在软件开发中经常要对文件进行读写,平时对一个文件进行读取都是用read,write,但是这两个函数只能一次次操作,并不对并行操作,效率有点低,比如下载一个文件使用多线程同时写一个文件,这个时候得用锁进行控制,虽然这样效率提高了,但也只能一次操作一次写,那么有没有多个操作同时写一个文件呢,这样效率就是大大提高了,pread和pwrite就可以多个线程同时操作一个文件从而提高读写效率。本篇记录Linux环境编程文件读写操作之pread,pwrite的基本用法。
首先查看帮助文档
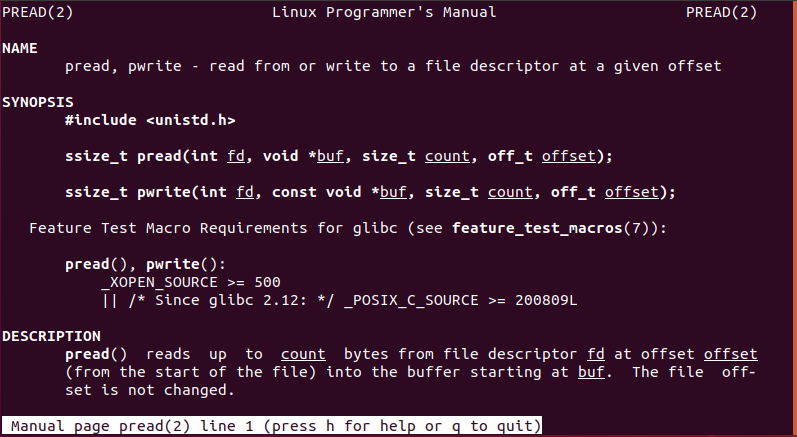
1.pread函数从指 定文件的指定位置读取指定长度的数据。
| 函数名 | pread |
| 相关函数 | pwrite |
| 表头文件 | #include <unistd.h> |
| 函数定义 | ssize_t pread(int fd, void *buf, size_t count, off_t offset); |
| 函数说明 |
参数说明: fd:文件描述符 buf:用户空间的缓冲区 count:表示要写入的字节数 offset:偏移量 |
| 返回值 | 成功返回实际读取的字节数,失败返回-1,错误码设置在errno里 |
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <error.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
const char *filename = "/home/scott/trunk/command2/pread_test.txt";
int fd = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
if(fd == -1) {
perror("Error opening file");
return 1;
}
// 定义缓冲区大小和偏移量
char buffer[256];
off_t offset = 8;// 偏移量设置为第8字节位置
size_t count = 28;// 读取28字节的数据
// 使用pread函数从指定偏移量处读取数据
ssize_t bytesRead = pread(fd, buffer, count, offset);
if(bytesRead == -1) {
perror("Error reading from file with pread");
close(fd);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 输出读取的内容
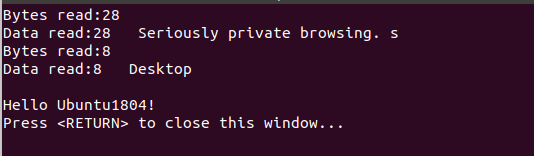
printf("Bytes read:%zd\n", bytesRead);
printf("Data read:%d %s\n", (int)bytesRead, buffer);
offset = 0;// 偏移量设置为第0字节位置
count = 8;// 读取2字节的数据
// 使用pread函数从指定偏移量处读取数据
bytesRead = pread(fd, buffer, count, offset);
if(bytesRead == -1) {
perror("Error reading from file with pread");
close(fd);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
buffer[8] = '\0';
// 输出读取的内容
printf("Bytes read:%zd\n", bytesRead);
printf("Data read:%d %s\n", (int)bytesRead, buffer);
close(fd);
cout << "Hello Ubuntu1804!" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
2.pwrite函数从指定文件的指定位置写入指定长度的数据。
| 函数名 | pwrite |
| 相关函数 | pread |
| 表头文件 | #include <unistd.h> |
| 函数定义 | ssize_t pwrite(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count, off_t offset); |
| 函数说明 |
参数说明: fd:文件描述符 buf:用户空间的缓冲区 count:表示要读取的字节数 offset:偏移量 |
| 返回值 | 成功返回实际写入的字节数,失败返回-1,错误码设置在errno里 |
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <error.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
const char *filename = "/home/scott/trunk/command2/pwrite_test.txt";
int fd = open(filename, O_RDWR|O_CREAT, 0644);
if(fd == -1) {
perror("Error opening file");
return 1;
}
// 定义缓冲区大小和偏移量
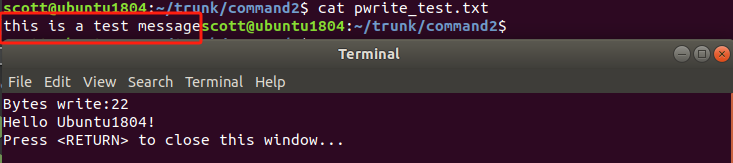
char buffer[256] = "this is a test message pwrite function";
off_t offset = 0;// 偏移量设置为第8字节位置
size_t count = 22;// 写入22字节的数据
// 使用pwrited函数从指定偏移量处 写入数据
ssize_t nwrite = pwrite(fd, buffer, count, offset);
if(nwrite == -1) {
perror("Error writeing from file with write");
close(fd);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
printf("Bytes write:%zd\n", nwrite);
close(fd);
cout << "Hello Ubuntu1804!" << endl;
return 0;
}运行结果
参考:





 本文介绍如何使用CSS样式表来美化Qt应用程序中的菜单项,包括设置背景色、字体颜色、边框等属性,提供了详细的代码示例。
本文介绍如何使用CSS样式表来美化Qt应用程序中的菜单项,包括设置背景色、字体颜色、边框等属性,提供了详细的代码示例。
















 2765
2765

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








