打开Spring Cache的核心缓存拦截器CacheInterceptor,可以看到具体实现:
public class CacheInterceptor extends CacheAspectSupport implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
@Override
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Method method = invocation.getMethod();
CacheOperationInvoker aopAllianceInvoker = new CacheOperationInvoker() {
@Override
public Object invoke() {
try {
return invocation.proceed();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ThrowableWrapper(ex);
}
}
};
try {
return execute(aopAllianceInvoker, invocation.getThis(), method, invocation.getArguments());
}
catch (CacheOperationInvoker.ThrowableWrapper th) {
throw th.getOriginal();
}
}
}
CacheInterceptor默认实现了Spring aop的MethodInterceptor接口,MethodInterceptor的功能是做方法拦截。拦截的方法都会调用invoke方法,在invoke方法里面主要缓存逻辑是在execute方法里面,该方法是继承了父类CacheAspectSupport。
protected Object execute(CacheOperationInvoker invoker, Object target, Method method, Object[] args) {
// Check whether aspect is enabled (to cope with cases where the AJ is pulled in automatically)
if (this.initialized) {
Class<?> targetClass = getTargetClass(target);
//获取执行方法上所有的缓存操作集合。如果有缓存操作则执行到execute(...),如果没有就执行invoker.invoke()直接调用执行方法了
Collection<CacheOperation> operations = getCacheOperationSource().getCacheOperations(method, targetClass);
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(operations)) {
return execute(invoker, method, new CacheOperationContexts(operations, method, args, target, targetClass));
}
}
return invoker.invoke();
}
集合Collection operations中存放了所有的缓存操作CachePutOperation、CacheableOperation、CacheEvictOperation,我们知道spring cache常用的三种缓存操作:
- @CachePut – 执行方法后,将方法返回结果存放到缓存中。不管有没有缓存过,执行方法都会执行,并缓存返回结果(unless可以否决进行缓存)。(当然,这里说的缓存都要满足condition条件)
- @Cacheable – 如果没有缓存过,获取执行方法的返回结果;如果缓存过,则直接从缓存中获取,不再执行方法。
- @CacheEvict – 如果设置了beforeIntercepte则在方法执行前进行缓存删除操作,如果没有,则在执行方法调用完后进行缓存删除操作。
private Object execute(final CacheOperationInvoker invoker, Method method, CacheOperationContexts contexts) {
// Special handling of synchronized invocation
if (contexts.isSynchronized()) {
CacheOperationContext context = contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class).iterator().next();
if (isConditionPassing(context, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT)) {
Object key = generateKey(context, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT);
Cache cache = context.getCaches().iterator().next();
try {
return wrapCacheValue(method, cache.get(key, new Callable<Object>() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
return unwrapReturnValue(invokeOperation(invoker));
}
}));
}
catch (Cache.ValueRetrievalException ex) {
// The invoker wraps any Throwable in a ThrowableWrapper instance so we
// can just make sure that one bubbles up the stack.
throw (CacheOperationInvoker.ThrowableWrapper) ex.getCause();
}
}
else {
// No caching required, only call the underlying method
return invokeOperation(invoker);
}
}
// 处理beforeIntercepte=true的缓存删除操作
processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), true,
CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT);
