最近公司要搞一个对外的http服务,具体业务就不说了。使用了Netty进行了这个服务的开发。
以前自己啃过《Netty权威指南》这本书,说实话,作为开发者,很多东西不实践,只看理论,毕竟印象不深,这次Netty服务的开发,在实践的基础上,对Netty的服务原理有了较深的理解。
下面就把自己这段时间对Netty的理解做一下记录。
一、Netty服务端开发代码
先上代码,Netty服务的开发基本套路如下:
EventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup(bossThreadNum);
EventLoopGroup work = new NioEventLoopGroup(workThreadNum);
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(boss, work)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerCodec());//注:该HttpServerCodec默认允许访问的最大url长度为4k,超过4k,会返回404错误
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(65536));
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpRequestHandler());
}
});
//绑定并且监听链接请求
ChannelFuture f = bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
logger.info("http server started.");
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
work.shutdownGracefully();
}1、生成两个NioEventLoopGroup对象boss和work,boss用来监听连接,work用来处理io读写和业务逻辑,具体见下面的原理分析
2、生成服务启动类ServerBootstrap对象bootstrap,将boss,work以及NioServerSocketChannal监听通道注册到bootstrap中去。
3、为每一个连接的客户端SocketChannel添加io事件处理类ChannelHanderAdapter类对象。如上图代码中的HttpServerCodec,HttpObjectAggregator,HttpRequestHandler. 其中HttpRequestHandler是我自己定义的Handler,具体的业务逻辑在该类中实现,如下:
public class HttpRequestHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<FullHttpRequest> {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HttpRequestHandler.class);
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, FullHttpRequest fullHttpRequest) throws Exception {
if ("/favicon.ico".equals(fullHttpRequest.uri())) {
return ;
}
// //TODO 处理量统计 上线删除
// Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
// if(StatisticUtils.thread_count.containsKey(thread)){
// StatisticUtils.thread_count.put(thread,StatisticUtils.thread_count.get(thread) + 1);
// }else{
// StatisticUtils.thread_count.put(thread,1L);
// }
HttpMethod method = fullHttpRequest.method();
logger.debug("Request Log : " + fullHttpRequest.toString());
WorkRequest request = null;
WorkResponse response = null;
//提取并解析协议
if (method == HttpMethod.GET) {
// 获取Get参数
URI uri = URI.create(fullHttpRequest.uri());
String query = uri.getQuery();
if(query == null){
response = new WorkResponse();
response.code = 500;
response.message = "warn: params is null";
response.isCheck = 0;
//返回消息
channelHandlerContext.writeAndFlush(response(response)).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
return ;
}
