最近,打算写长篇博客介绍ARM 的体系结构,也算是学习笔记,两年工作的一些积累的总结吧:
Topic 1:大小端
大小端(big- endian, little- endian)影响到数据在存储器中的存放顺序。
大端模式(big- endian), 高字节放在放低地址,低字节放在高地址;
小端模式(little- endian), 高字节放在高地址,低字节放在低地址。
助记: 以低字节存放的位置来看:
大低高,小低低
真正理解这个大小端概念需要明白,存储器是按照字节为存储单元编号的,小端模式可以理解为,从数据的小端(即低位)开始存放数据,因为存储单元的编号是从低到高的,因此就出现了,低字节放在低地址,高字节放在高地址。而且, ARM,x86,一般都是小端模式(LSB)。PowerPC/MIPS 一般为大端模式(MSB)。
$file zip
zip: ELF 32-bit LSB executable,ARM, version 1 (SYSV), for GNU/Linux 2.6.34, dynamically linked (uses shared libs), for GNU/Linux 2.6.34, stripped
$file /bin/ls
/bin/ls: ELF 32-bit LSB executable, Intel 80386, version 1 (SYSV), for GNU/Linux 2.6.9, dynamically linked (uses shared libs), for GNU/Linux 2.6.9, stripped
$file ls
ls: ELF 32-bit MSB executable,PowerPC or cisco 4500, version 1 (SYSV), for GNU/Linux 2.6.34, dynamically linked (uses shared libs), for GNU/Linux 2.6.34, stripped
$file ls
ls: ELF 32-bit MSB executable,MIPS, MIPS32 rel2 version 1 (SYSV), for GNU/Linux 2.6.34, dynamically linked (uses shared libs), for GNU/Linux 2.6.34, stripped
摘一个uboot 的lds 看一下,
OUTPUT_FORMAT("elf32-littlearm", "elf32-littlearm", "elf32-littlearm")
OUTPUT_ARCH(arm)
ENTRY(_start)
SECTIONS
{
. = 0x00000000;
. = ALIGN(4);
.text :
{
cpu/arm1136/start.o (.text)
*(.text)
}
. = ALIGN(4);
.rodata : { *(.rodata) }
. = ALIGN(4);
.data : { *(.data) }
. = ALIGN(4);
.got : { *(.got) }
. = .;
__u_boot_cmd_start = .;
.u_boot_cmd : { *(.u_boot_cmd) }
__u_boot_cmd_end = .;
. = ALIGN(4);
__bss_start = .;
.bss : { *(.bss) }
_end = .;
}最终链接生成的elf 格式是 little ARM,表示就是小端模式,用linux file/readelf 命令也可以获取到一个可执行文件大小端信息。
举例说明存储方法:
对于四字节数据,0x12345678,
以小端模式存到0x80002000开始的存储单元中:
| 小端模式(Little Endian) | |
| 存储单元编号 | 存储单元 |
| 0x80002000 | 0x78 |
| 0x80002001 | 0x56 |
| 0x80002002 | 0x34 |
| 0x80002003 | 0x12 |
以大端模式存到0x80002000开始的存储单元中:
| 大端模式(Big Endian) | |
| 存储单元编号 | 存储单元 |
| 0x80002000 | 0x12 |
| 0x80002001 | 0x34 |
| 0x80002002 | 0x56 |
| 0x80002003 | 0x78 |
思考,如何使用C预压检查机器是大端模式还是小端模式呢?
/*
============================================================================
Name : endian_check.c
Author : qiang
Version :
Copyright : Your copyright notice
Description : Hello World in C, Ansi-style
============================================================================
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void) {
int x = 1;
if(*(char*) &x ==1) {
printf("Little-Endian. \n");
}
else {
printf("Big-Endian. \n");
}
puts("!!!Hello World!!!"); /* prints !!!Hello World!!! */
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
output:
Little-Endian.
!!!Hello World!!!
