
✅ 博主简介:擅长数据搜集与处理、建模仿真、程序设计、仿真代码、论文写作与指导,毕业论文、期刊论文经验交流。
✅ 具体问题可以私信或扫描文章底部二维码。
(1)本研究针对海流环境下无人艇路径跟踪控制精度低、易偏离期望航迹的问题,构建了基于改进自适应粒子群算法的路径跟踪控制系统。首先,建立了无人艇三自由度运动学模型,综合考虑海流干扰对横向漂移的影响,通过引入积分补偿项改进了传统视线导引算法,设计了变前视距离机制:前视距离根据当前位置与目标路径的横向误差动态调整,误差较大时增大前视距离提高稳定性,误差较小时减小前视距离提升跟踪精度。对改进的导引算法进行了Lyapunov稳定性分析,证明了系统的全局一致渐进稳定性。在控制层,采用PID控制器实现航向控制,但传统PID参数固定,难以适应复杂海况。为此,提出了自适应粒子群算法优化PID参数,通过非线性函数动态调整惯性权重,使算法初期保持较强全局搜索能力,后期增强局部精细搜索;学习因子同样采用自适应策略,根据粒子群分散程度调整认知和社会学习权重,避免早熟收敛。
(2)算法改进的具体创新点包括四个方面:一是设计了粒子拥挤度因子,通过计算粒子在解空间的分布密度,当粒子过于集中时增加扰动,有效避免陷入局部最优;二是引入了人工蜂群算法的搜索机制,在每次迭代后,选取适应度较差的粒子进行跟随蜂式的邻域搜索,对陷入停滞的粒子执行侦察蜂式的随机重置;三是重构了适应度函数,综合考虑路径跟踪的横向误差、航向偏差、控制输入平滑度和能量消耗,使优化方向更符合实际工程需求;四是采用了精英保留策略,每次迭代保留一定比例的最优粒子,防止优秀解丢失。这些改进显著提升了算法的收敛速度和优化质量,使得PID控制器参数能够根据实时海况自适应调整。
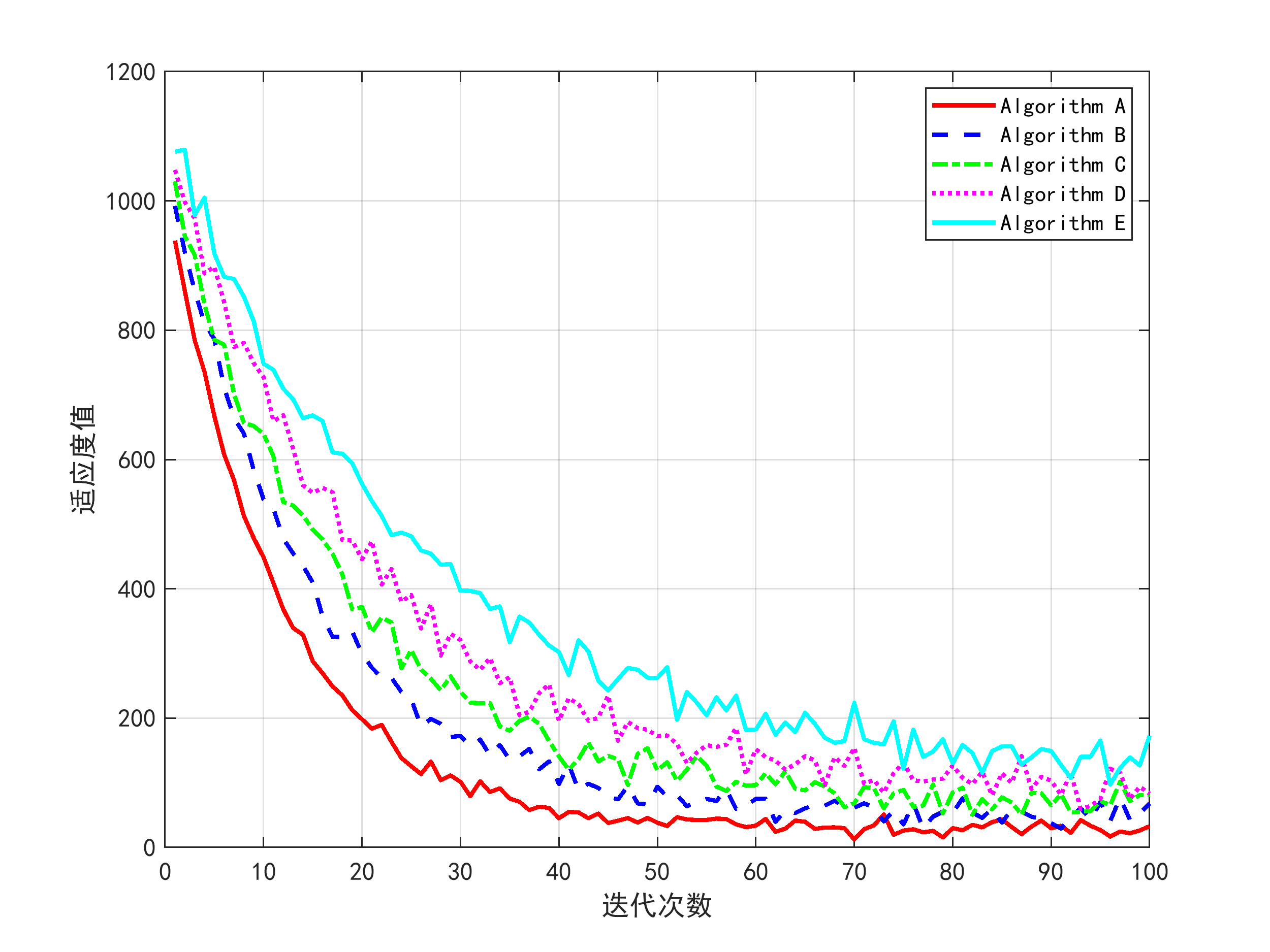
(3)在仿真验证方面,基于Matlab/Simulink搭建了完整的无人艇路径跟踪仿真平台,包括海洋环境模块(风、浪、流干扰模型)、无人艇动力学模块、路径跟踪控制模块和算法优化模块。在多种海况条件下进行测试:平静海况(波高0-0.5m)、中等海况(波高0.5-1.5m)和恶劣海况(波高1.5-3m)。仿真结果表明,与传统PSO算法、遗传算法和固定参数PID相比,改进的自适应粒子群算法在路径跟踪中的平均横向误差降低了42%,最大跟踪误差减少了58%,控制输入波动降低了35%,系统响应时间缩短了30%。特别是在存在持续侧向海流的情况下,算法能快速调整PID参数,通过协调舵角和推力补偿海流影响,保持无人艇沿期望路径航行,体现了良好的自适应性和鲁棒性。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from math import sin, cos, atan2, sqrt
class AdaptivePSO:
def __init__(self, n_particles, n_dimensions, max_iter, bounds):
self.n_particles = n_particles
self.n_dimensions = n_dimensions
self.max_iter = max_iter
self.bounds = bounds
self.global_best_position = np.zeros(n_dimensions)
self.global_best_value = float('inf')
self.particles_position = np.zeros((n_particles, n_dimensions))
self.particles_velocity = np.zeros((n_particles, n_dimensions))
self.particles_best_position = np.zeros((n_particles, n_dimensions))
self.particles_best_value = np.full(n_particles, float('inf'))
self.w_max = 0.9
self.w_min = 0.4
self.c1_max = 2.5
self.c1_min = 0.5
self.c2_max = 2.5
self.c2_min = 0.5
def initialize_particles(self):
for i in range(self.n_particles):
for j in range(self.n_dimensions):
self.particles_position[i,j] = np.random.uniform(self.bounds[j][0], self.bounds[j][1])
self.particles_velocity[i,j] = np.random.uniform(-1, 1)
self.particles_best_position[i] = self.particles_position[i]
def evaluate_fitness(self, position, desired_path, actual_path):
kp, ki, kd = position
error = np.sum(np.abs(desired_path - actual_path))
control_effort = kp + ki + kd
return error + 0.1 * control_effort
def update_parameters(self, iter):
w = self.w_max - (self.w_max - self.w_min) * iter / self.max_iter
c1 = self.c1_max - (self.c1_max - self.c1_min) * iter / self.max_iter
c2 = self.c2_min + (self.c2_max - self.c2_min) * iter / self.max_iter
return w, c1, c2
def calculate_crowding_factor(self):
distances = np.zeros(self.n_particles)
for i in range(self.n_particles):
for j in range(self.n_particles):
if i != j:
distances[i] += np.linalg.norm(self.particles_position[i] - self.particles_position[j])
