境
- 资源清理:在程序退出前执行清理操作
- 数组操作:高效地复制数组数据
(4)注意事项
-
nanoTime()方法主要用于测量相对时间,而不是获取当前时间 -
arraycopy()方法执行的是浅拷贝- 对于基本类型是按值复制的
- 对于引用类型数组(例如Object[],String[]),只复制引用,而不会复制引用指向的对象本身。即源数组和目标数组的元素仍然指向同一个对象,修改其中一个会影响另一个。
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // String[] src = {"A", "B", "C"}; // String[] dest = new String[3]; // System.arraycopy(src, 0, dest, 0, src.length); // dest[0] = "X"; // 修改 dest[0],不会影响 src[0] // // 此时修改的是 dest[0] 的引用,而不是修改引用指向的对象 // System.out.println(src[0]); // 输出 "A" // System.out.println(dest[0]); // 输出 "X" // 但如果修改的是对象内部状态: class Person { String name; Person(String name) { this.name = name; } } Person[] src = {new Person("Alice")}; Person[] dest = new Person[1]; System.arraycopy(src, 0, dest, 0, 1); dest[0].name = "Bob"; // 修改 dest[0] 会影响 src[0],因为它们指向同一个对象 System.out.println(src[0].name); // 输出 "Bob" } } -
exit()方法会立即终止JVM -
gc()只是建议JVM进行垃圾回收,不保证立即执行
八、BigInteger和BigDecimal类【大数据处理】
BigInteger类
BigInteger是Java中用于表示任意精度整数的类,位于java.math包中。它可以表示理论上无限大的整数(仅受内存限制),解决了基本数据类型(如int、long)的范围限制问题。
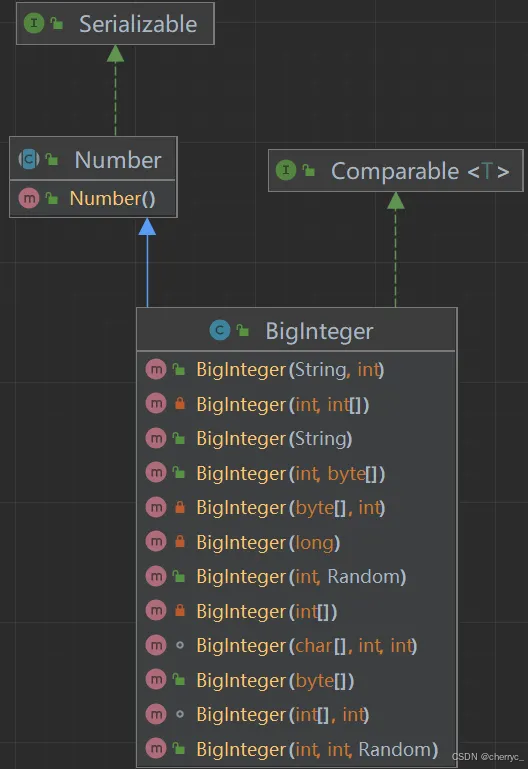
(1)主要特点
- 不可变(immutable)类,所有操作返回新对象
- 支持任意精度的整数运算
- 提供丰富的数学运算方法,不能用+-*/
- 线程安全
(2)常用构造方法
BigInteger(String val) // 通过字符串构造
BigInteger(byte[] val) // 通过字节数组构造
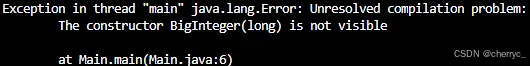
private函数,不能直接传入long/int构造
(3)常用方法
-
算术运算
BigInteger add(BigInteger val) // 加法 BigInteger subtract(BigInteger val) // 减法 BigInteger multiply(BigInteger val) // 乘法 BigInteger divide(BigInteger val) // 除法 BigInteger mod(BigInteger m) // 取模 BigInteger pow(int exponent) // 幂运算 -
比较运算
int compareTo(BigInteger val) // 比较大小 boolean equals(Object x) // 判断相等 -
位运算
BigInteger and(BigInteger val) // 与 BigInteger or(BigInteger val) // 或 BigInteger not() // 非 BigInteger shiftLeft(int n) // 左移 BigInteger shiftRight(int n) // 右移 -
转换方法
int intValue() // 转为int long longValue() // 转为long String toString() // 转为字符串 String toString(int radix) // 按指定进制转为字符串
(4)使用示例
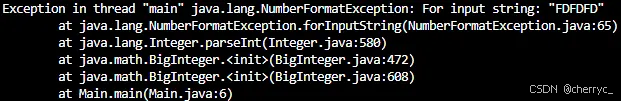
BigInteger a = new BigInteger("12345678901234567890");
BigInteger b = new BigInteger("98765432109876543210");
BigInteger sum = a.add(b); // 加法
BigInteger product = a.multiply(b); // 乘法
System.out.println("和: " + sum);
System.out.println("积: " + product);
BigDecimal类
BigDecimal是Java中用于表示任意精度十进制数的类,也位于java.math包中。它解决了浮点数计算时的精度问题(如double和float的精度损失)。
