在Linux环境下编程,有时我们需要设置一些环境变量,方便程序中的使用,例如,程序路径太长,使用时可以设置环境变量,相当于给长的路径设置一个别名,本篇记录使用setenv, unsetenv,putenv函数的基本使用。
开发环境 Ubuntu1804
1.setenv函数设置环境变量
| 函数名 | setenv |
| 相关函数 | unsetenv |
| 表头文件 | #include<stdlib.h> |
| 函数定义 | int setenv(const char *name, const char *value, int overwrite); |
| 函数说明 | 设置环境变量,参数name是变量名,value变量名的值,overwrite表示变量名存在是否覆盖,返回值为int |
| 返回值 | 设置成功返回0,非0设置失败 |
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char* path{ nullptr };
path = getenv("CPP_DEMO_DIR");
if (path != nullptr)
{
printf("CPP_DEMO_DIR = %s\n", path);
}
else
{
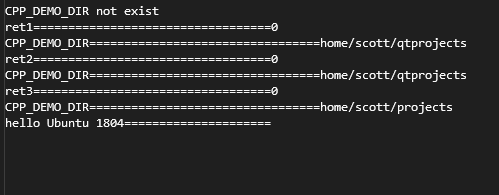
printf("CPP_DEMO_DIR not exist\n");
}
// /home/scott/qtprojects /home/scott/projects
//int setenv(const char *name, const char *value, int overwrite);
//name:环境变量名, value:设置环境变量的值, overwrite表示是否覆盖已存在的环境变量的值,0不覆盖, 1:覆盖
int ret1 = setenv("CPP_DEMO_DIR", "home/scott/qtprojects", 0);
cout << "ret1==================================" << ret1 << endl;
path = getenv("CPP_DEMO_DIR");
cout << "CPP_DEMO_DIR=================================" << path << endl;
int ret2 = setenv("CPP_DEMO_DIR", "home/scott/projects", 0);//存在不会覆盖
cout << "ret2==================================" << ret2 << endl;
path = getenv("CPP_DEMO_DIR");
cout << "CPP_DEMO_DIR=================================" << path << endl;
int ret3 = setenv("CPP_DEMO_DIR", "home/scott/projects", 1);//存在就覆盖
cout << "ret3==================================" << ret3 << endl;
path = getenv("CPP_DEMO_DIR");
cout << "CPP_DEMO_DIR=================================" << path << endl;
cout << "hello Ubuntu 1804=====================" << endl;
return 0;
}运行结果:
2.unsetenv函数取消环境变量
| 函数名 | unsetenv |
| 相关函数 | setenv |
| 表头文件 | #include<stdlib.h> |
| 函数定义 | int unsetenv(const char *name); |
| 函数说明 | 取消环境变量,参数name是变量名,返回值为int |
| 返回值 | 取消成功返回0,非0取消失败 |
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char* path{ nullptr };
path = getenv("PWD");
if (path != nullptr)
{
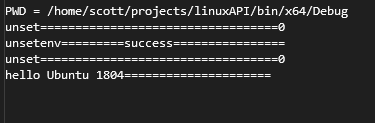
printf("PWD = %s\n", path);
//int unsetenv(const char *name);
int unset = unsetenv("PWD");//取消设置环境变量的值
cout << "unset==================================" << unset << endl;
path = getenv("PWD");
if (path == nullptr)
{
cout << "unsetenv=========success================" << endl;
}
unset = unsetenv("AAA");//取消不存在的环境变量
cout << "unset==================================" << unset << endl;
}
else
{
printf("PWD not exist\n");
}
cout << "hello Ubuntu 1804=====================" << endl;
return 0;
}运行结果:
3.puttenv函数修改或添加环境变量
| 函数名 | puttenv |
| 相关函数 | setenv |
| 表头文件 | #include<stdlib.h> |
| 函数定义 | int putenv(char *string); |
| 函数说明 | 设置环境变量,参数name是变量名,value变量名的值,overwrite表示变量名存在是否覆盖,返回值为int |
| 返回值 | 设置成功返回0,非0设置失败 |
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char* path{ nullptr };
path = getenv("PWD");
if (path != nullptr)
{
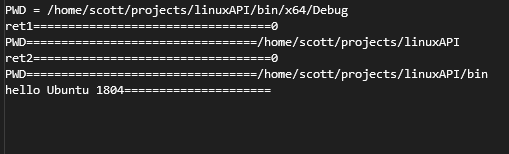
printf("PWD = %s\n", path);
}
else
{
printf("PWD exist\n");
}
// PWD = /home/scott/projects/linuxAPI/bin/x64/Debug
//int putenv(char *string);
//设置环境变量,格式 PWD=/home/scott/projects/linuxAPI
int ret1 = putenv("PWD=/home/scott/projects/linuxAPI");
cout << "ret1==================================" << ret1 << endl;
path = getenv("PWD");
cout << "PWD=================================" << path << endl;
int ret2 = putenv("PWD=/home/scott/projects/linuxAPI/bin");;//存在会覆盖
cout << "ret2==================================" << ret2 << endl;
path = getenv("PWD");
cout << "PWD=================================" << path << endl;
cout << "hello Ubuntu 1804=====================" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:





 本文介绍了用于用户账号管理的一系列标准库函数,包括获取、设置用户和组信息的函数,如getpwent、getpwuid、getgrgid等,以及与用户权限相关的函数如setuid、setgid等。
本文介绍了用于用户账号管理的一系列标准库函数,包括获取、设置用户和组信息的函数,如getpwent、getpwuid、getgrgid等,以及与用户权限相关的函数如setuid、setgid等。
















 2427
2427

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