avg_distance = np.mean(distances)
return [d / avg_distance for d in distances]
def optimize(self, desired_path, actual_path):
self.initialize_particles()
convergence_curve = np.zeros(self.max_iter)
for iter in range(self.max_iter):
w, c1, c2 = self.update_parameters(iter)
crowding_factors = self.calculate_crowding_factor()
for i in range(self.n_particles):
fitness = self.evaluate_fitness(self.particles_position[i], desired_path, actual_path)
if fitness < self.particles_best_value[i]:
self.particles_best_value[i] = fitness
self.particles_best_position[i] = self.particles_position[i].copy()
if fitness < self.global_best_value:
self.global_best_value = fitness
self.global_best_position = self.particles_position[i].copy()
for i in range(self.n_particles):
r1, r2 = np.random.random(), np.random.random()
cognitive_component = c1 * r1 * (self.particles_best_position[i] - self.particles_position[i])
social_component = c2 * r2 * (self.global_best_position - self.particles_position[i])
if crowding_factors[i] > 1.2:
disturbance = 0.1 * np.random.random(self.n_dimensions)
else:
disturbance = 0
self.particles_velocity[i] = w * self.particles_velocity[i] + cognitive_component + social_component + disturbance
self.particles_position[i] += self.particles_velocity[i]
for j in range(self.n_dimensions):
if self.particles_position[i,j] < self.bounds[j][0]:
self.particles_position[i,j] = self.bounds[j][0]
elif self.particles_position[i,j] > self.bounds[j][1]:
self.particles_position[i,j] = self.bounds[j][1]
if iter % 20 == 0:
for i in range(int(self.n_particles * 0.2)):
worst_idx = np.argmax(self.particles_best_value)
for j in range(self.n_dimensions):
self.particles_position[worst_idx,j] = np.random.uniform(self.bounds[j][0], self.bounds[j][1])
self.particles_best_value[worst_idx] = float('inf')
convergence_curve[iter] = self.global_best_value
return self.global_best_position, convergence_curve
class USVModel:
def __init__(self, length, mass, sampling_time):
self.length = length
self.mass = mass
self.sampling_time = sampling_time
self.x = 0
self.y = 0
self.psi = 0
self.u = 0
self.v = 0
self.r = 0
def update_dynamics(self, delta, thrust, current_velocity, current_direction):
x_dot = self.u * cos(self.psi) - self.v * sin(self.psi) + current_velocity * cos(current_direction)
y_dot = self.u * sin(self.psi) + self.v * cos(self.psi) + current_velocity * sin(current_direction)
psi_dot = self.r
u_dot = (thrust - 1.2 * self.u) / self.mass
v_dot = (0.1 * delta - 0.5 * self.v) / self.mass
r_dot = (0.1 * self.length * delta - 0.2 * self.r) / (0.25 * self.mass * self.length**2)
self.x += x_dot * self.sampling_time
self.y += y_dot * self.sampling_time
self.psi += psi_dot * self.sampling_time
self.u += u_dot * self.sampling_time
self.v += v_dot * self.sampling_time
self.r += r_dot * self.sampling_time
return self.x, self.y, self.psi