(1)主要特点
- 不可变(immutable)类
- 提供精确的十进制运算
- 支持任意精度的定点数
- 提供多种舍入模式
- 线程安全
(2)常用构造方法
BigDecimal(String val) // 推荐使用字符串构造
BigDecimal(double val) // 不推荐,可能有精度损失
BigDecimal(int val) // 通过int构造
BigDecimal(long val) // 通过long构造
(2)常用方法
-
算术运算
BigDecimal add(BigDecimal val) // 加法 BigDecimal subtract(BigDecimal val) // 减法 BigDecimal multiply(BigDecimal val) // 乘法 BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal val) // 除法,可能抛出ArithmeticException(结果为无限循环小数) BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal val, RoundingMode roundingMode) BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal val, int scale, RoundingMode roundingMode) // 带精度的除法 BigDecimal pow(int n) // 幂运算BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal val, RoundingMode roundingMode)- 自动确定小数位数:结果的小数位数(
scale)由被除数和除数的精度决定,遵循以下规则: 结果的小数位数 = max(被除数的小数位数, 除数的小数位数) - 适用于不关心具体小数位数,但需要保证结果合法(不抛出异常)的情况
divide(BigDecimal val, int scale, RoundingMode roundingMode)- 显式指定小数位数:通过参数
scale直接控制结果的小数位数
- 自动确定小数位数:结果的小数位数(
-
舍入控制
BigDecimal setScale(int newScale) // 设置小数位数 BigDecimal setScale(int newScale, RoundingMode roundingMode) // 设置小数位数和舍入模式 -
比较运算
int compareTo(BigDecimal val) // 比较大小 boolean equals(Object x) // 判断相等 -
转换方法
int intValue() // 转为int long longValue() // 转为long double doubleValue() // 转为double float floatValue() // 转为float String toString() // 转为字符串
(3)舍入模式(RoundingMode)
ROUND_UP:远离零方向舍入ROUND_DOWN:向零方向舍入ROUND_CEILING:向正无穷方向舍入ROUND_FLOOR:向负无穷方向舍入ROUND_HALF_UP:四舍五入ROUND_HALF_DOWN:五舍六入ROUND_HALF_EVEN:银行家舍入法
(4)使用示例
BigDecimal d1 = new BigDecimal("0.1");
BigDecimal d2 = new BigDecimal("0.2");
BigDecimal sum = d1.add(d2); // 精确加法
System.out.println("0.1 + 0.2 = " + sum); // 输出0.3,没有浮点数精度问题
BigDecimal d3 = new BigDecimal("10");
BigDecimal d4 = new BigDecimal("3");
// 带精度的除法
BigDecimal result = d3.divide(d4, 4, RoundingMode.ROUND_HALF_UP);
System.out.println("10 / 3 ≈ " + result); // 输出3.3333
比较与选择
| 特性 | BigInteger | BigDecimal |
|---|---|---|
| 用途 | 大整数运算 | 高精度小数运算 |
| 精度 | 任意精度整数 | 任意精度小数 |
| 适用场景 | 加密、大数计算 | 财务计算、科学计算 |
| 构造推荐 | 使用字符串构造 | 使用字符串构造 |
| 性能 | 比基本类型慢 | 比浮点数慢 |
九、日期类
Java 提供了多套日期时间处理的 API,从早期的 Date 和 Calendar 到 Java 8 引入的现代 java.time 包。
(1)传统日期时间类 (Java 8 之前)
1.1 java.util.Date JDK1.0
- 作用:表示特定的瞬间,精确到毫秒
- 问题:
- 年份从1900年开始计算