这段代码之所以能够判断出机器的打小端模式在于指针的类型,看下objdump 出来的汇编(ldrb):
000082f0 <main>:
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void) {
82f0: e92d4800 push {fp, lr}
82f4: e28db004 add fp, sp, #4
82f8: e24dd008 sub sp, sp, #8
int x = 1;
82fc: e3a03001 mov r3, #1
8300: e50b3008 str r3, [fp, #-8]
if(*(char*) &x ==1) {
8304: e24b3008 sub r3, fp, #8
8308: e5d33000 ldrb r3, [r3]
830c: e3530001 cmp r3, #1
8310: 1a000004 bne 8328 <main+0x38>
printf("Little-Endian. \n");
8314: e59f303c ldr r3, [pc, #60] ; 8358 <main+0x68>
8318: e08f3003 add r3, pc, r3
831c: e1a00003 mov r0, r3
8320: ebffffcb bl 8254 <puts@plt>
8324: ea000003 b 8338 <main+0x48>
}
else {
printf("Big-Endian. \n");
8328: e59f302c ldr r3, [pc, #44] ; 835c <main+0x6c>
832c: e08f3003 add r3, pc, r3
8330: e1a00003 mov r0, r3
8334: ebffffc6 bl 8254 <puts@plt>
}
从 AAPCS 文档上摘取的关于 little endian & big endian 的解释:
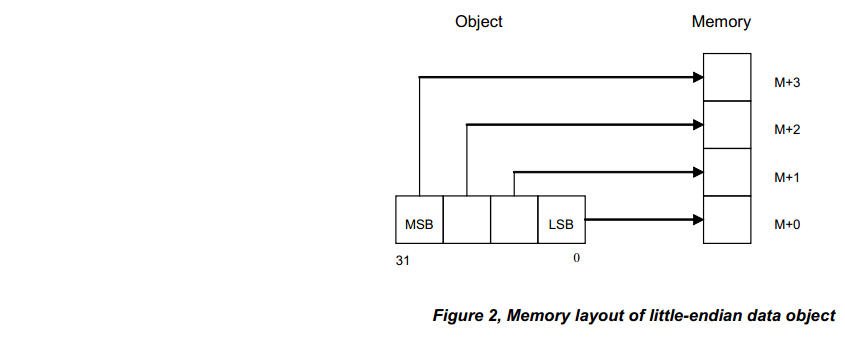
这篇博客写的也不错:http://blog.youkuaiyun.com/yasaken/article/details/7243757
Topic 2:AAPCS & ARM Core Register
AAPCS(Procedure Call Stand for ARM Architechture): ARM 架构下应用程序例程调用二进制接口规范。
学习AAPCS 最好的方法是在ARM官方网站,下载AAPCS的spec, PDF 名称为Procedure Call Standard for the ARM Architecture.pdf
下载网址:http://infocenter.arm.com/help/index.jsp
The ARM architecture defines a core instruction set plus a number of additional instructions implemented by co-processors.
The core instruction set can access the core registers and co-processors can provide additional registers whiche are available for specific operations.
There are 16,32-bit core(integer) registers visible to the ARM and Thumb instruction sets.
These are labeled r0-r15 or R0-R15. Register names may appear in assembly language in either upper case or lower case.