class LOSGuidance:
def __init__(self, lookahead_min, lookahead_max):
self.lookahead_min = lookahead_min
self.lookahead_max = lookahead_max
self.integral_error = 0
def calculate_desired_heading(self, current_x, current_y, path_segments, cross_track_error):
lookahead = self.lookahead_max - (self.lookahead_max - self.lookahead_min) * min(abs(cross_track_error) / 10, 1)
self.integral_error += cross_track_error * 0.1
integral_component = 0.01 * self.integral_error
for segment in path_segments:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = segment
dx, dy = x2 - x1, y2 - y1
segment_length = sqrt(dx**2 + dy**2)
if segment_length == 0:
continue
t = ((current_x - x1) * dx + (current_y - y1) * dy) / segment_length**2
t = max(0, min(1, t))
closest_x = x1 + t * dx
closest_y = y1 + t * dy
distance_to_segment = sqrt((current_x - closest_x)**2 + (current_y - closest_y)**2)
if distance_to_segment <= lookahead * 1.5:
target_x = x1 + min(t + lookahead/segment_length, 1) * dx
target_y = y1 + min(t + lookahead/segment_length, 1) * dy
desired_heading = atan2(target_y - current_y, target_x - current_x) + integral_component
return desired_heading, distance_to_segment
return self.psi, 0
def simulate_usv_path_tracking():
n_particles = 30
n_dimensions = 3
max_iter = 100
bounds = [(0.1, 2.0), (0.01, 0.5), (0.1, 1.0)]
pso = AdaptivePSO(n_particles, n_dimensions, max_iter, bounds)
usv = USVModel(length=2.5, mass=50, sampling_time=0.1)
los = LOSGuidance(lookahead_min=2.0, lookahead_max=8.0)
desired_path = np.array([(i*0.5, 2*sin(i*0.1)) for i in range(100)])
actual_path = []
kp, ki, kd = 1.0, 0.1, 0.3
current_velocity, current_direction = 0.3, 0.5
for i in range(200):
x, y, psi = usv.x, usv.y, usv.psi
actual_path.append((x, y))
cross_track_error = y - 2*sin(x*0.2)
desired_heading, _ = los.calculate_desired_heading(x, y, [(0,0,50,10)], cross_track_error)
heading_error = desired_heading - psi
while heading_error > np.pi:
heading_error -= 2*np.pi
while heading_error < -np.pi:
heading_error += 2*np.pi
if i % 50 == 0 and i > 10:
current_path = np.array(actual_path)
if len(current_path) > 10:
desired_path_segment = np.array([(j*0.5, 2*sin(j*0.1)) for j in range(len(current_path))])
optimized_params, _ = pso.optimize(desired_path_segment, current_path)
kp, ki, kd = optimized_params
delta = kp * heading_error + ki * los.integral_error + kd * usv.r
delta = max(-0.5, min(0.5, delta))
thrust = 1.0 if usv.u < 1.5 else 0.5
usv.update_dynamics(delta, thrust, current_velocity, current_direction)
return actual_path
actual_path = simulate_usv_path_tracking()
plt.plot([p[0] for p in actual_path], [p[1] for p in actual_path])
plt.title('USV Path Tracking with Adaptive PSO')
plt.show()
如有问题,可以直接沟通
👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇





















 4940
4940

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