- 月份从0开始(0表示一月)
- 大部分方法已废弃(
getYear(),setMonth()等)
// 构造函数
Date date = new Date(); // 当前时间
Date date2 = new Date(long ...); // 将毫秒数转换为时间(从1900开始)
System.out.println(date); // 默认格式输出,如: Thu Jun 09 15:45:30 CST 2022
1.2 java.util.Calendar
-
作用:比Date更强大的日期操作类,是一个抽象类
-
问题:
- API设计复杂
- 可变对象(非线程安全)
- 月份依然从0开始
// Calendar calendar = new Calender(); x 构造器private
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance(); // 获取实例
calendar.set(2022, Calendar.JUNE, 9); // 2022年6月9日
int year = calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR);
// System.out.println(calendar);输出内容<保存各字段信息>
java.util.GregorianCalendar[time=1758811261899,areFieldsSet=true,areAllFieldsSet=true,lenient=true,zone=sun.util.calendar.ZoneInfo[id="Asia/Shanghai",offset=28800000,dstSavings=0,useDaylight=false,transitions=31,lastRule=null],firstDayOfWeek=1,minimalDaysInFirstWeek=1,ERA=1,YEAR=2025,MONTH=8,WEEK_OF_YEAR=39,WEEK_OF_MONTH=4,DAY_OF_MONTH=25,DAY_OF_YEAR=268,DAY_OF_WEEK=5,DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_MONTH=4,AM_PM=1,HOUR=10,HOUR_OF_DAY=22,MINUTE=41,SECOND=1,MILLISECOND=899,ZONE_OFFSET=28800000,DST_OFFSET=0]
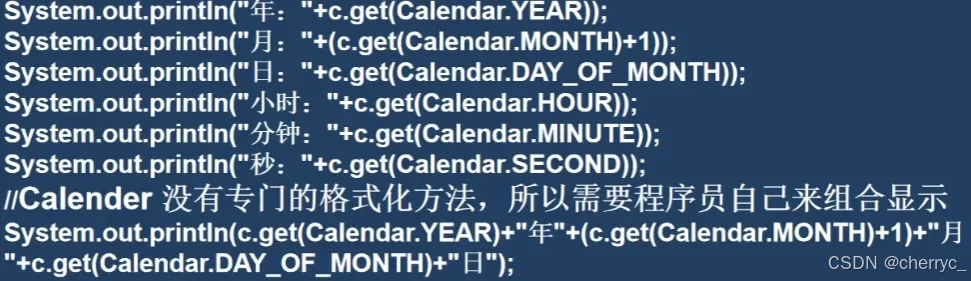
1.3 java.text.SimpleDateFormat
- 作用:日期格式化和解析【
ParseException】(日期→文本,文本→日期)
- 问题:
- 非线程安全
- 格式化模式易混淆
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
String formatted = sdf.format(new Date()); // 格式化
Date parsed = sdf.parse("2022-06-09"); // 解析
(2)Java 8 新日期时间 API (java.time)
Java 8 引入的全新API,解决了旧API的所有问题。
2.1 核心类
LocalDate
-
只包含日期(年-月-日)
-
可以进行日期加减:
-
不可变且线程安全
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now(); // 2025-09-25
LocalDate specificDate = LocalDate.of(2022, Month.JUNE, 9);
int year = specificDate.getYear(); // 2022
Month month = specificDate.getMonth(); // JUNE
int m = specificDate.getMonthValue(); // 6
int day = specificDate.getDayOfMonth(); // 9
LocalTime
- 只包含时间(时:分:秒.纳秒)
- 不可变且线程安全
LocalTime now = LocalTime.now();
LocalTime specificTime = LocalTime.of(15, 45, 30);
int hour = specificTime.getHour(); // 1
LocalDateTime
- 包含日期和时间
- 不可变且线程安全
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now(); // 2025-09-25T22:52:23.347
LocalDateTime specificDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2022, Month.JUNE, 9, 15, 45);
ZonedDateTime
- 带时区的日期时间
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));
