我对于流的理解是这样的,计算机的本质本来就是对输入的数据进行操作,然后将结果输出的一种工具,数据在各个数据源节点之间进行流动,感觉流就是对这种状态的一种抽象,一个数据流表示的就是一系列数据序列,java存在现成的类库可以实现数据的主动获取和处理,这些操作数据的类库构成了java的I/O体系。
流根据不同的方面可以分成不同的类型,根据流向可分为输入流和输出流;根据操作的数据单元不同可分为字节流(8bit)和字符流(16bit,Unicode编码)。
在这里将流分成字节流和字符流来对java中相应的处理类做一下分类,I/O一般用于对在文件和网络之间流动的数据做处理,以处理以文件为载体的数据作为实例。
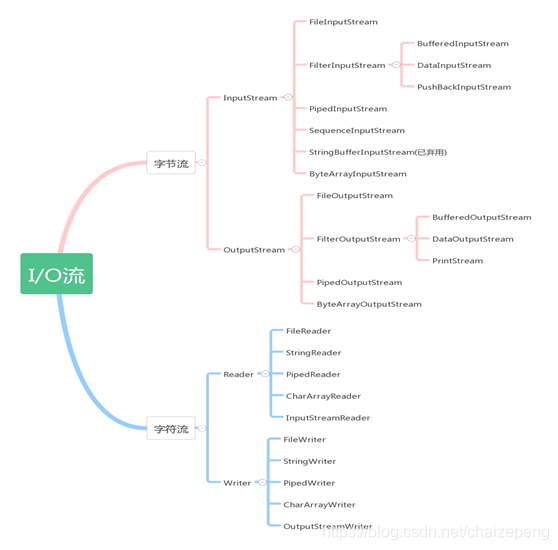
介绍一下常用到的流,先说一下字节流,处理字节流的两个顶级抽象父类是处理输入流的InputStream和处理输出流的OutputStream。当处理文件时,可以使用他们的子类 FileInputStream 和 FileOutputStream,代码如下:
public class StreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StreamTest test = new StreamTest();
// test.testFileInputStream();
// test.testFileOutputStream();
test.testCopyFile();
}
/**
* 使用输入流读取文件中的信息,然后打印
* @author chaizepeng
*
*/
public void testFileInputStream() {
InputStream inputStream = null;
File file = new File("E:\\test\\input.txt");
try {
inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);//将文件中的数据读入到输入流中
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
inputStream.read(b);//从输入流中读取1024个字节
String s = new String(b, "utf-8");
System.out.println(s);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//使用流操作非常耗资源,所以在使用完之后要及时关闭
if (inputStream != null) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 使用输出流写出数据到文件中
* @author chaizepeng
*
*/
public void testFileOutputStream() {
File file = new File("E:\\test\\output.txt");
OutputStream outputStream = null;
try {
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);//将数据流指向指定的文件
String s = "hello world";
byte[] bytes = s.getBytes("utf-8");
outputStream.write(bytes);//将字节数组中的数据写入到输出流指向的文件中
outputStream.flush();//刷新输出流,保证数据写入成功
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//使用流操作非常耗资源,所以在使用完之后要及时关闭
if (outputStream != null) {
try {
outputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 将 E:\\test\\input.txt 复制到 E:\\test\\copy.txt
* @author chaizepeng
*
*/
public void testCopyFile() {
InputStream inputStream = null;
OutputStream outputStream = null;
File file = new File("E:\\test\\copy.txt");
if (!file.exists()) {
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
inputStream = new FileInputStream("E:\\test\\input.txt");//将文件中的数据读入到输入流中
//想往文件中追加信息时,使用另一个构造器即可:new FileOutputStream(file,true)
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);//将输出流对准一个文件
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = inputStream.read(b,0,b.length)) != -1) {//每次读取1024个字节
outputStream.write(b,0,len);//将读取到的字节序列写入到输出流对应的文件中,知道输入流在文件中获取到的数据列长度为0
}
outputStream.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//使用流操作非常耗资源,所以在使用完之后要及时关闭
try {
if (outputStream != null) {
outputStream.close();
}
if (inputStream != null) {
inputStream.close();
}
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
想将数据从内存中读出并写入到另一块内存中时可以使用子类 ByteArrayInputStream 和 ByteArrayOutputStream ,代码如下:
public class ByteArrayStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteArrayStreamTest test = new ByteArrayStreamTest();
test.testByteArrayStream();
}
/**
* 用于在内存中输入和输出,不必依赖磁盘,也就是不用创建File类
* 因为处理的是内存中的数据,所以也不是非要关闭资源不可
*/
public void testByteArrayStream() {
//ByteArrayInputStream 用于从内存中(不是在磁盘上)读入数据并创建一个输入流对象
byte []b = "hello world".getBytes();
ByteArrayInputStream inputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(b);
ByteArrayOutputStream outputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream(1024);
byte []temp = new byte[4];//创建一个临时的数组,用于转移数据
int len = 0;
