面试题07.重建二叉树
题目链接
前序遍历找到当前子树根节点
中序遍历将左右子树继续下分
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if(preorder.length==0||preorder==null){
return null;
}
Map<Integer,Integer> indexMap=new HashMap<Integer,Integer>();
int length=preorder.length;
for(int i=0;i<length;i++){
indexMap.put(inorder[i],i);
}
return buildTree(preorder,0,length-1,inorder,0,length-1,indexMap);
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder,int preStart,int preEnd,int[] inorder,int orderStart,int orderEnd,Map<Integer,Integer> indexMap){
if(preStart>preEnd){
return null;
}
//先通过前序遍历找到当前子树根节点
int rootVal=preorder[preStart];
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(rootVal);
if(preStart==preEnd){
return root;
}else{
//中序遍历继续划分子树
int rootIndex=indexMap.get(rootVal);
int leftNode=rootIndex-orderStart,rightNode=orderEnd-rootIndex;
TreeNode left=buildTree(preorder,preStart+1,preStart+leftNode,inorder,orderStart,rootIndex-1,indexMap);
TreeNode right=buildTree(preorder,preStart+leftNode+1,preEnd,inorder,rootIndex+1,orderEnd,indexMap);
root.left=left;
root.right=right;
return root;
}
}
}
面试题26. 树的子结构
题目链接
给定A树和B树,判断B树是否是A树子树。
- B树是A树子树:
B树=A树,A树.左子树=B树,A树.右子树=B树 - 判断两棵树相等:
树节点值相等;两棵树左右子树相等。
对这两个情况以此判断。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSubStructure(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {
if(A==null || B==null){
return false;
}
return isSameTree(A,B) || isSubStructure(A.left,B) || isSubStructure(A.right,B);
}
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode A,TreeNode B){
if(B==null) return true;
if(A==null) return false;
return A.val==B.val && isSameTree(A.left,B.left) &&isSameTree(A.right,B.right);
}
}
面试题27. 二叉树的镜像
题目链接
解法一:递归
先将当前树节点的左右子树交换,再继续向下递归交换左右子树各自的子树。直到处理完,root==null时返回。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return null;
TreeNode tmp=root.left;
root.left=root.right;
root.right=tmp;
mirrorTree(root.left);
mirrorTree(root.right);
return root;
}
}
解法二:迭代(栈)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return null;
Stack<TreeNode> st=new Stack<TreeNode>();
st.push(root);
while(!st.empty()){
TreeNode node=st.pop();
TreeNode tmp=node.left;
node.left=node.right;
node.right=tmp;
if(node.left!=null) st.push(node.left);
if(node.right!=null) st.push(node.right);
}
return root;
}
}
面试题28. 对称的二叉树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return true;
}
return isSame(root.left,root.right);
}
private boolean isSame(TreeNode left,TreeNode right){
if(left==null && right==null){
return true;
}
if(left==null || right==null){
return false;
}
return (left.val==right.val) && isSame(left.left,right.right) && isSame(left.right,right.left);
}
}
从上到下打印二叉树
面试题32 - I.
从上到下打印出二叉树的每个节点,同一层的节点按照从左到右的顺序打印。题目
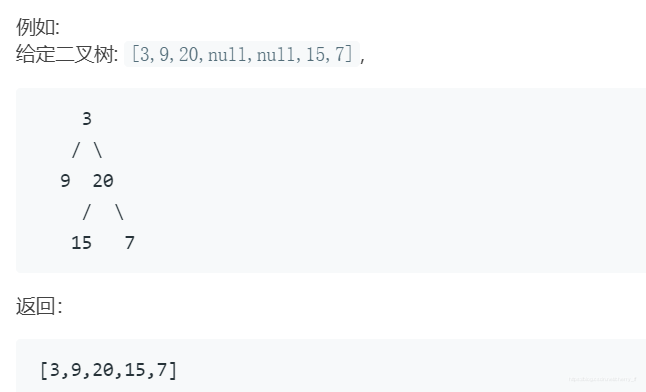
要依次得到左右节点,使用LinkedList,实现deque功能。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[] levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res=new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(root==null){
return new int[res.size()];
}
LinkedList<TreeNode> st=new LinkedList<>();
st.add(root);
while(st.size()>0){
TreeNode tmp=st.removeFirst();
res.add(tmp.val);
if(tmp.left!=null){
st.add(tmp.left);
}
if(tmp.right!=null){
st.add(tmp.right);
}
}
int[] ans=new int[res.size()];
for(int i=0;i<res.size();i++){
ans[i]=res.get(i);
}
return ans;
}
}
面试题32 - II
从上到下按层打印二叉树,同一层的节点按从左到右的顺序打印,每一层打印到一行。题目

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null){
return res;
}
LinkedList<TreeNode> list=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
list.add(root);
while(list.size()>0){
List<Integer> tmp=new ArrayList<Integer>();
int length=list.size();
for(int i=0;i<length;i++){
TreeNode now=list.removeFirst();
tmp.add(now.val);
if(now.left!=null) list.add(now.left);
if(now.right!=null) list.add(now.right);
}
res.add(tmp);
}
return res;
}
}
面试题32 - III
请实现一个函数按照之字形顺序打印二叉树,即第一行按照从左到右的顺序打印,第二层按照从右到左的顺序打印,第三行再按照从左到右的顺序打印,其他行以此类推。
添加链接描述