AAPCS 中16个通用寄存器的作用参考下面的截图:
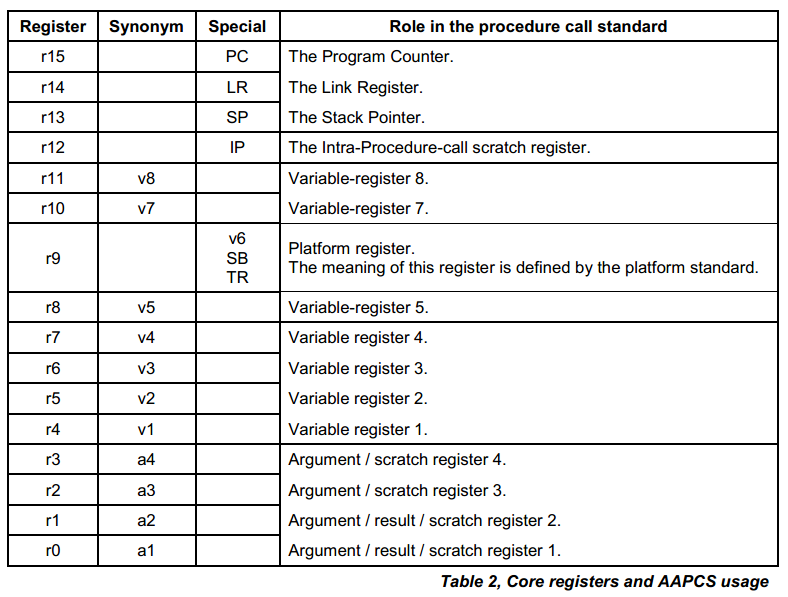
着重解释一下 R13,栈指针,压栈的过程和出栈在函数调用的过程中分量太重了:
Stack Point Register
- R13 indicates the stack point(address) of the current processor mode
- Each processor modes have its own SP(Stack Point)
§ARM state (32 bit Instruction)
- you can usually see the below assembly code at the entry of the function
STMDB R13!,{R0-R3,R14} // stores the link register(LR – R14) to return and
// general-purpose registers into the stack
- you can usually see the below assembly code at the end of the function
LDMIA R13!,{R0-R3,PC} // recovers the PC(Program Counter) using the LR
§Thumb state (16 bit Instruction)
- you can usually see the below assembly code at the entry of the function
PUSH {R0-R3,R14} // R13 is fixed for the stack
// stores the general-purpose registers and LR
- you can usually see the below assembly code at the end of the function
POP {R0-R3,PC} // recovers the PC using the LR
下面这张图展示了 ARM 各种工作模式共享哪些 寄存器,分别各自拥有哪些 寄存器。
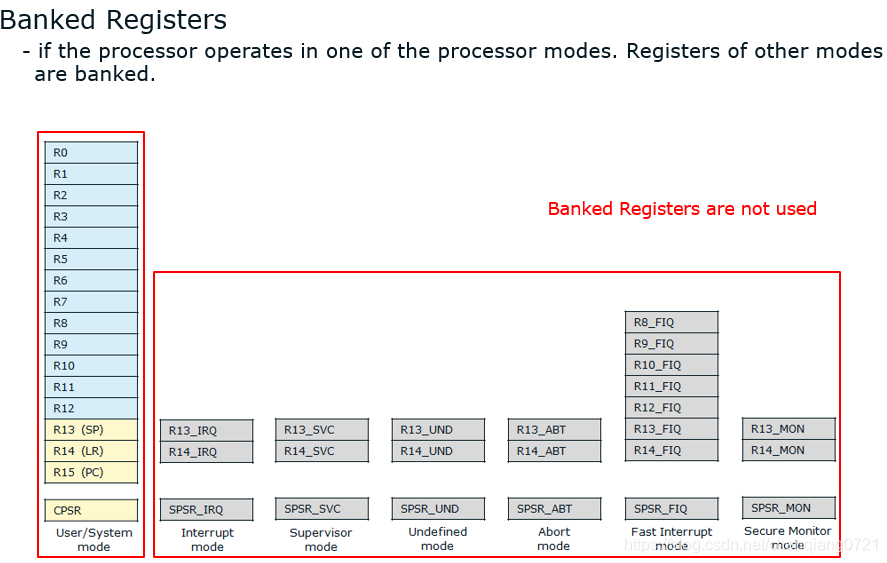
参考文章:
http://blog.claudxiao.net/2011/10/aapcs/
http://bbs.eeworld.com.cn/attachments/stm32/1300270808_0.pdf
Topic 3:ARM 工作模式
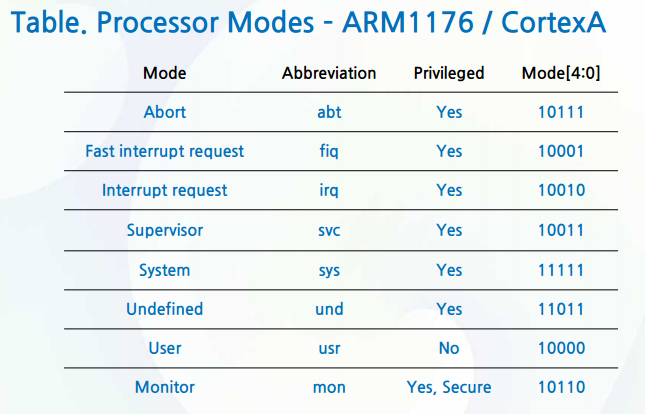
Processor Mode
- Processor mode determines which registers will be used and has the permission to access the CPSR.