// 从缓存中查找,是否有匹配@Cacheable的缓存数据
Cache.ValueWrapper cacheHit = findCachedItem(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class));
// 如果@Cacheable没有被缓存,那么就需要将数据缓存起来,这里将@Cacheable操作收集成CachePutRequest集合,以便后续做@CachePut缓存数据存放。
List<CachePutRequest> cachePutRequests = new LinkedList<CachePutRequest>();
if (cacheHit == null) {
collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class),
CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT, cachePutRequests);
}
Object cacheValue;
Object returnValue;
//如果没有@CachePut操作,就使用@Cacheable获取的结果(可能也没有@Cableable,所以result可能为空)。
if (cacheHit != null && cachePutRequests.isEmpty() && !hasCachePut(contexts)) {
//如果没有@CachePut操作,并且cacheHit不为空,说明命中缓存了,直接返回缓存结果
cacheValue = cacheHit.get();
returnValue = wrapCacheValue(method, cacheValue);
}
else {
// 否则执行具体方法内容,返回缓存的结果
returnValue = invokeOperation(invoker);
cacheValue = unwrapReturnValue(returnValue);
}
// Collect any explicit @CachePuts
collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CachePutOperation.class), cacheValue, cachePutRequests);
// Process any collected put requests, either from @CachePut or a @Cacheable miss
for (CachePutRequest cachePutRequest : cachePutRequests) {
cachePutRequest.apply(cacheValue);
}
// Process any late evictions
processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), false, cacheValue);
return returnValue;
}
//根据key从缓存中查找,返回的结果是ValueWrapper,它是返回结果的包装器
private Cache.ValueWrapper findCachedItem(Collection<CacheOperationContext> contexts) {
Object result = CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT;
for (CacheOperationContext context : contexts) {
if (isConditionPassing(context, result)) {
Object key = generateKey(context, result);
Cache.ValueWrapper cached = findInCaches(context, key);
if (cached != null) {
return cached;
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No cache entry for key '" + key + "' in cache(s) " + context.getCacheNames());
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
private Cache.ValueWrapper findInCaches(CacheOperationContext context, Object key) {
for (Cache cache : context.getCaches()) {
Cache.ValueWrapper wrapper = doGet(cache, key);
if (wrapper != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Cache entry for key '" + key + "' found in cache '" + cache.getName() + "'");
}
return wrapper;
}
}
return null;
}
具体整个流程是这样的:
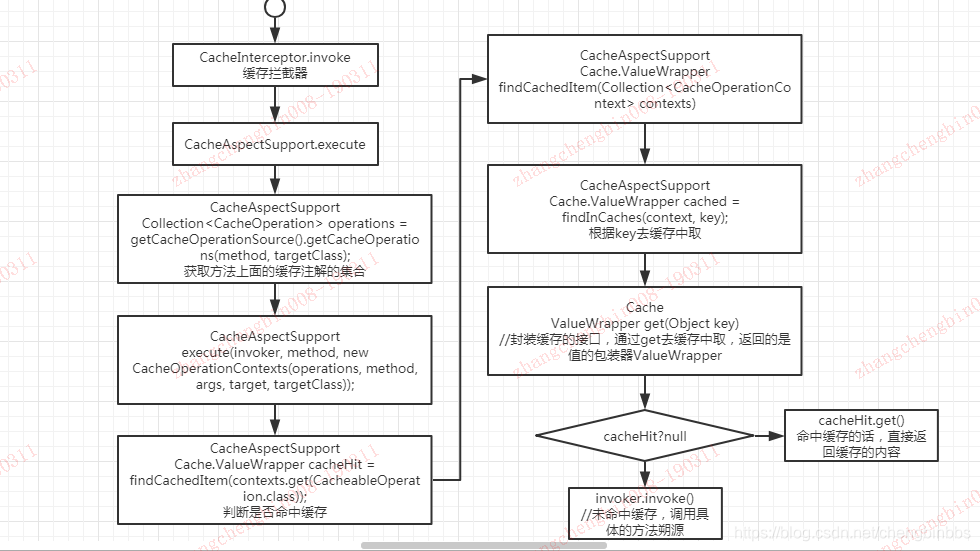
参考:https://my.oschina.net/xiaoqiyiye/blog/1624344
 Spring Cache 深入理解 CacheInterceptor
Spring Cache 深入理解 CacheInterceptor





 本文探讨了Spring Cache的核心组件CacheInterceptor,它作为MethodInterceptor实现方法拦截。主要逻辑集中在execute方法中,处理CachePutOperation、CacheableOperation、CacheEvictOperation等缓存操作。@CachePut在满足条件的情况下更新缓存,@Cacheable根据缓存情况决定是否执行方法,@CacheEvict可在方法前后删除缓存。
本文探讨了Spring Cache的核心组件CacheInterceptor,它作为MethodInterceptor实现方法拦截。主要逻辑集中在execute方法中,处理CachePutOperation、CacheableOperation、CacheEvictOperation等缓存操作。@CachePut在满足条件的情况下更新缓存,@Cacheable根据缓存情况决定是否执行方法,@CacheEvict可在方法前后删除缓存。
















 784
784

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