Instant
- 时间戳(从1970-01-01T00:00:00Z开始的秒/纳秒数)
- 适合机器时间计算
- 类似于Date,提供了一系列和Date类转换的方式
Instant instant = Instant.now();
long epochSecond = instant.getEpochSecond();
2.2 工具类
Period
- 日期之间的间隔(年/月/日)
LocalDate start = LocalDate.of(2020, 1, 1);
LocalDate end = LocalDate.of(2022, 6, 9);
Period period = Period.between(start, end);
int years = period.getYears(); // 2
int months = period.getMonths(); // 5
Duration
- 时间之间的间隔(小时/分/秒/纳秒)
LocalTime startTime = LocalTime.of(10, 0);
LocalTime endTime = LocalTime.of(15, 30);
Duration duration = Duration.between(startTime, endTime);
long hours = duration.toHours(); // 5
DateTimeFormatter
- 线程安全的日期格式化
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String formatted = LocalDateTime.now().format(formatter);
LocalDateTime parsed = LocalDateTime.parse("2022-06-09 15:45:30", formatter);
-
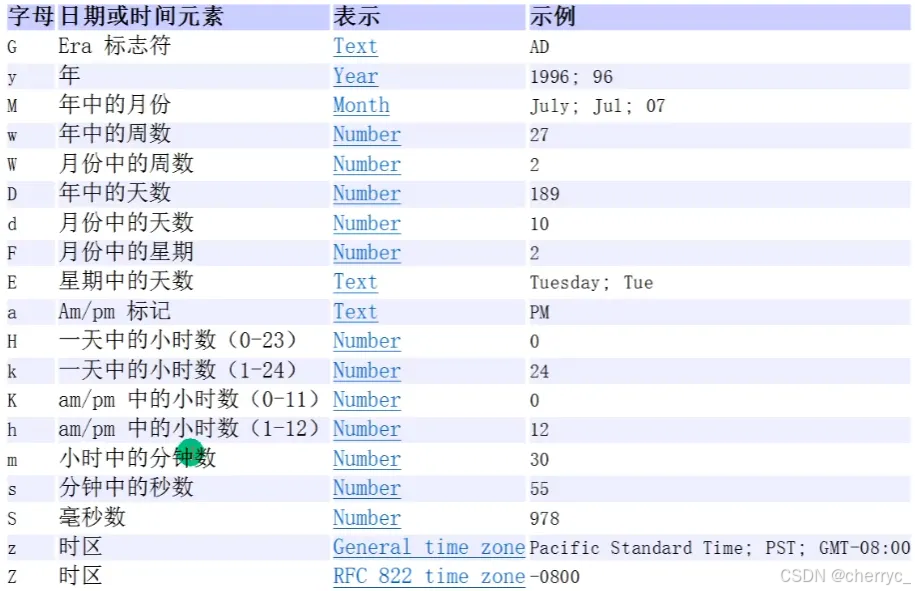
常用模式参数:
1. 年相关
字母 含义 示例 输出示例 y 年份 yyyy 2023 u 年份(ISO) uuuu 2023 Y 周年份 YYYY 2023 2. 月相关
字母 含义 示例 输出示例 M 月份 MM 07 (7月) MMM Jul (英文缩写) MMMM July (英文全称) L 月份(独立形式) LL 07 3. 日相关
字母 含义 示例 输出示例 d 月中的日 dd 09 D 年中的日 DDD 190 (第190天) F 月中的周 F 2 (第2周) 4. 星期相关
字母 含义 示例 输出示例 E 星期 EEE Mon EEEE Monday e 星期(本地化) e 1 (周一) 5. 时间相关
字母 含义 示例 输出示例 H 小时(0-23) HH 15 h 小时(1-12) hh 03 k 小时(1-24) kk 15 K 小时(0-11) KK 03 m 分钟 mm 45 s 秒 ss 30 S 毫秒 SSS 789 n 纳秒 nnnnnnnnn 123456789 6. 上午/下午
字母 含义 示例 输出示例 a 上午/下午标记 a PM 7. 时区相关
字母 含义 示例 输出示例 z 时区名称 zzzz China Standard Time Z 时区偏移量 Z +0800 X 时区偏移量(X=Z) XXX +08:00 O 本地化时区 O GMT+8 特殊字符处理:
-
转义字符:使用单引号
'包裹特殊字DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("'Today is' yyyy-MM-dd"); // 输出:Today is 2023-07-09 -
常用分隔符:,
/,:, `` (空格) 等可以直接使用DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss"); // 输出:2023/07/09 15:45:30
-
(3)新旧API转换
// Date -> Instant
Instant instant = new Date().toInstant();
// Instant -> Date
Date date = Date.from(Instant.now());
// Calendar -> ZonedDateTime
ZonedDateTime zdt = Calendar.getInstance().toInstant().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault());
(4)常见问题
- 为什么月份从1开始?
java.time中月份从1开始(1=January),更符合人类习惯
- 如何处理闰秒?
Instant不包含闰秒信息- 需要特殊处理可使用
java.time.chrono包
- 性能考虑:
java.time类都是不可变且线程安全的- 创建开销略高于旧API,但避免了同步和错误风险





















 950
950

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