logger.debug("url query : " + query);
request = queryToRequest(query);
}
......//其他逻辑省略
}
}因为继承了SimpleChannelInboundHandler类,只需要重写channelRead0方法即可
4、绑定监听端口,然后启动:bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
以上就是Netty服务开发的套路流程。
二、Netty工作原理
关于Netty工作原理,先盗一张图:
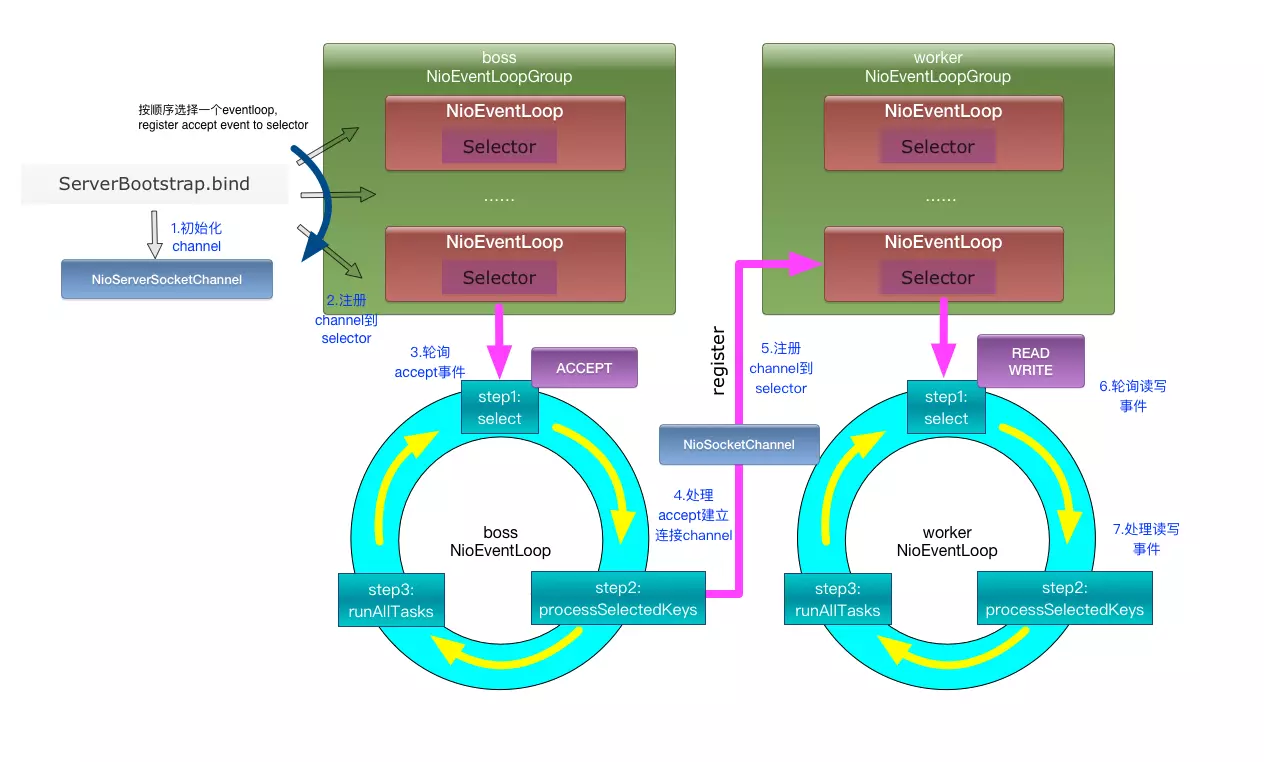
1、对于boss = new NioEventLoopGroup(bossThreadNum)这段代码,虽然我们设置了多个线程,但是当我们服务端只绑定一个端口的时候,实际上boss轮询组只会将NioServerSocketChannel注册到其中一个NioEventLoop轮询器的Selector上,(上图中的1,2步骤)。
2、通俗来讲,boss中这个Selector的作用就是监听外部连接。一旦有外部连接过来,与其建立通信,并生成NioSocketChannel,将该NioSocketChannel注册到work的其中一个NioEventLoop上(上图3,4,5步骤)。
3、work中的Selector的作用。简单来讲,就是进行了如下流程的数据处理:从NioSocketChannel中读取数据 ---> 把请求的数据调用Handler进行业务逻辑的处理 ----> 将处理之后得到的结果写出到NioSocketChannel中发送出去(上图6,7步骤)。
以上是我自己理解描述的Netty服务端工作原理流程,如果有不对的地方,还请大佬们指出。
其实这个原理和thrift服务端TThreadedSelectorServer模式的工作原理很类似(Thrift服务端工作模式及原理)。这里的boss相当于thrift的Acceptor,而work把thrift的Selector和业务处理线程合并了。
其实Netty也提供了将i/o读写和业务处理分离的代码处理逻辑,见下节
三、Netty的i/o读写线程和业务处理线程分离
为什么要将i/o读写和业务处理线程进行分离呢?对于业务处理比较简单的服务,这两者可以合并,不会影响服务处理性能。但是对于业务处理比较复杂耗时的服务,比如频繁的数据库访问等操作,会阻塞I/O,导致响应消息无法及时发送。
Netty的io和业务分离代码很简单,如下:
EventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup(bossThreadNum);
EventLoopGroup work = new NioEventLoopGroup(workThreadNum);//work转化为网络读写轮询器
EventExecutorGroup businessGroup = new DefaultEventExecutorGroup(executeThreadNum);//业务处理流程被分离出来
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(boss, work)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerCodec());//注:该HttpServerCodec默认允许访问的最大url长度为4k,超过4k,会返回404错误
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(65536));
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(businessGroup, new HttpRequestHandler());
}
});
//绑定并且监听链接请求
ChannelFuture f = bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
logger.info("http server started.");
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
work.shutdownGracefully();
}增加一个EventExecutorGroup对象,在对SocketChannel添加Handler的时候,注册进去即可。如此便实现了i/o和业务处理的分离。
四、ThreadLocal线程安全保证机制
在开发服务,处理业务逻辑的时候,要时刻注意保证线程的安全性,由此,在这次服务开发过程中,大量使用和实践了ThreadLocal对象,对其理解和使用方式更深一步,具体原理,在此不再赘述。





 本文详细介绍了使用Netty开发HTTP服务的过程,包括代码示例和服务端工作原理。探讨了如何通过Netty处理HTTP请求,实现IO读写与业务处理的线程分离,以及ThreadLocal在保证线程安全中的应用。
本文详细介绍了使用Netty开发HTTP服务的过程,包括代码示例和服务端工作原理。探讨了如何通过Netty处理HTTP请求,实现IO读写与业务处理的线程分离,以及ThreadLocal在保证线程安全中的应用。
















 1199
1199

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