- Processor modes are separated into Privileged mode and Unprivileged mode
Privileged mode
- can access all of the system resource(Memory, Coprocessor, CPSR .. Etc)
- can change the processor mode by modifying the control field(Bits[07:00]) of CPSR
- can enable/disable the interrupts by modifying I,F bits of CPSR
- All processor modes are in Privileged mode except User mode
Unprivileged mode
- there is limitation to access the system resource
- control filed of CPSR is read only(can not change the Processor mode)
- flags field and other fields can read or write
- can change the mode by Exception, Interrupt or SWI(SoftWare Interrupt) only
- User Mode is in Unprivileged mode only
•User mode
- normal program execution mode. It can not change the processor mode.
•FIQ mode
-The operating mode to handle fast interrupt requests
•IRQ mode
-The operating mode to handle normal interrupt requests
•Supervisor mode
-ARM switches its mode to SVC Mode when a reset or a software interrupt
(SWI) occurs
•Abort mode
-ARM switches to Abort Mode if an error occurs while reading from or writing to memory.
•Undefined mode
-ARM switches to Undefined Mode if the processor tries to execute an unrecognized instruction
•System mode
-The purpose for this mode is the same as the user mode, except that this mode is a privileged mode(can disable/enable the interrupts and change the processor mode)
•Secure Monitor mode
- This mode is a secure mode for TrustZone Secure Monitor code.
ARM1176 supports it.
Linux Kernel 内核态运行在 ARM Supervisor 工作模式,用户态运行在 user mode, 当调用 系统调用 API open/ write/iotcl 时,执行 SWI 软中断,ARM 工作模式从 user mode 切换成 supervisor mode。 需要注意的是 user mode 是非特权模式,不能打开关闭中断。而 supervisor mode 很明显可以打开关闭中断,因为 linux kernel 里面有一堆代码打开关闭中断。
当发生 data abort / prefetch abort 读写数据中断 / 取指令中断 的时候,ARM 会切换工作模式到 Abort mode。 (数据段 、代码段内存访问错误)
当 ARM 处理器发现要执行的指令无法识别的时候,会将工作模式切换成 Undefined mode
当发生 中断 irq / 快中断 fiq 时候, ARM 会将工作模式切换到 中断模式 / 快中断模式。
Topic 4:ARM Exception
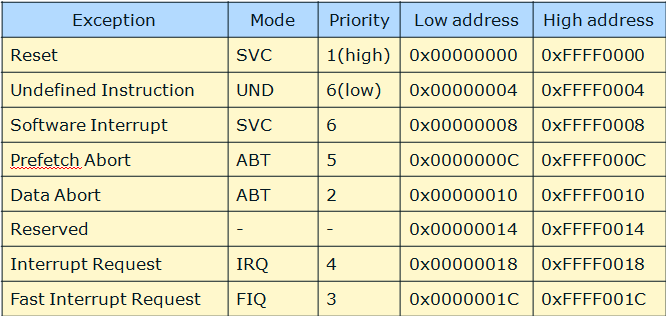
当发生 reset 异常 (power on reset)的时候, ARM 处理器会切换到 SVC 工作模式,同时将 PC 指向 0xFFFF0000 地址。





 本文深入探讨了ARM体系结构的关键概念,包括大小端模式的区别及其在不同处理器中的应用,AAPCS调用标准及ARM核心寄存器的作用,ARM的工作模式与异常处理机制等。
本文深入探讨了ARM体系结构的关键概念,包括大小端模式的区别及其在不同处理器中的应用,AAPCS调用标准及ARM核心寄存器的作用,ARM的工作模式与异常处理机制等。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