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null){
return res;
}
LinkedList<TreeNode> list=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
list.add(root);
int index=0;
while(list.size()>0){
List<Integer> tmp=new ArrayList<Integer>();
int length=list.size();
for(int i=0;i<length;i++){
TreeNode now=list.removeFirst();
tmp.add(now.val);
if(now.left!=null) list.add(now.left);
if(now.right!=null) list.add(now.right);
}
if((++index)%2==0){
Collections.reverse(tmp);
}
res.add(tmp);
}
return res;
}
}
面试题33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
题目链接
本题关键:利用二叉搜索树的左子树<根节点<右子树的特征
方法一:递归。
按照二叉搜索树的特点,在子树中迭代判断。
class Solution {
public boolean verifyPostorder(int[] postorder) {
int length=postorder.length;
return check(postorder,0,length-1);
}
private boolean check(int[]postorder,int l,int r){
if(l>=r){
return true;
}
int root=postorder[r];
int p=0;
while(postorder[p]<root) p++;
int m=p;
while(postorder[p]>root) p++;
return p==r && check(postorder,l,m-1) && check(postorder,m,r-1);
}
}
比较起来递归的方法要快
方法二:栈
class Solution {
public boolean verifyPostorder(int[] postorder) {
int length=postorder.length;
Stack<Integer> st=new Stack<>();
int root=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int i=length-1;i>=0;i--){
if(root<postorder[i]) return false;
while(!st.empty() && postorder[i]<st.peek()){
root=st.pop();
}
st.add(postorder[i]);
}
return true;
}
}
面试题34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> tmp=new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
getSum(root,sum);
return res;
}
void getSum(TreeNode root,int sum){
if(root==null){
return;
}
tmp.add(root.val);
sum-=root.val;
if(sum==0 && root.left==null && root.right==null){
res.add(new ArrayList(tmp)); // 这里注意不能直接res.add(tmp);
}
getSum(root.left,sum);
getSum(root.right,sum);
tmp.remove(tmp.size()-1);
}
}
面试题36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
题目链接
题目看起来比较复杂,实际是将二叉搜索树转换为一个 “排序的循环双向链表” ,其中包含三个要素:
-
排序链表: 节点从小到大排序 --> 使用中序遍历, “从小到大”访问树的节点;
-
双向链表
-
循环链表
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val,Node _left,Node _right) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
Node pre,head;
public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) {
if(root==null){
return null;
}
dfs(root);
pre.right=head;head.left=pre;
return head;
}
void dfs(Node cur){
if(cur==null){
return;
}
dfs(cur.left);
if(pre!=null) pre.right=cur;
else head=cur;
cur.left=pre;
pre=cur;
dfs(cur.right);
}
}
面试题54. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int ans=0,count=0;
public int kthLargest(TreeNode root, int k) {
getKthLargest(root,k);
return ans;
}
private void getKthLargest(TreeNode root,int k){
if(root.right!=null) getKthLargest(root.right,k);
count++;
if(count==k){
ans=root.val;
return;
}
if(root.left!=null) getKthLargest(root.left,k);
}
}
面试题55 - I. 二叉树的深度
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int maxDepth=0;
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
getDepth(root,1);
return maxDepth;
}
void getDepth(TreeNode root,int h){
if(root==null){
return;
}
if(root.left==null && root.right==null){
if(h>maxDepth) maxDepth=h;
}
getDepth(root.left,h+1);
getDepth(root.right,h+1);
}
}
面试题55 - II. 平衡二叉树
题目
输入一棵二叉树的根节点,判断该树是不是平衡二叉树。如果某二叉树中任意节点的左右子树的深度相差不超过1,那么它就是一棵平衡二叉树。
做的时候卡壳是因为忽然想不到如果递归求树的高度,那么怎么返回布尔值判断是否差距为1,其实直接返回高度/ -1 就可以了啊
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return getHeight(root)==-1?false:true;
}
private int getHeight(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
int right=getHeight(root.right)+1;
if(right==-1) return -1;
int left=getHeight(root.left)+1;
if(left==-1) return -1;
if(Math.abs(right-left)<=1){
return Math.max(left,right);
}else{
return -1;
}
}
}
最近公共祖先
面试题68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
题目
二叉树的解法也可以解这里的二叉搜索树。这里给出针对二叉搜索树的解法。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
//这里关键是注意二叉搜索树的特性
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
int pVal=p.val;
int qVal=q.val;
TreeNode node=root;
while(node!=null){
int parentVal=node.val;
if(pVal<parentVal&&qVal<parentVal){
node=node.left;
}
else if(pVal>parentVal&&qVal>parentVal){
node=node.right;
}
else{
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
}
面试题68 - II. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root==null){
return null;
}
if(root==p||root==q){
return root;
}
TreeNode left=lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode right=lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(left!=null && right!=null){
return root;
}
if(left!=null){
return left;
}
if(right!=null){
return right;
}
return null;
}
}







 本文深入解析了二叉树及其衍生结构的多种经典面试题,包括重建二叉树、判断子结构、镜像翻转、对称检测、层次遍历、后序遍历验证、路径和查找、转换为双向链表、寻找第k大节点、深度计算、平衡判断、最近公共祖先等,提供了详细的算法思路与代码实现。
本文深入解析了二叉树及其衍生结构的多种经典面试题,包括重建二叉树、判断子结构、镜像翻转、对称检测、层次遍历、后序遍历验证、路径和查找、转换为双向链表、寻找第k大节点、深度计算、平衡判断、最近公共祖先等,提供了详细的算法思路与代码实现。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








