文章目录
一、解析引擎
上一篇文章说了shardingsphere数据加密的整体流程,已经SQL的一生>整体数据加解密的流程
1.什么是SQL解析
SQL 是比较简单的。 不过,它依然是一门完善的编程语言,因此对 SQL 的语法进行解析,与解析其他编程语言(如:Java 语言、C 语言、Go 语言等)并无本质区别。
解析过程分为词法解析和语法解析。 词法解析器用于将 SQL 拆解为不可再分的原子符号,称为 Token。并根据不同数据库方言所提供的字典,将其归类为关键字,表达式,字面量和操作符。 再使用语法解析器将词法解析器的输出转换为抽象语法树。
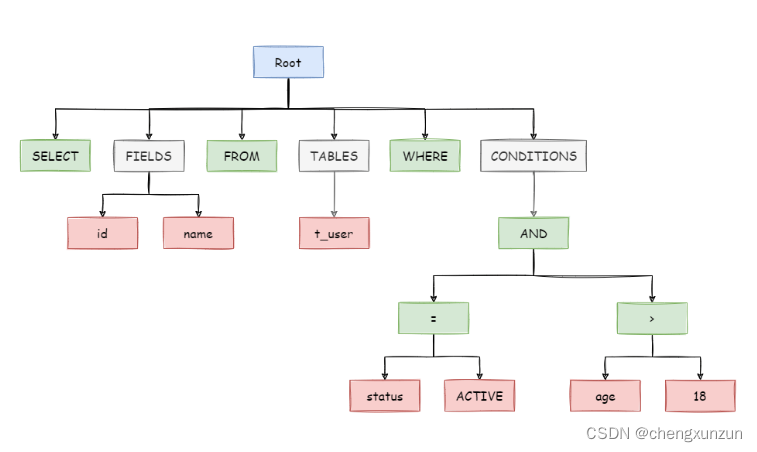
再shardingsphere官网中,有一个sql解析为语法树的例子:
SELECT id, name FROM t_user WHERE status = 'ACTIVE' AND age > 18
2.具体sql解析流程
由mysql编解码引擎来解码,MySQLPacketCodecEngine的decode方法
向启动的代理中发送一个sql,如SELECT * FROM tttttt1_copy1,如果想要捕捉请求的报文,可以在decode中,添加代码
必须转化为ascii码,咱们才可以看明白,二进制->十六进制->ascii码。这个报文的十六进制:
1E 00 00 00 03 53 45 4C 45 43 54 20 2A 20 46 52 4F 4D 20 60 74 74 74 74 74 74 31 5F 63 6F 70 79 31 60
转换为:ascii码:
SELECT * FROM tttttt1_copy1 ,53 对应的是S
public void decode(final ChannelHandlerContext context, final ByteBuf in, final List<Object> out) {
// 自己写的,将二进制01转为为16进制
System.out.println("ByteBuf readableBytes length: " + in.readableBytes());
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < in.readableBytes(); i++) {
sb.append(String.format("%02X ", in.getByte(i)));
}
System.out.println("sixteen ByteBuf hex: " + sb);
int payloadLength = in.markReaderIndex().readUnsignedMediumLE();
int remainPayloadLength = SEQUENCE_LENGTH + payloadLength;
if (in.readableBytes() < remainPayloadLength) {
in.resetReaderIndex();
return;
}
short sequenceId = in.readUnsignedByte();
context.channel().attr(MySQLConstants.MYSQL_SEQUENCE_ID).get<




 文章详细描述了Shardingsphere中的SQL解析过程,包括词法解析和语法解析,以及ANTLR在生成解析器中的应用。重点介绍了从MySQL编解码到CommandExecutor的具体步骤,展示了SQL解析如何转化为抽象语法树并执行。
文章详细描述了Shardingsphere中的SQL解析过程,包括词法解析和语法解析,以及ANTLR在生成解析器中的应用。重点介绍了从MySQL编解码到CommandExecutor的具体步骤,展示了SQL解析如何转化为抽象语法树并执行。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1613
1613










