instanceof 和 isInstance
一、instanceof 关键字
instanceof :
java的一个二元运算符,也是一个关键字
判断左边对象是否是右边类本身或者子类
A instanceof B:
A为对象实例(A只能为引用数据类型),B为类名@Data
@SuperBuilder
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Test<T> {
}
public interface TestInterface {
}
@Data
@SuperBuilder
@AllArgsConstructor
public class MyTest extends Test<Character> implements TestInterface{
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyTest myTest = MyTest.builder().build();
System.out.println(myTest instanceof MyTest);//true
System.out.println(myTest instanceof Test);//true
System.out.println(myTest instanceof TestInterface);//true
System.out.println("hello world" instanceof String);//true
System.out.println("hello world" instanceof Object);//true
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
System.out.println(list instanceof ArrayList);//true
System.out.println(list instanceof Object);//true
System.out.println(null instanceof Object);//false
System.out.println(null instanceof String);//false
System.out.println(null instanceof MyTest);//false
}
}
注意左边只能为引用数据类型,否则会报错:
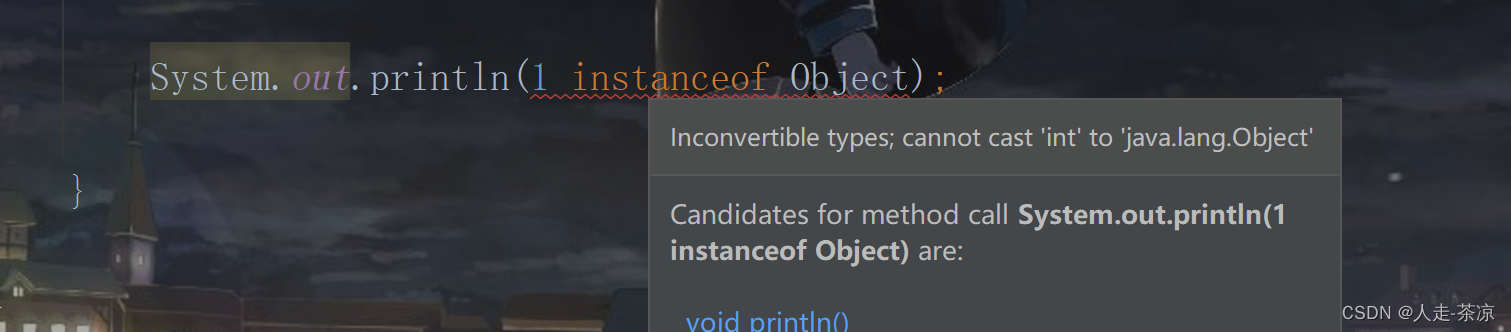
向上转型(多态):
子类对象可以向上转为父类对象,接口实现类对象可以向上转为接口对象。
null instanceof 都为false:
因为引用类型的默认值都为null,所以null可以转换成为任何类型,不属于任何类型
二、isInstance()方法
MyTest.class.isInstance(myTest)
注意自动拆装箱是在JDK1.5以后引入的
MyTest myTest = MyTest.builder().build();
//不推荐通过子类调用isInstance(),可能需要强转
System.out.println(MyTest.class.isInstance(myTest));//true
System.out.println(MyTest.class.isInstance(Test.builder().build()));//false
System.out.println(MyTest.class.isInstance((TestInterface)myTest));//true
System.out.println(MyTest.class.isInstance(new Object()));//false
//推荐把父类写在前面,即父类调用方法
System.out.println(TestInterface.class.isInstance(myTest));//true
System.out.println(Test.class.isInstance(myTest));//true
System.out.println(Object.class.isInstance(myTest));//true
System.out.println(Object.class.isInstance(new Object()));//true
System.out.println(Test.class.isInstance(new Object()));//false
List<Object> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
System.out.println(List.class.isInstance(arrayList));//true
System.out.println(List.class.isInstance(new Object()));//false
System.out.println(List.class.isInstance(new LinkedList<>()));//true
//参数可以是基本类型 自动做了装箱操做
System.out.println(Integer.class.isInstance(1));//true
System.out.println(Integer.class.isInstance(1.1));//false
System.out.println(Double.class.isInstance(1.6));//true
System.out.println(Double.class.isInstance(1));//false





 本文详细介绍了Java中的instanceof关键字用于判断对象是否为指定类或其子类,以及isInstance()方法的使用场景,包括对象类型检查、多态和基本类型转换。
本文详细介绍了Java中的instanceof关键字用于判断对象是否为指定类或其子类,以及isInstance()方法的使用场景,包括对象类型检查、多态和基本类型转换。
















 887
887