while ((len = inputStream.read(temp,0,temp.length) ) != -1) {
outputStream.write(temp,0,len);//将内存中
}
System.out.println(outputStream.toString());//在输出流中获取写入到指定内存的数据
}
}
说一下字符流,例如:当处理一些中文文件时,使用字节流如果遇到突发事件可能会因为编码问题导致文件损坏,处理一些中文文件时可以选择字符流(处理文本文件时都可使用,为了不必要的麻烦,最好使用字节流),处理一些非文本文件时必须使用字节流。字符流的两个顶级接口是Reader和Writer,如果处理文件时可以使用FileReader和FileWriter,代码如下:
public class CharStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CharStreamTest test = new CharStreamTest();
test.testReaderTest();
}
/**
* 将E:\\test\\reader.txt 复制到 E:\\test\\writer.txt
*
*/
public void testReaderTest() {
FileWriter writer = null;
FileReader reader = null;
File file = new File("E:\\test\\writer.txt");
if (!file.exists()) {
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
reader = new FileReader("E:\\test\\reader.txt");
writer = new FileWriter(file);
char []b = new char[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = reader.read(b, 0, b.length)) != -1) {
writer.write(b, 0, len);
}
writer.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//使用流操作非常耗资源,所以在使用完之后要及时关闭
try {
if (writer != null) {
writer.close();
}
if (reader != null) {
reader.close();
}
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
为了提高读入和写出的效率,java提供了缓冲流,使用缓冲流就相当于在内存中直接获取数据,而不需要频繁的去调用外部方法操作磁盘,大大提高了效率,缓冲流中维护了一个内存数组,每次读取数据时都在数组中获取,通过一定的机制当数组中没有数据或者数据已经读取完时就会调用一次应用的c或c++的方法操作一次磁盘,提高了效率。源码分析如下:
//通过源码来解释为什么缓冲流效率高
//首先看一下不使用缓冲流
//FileInputStream中的read方法,全都是最后调用native修饰的c或者c++的方法
//也就是说当使用FileInputStream去读取数据时,每读取一次,都会去磁盘中获取一次数据
//每次都去访问磁盘导致效率底
public int read() throws IOException {
return read0();
}
private native int read0() throws IOException;
private native int readBytes(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException;
public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException {
return readBytes(b, 0, b.length);
}
public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
return readBytes(b, off, len);
}
//BufferedInputStream中的read方法,
//创建缓冲流对象时,维护了一个数组,
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size) {
buf = new byte[size];
}
//调用的read方法
public synchronized int read(byte b[], int off, int len){
//删减一些代码,read中会调用read1方法
int nread = read1(b, off + n, len - n);
//在内存数组中获取数据,而不是去磁盘中获取,这也就是网上一直所说的不再是读一次获取一次,而是一次性读取多个放到内存中,大大节省了效率
System.arraycopy(getBufIfOpen(), pos, b, off, cnt);
}
//调用的read1方法
private int read1(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException {
//删减一些代码,read1中会调用InputStream中的read方法
getInIfOpen().read(b, off, len);
}
//调用的read1方法getInIfOpen
private InputStream getInIfOpen() throws IOException {
//而返回的正好是构造缓冲流时传入的字节流in,所以说到底,最后直接去磁盘获取数据的还是应用的c/c++的代码,只不过一次获取固定大小长度的字节数据放到缓冲流类中维护的内存数组中
InputStream input = in;
if (input == null)
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
return input;
}
针对字节流提供了BufferedInputStream 和 BufferedOutputStream 两个缓冲流,用法如下:
public class BufferStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferStreamTest test = new BufferStreamTest();
test.testInputBufferedStream();
}
public void testInputBufferedStream() {
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = null;
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = null;
File file = new File("E:\\test\\bufferedoutput.ppt");
try {
bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:\\czp\\Learning Materials\\笔记\\io.ppt"));
bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = bufferedInputStream.read(b ,0 ,b.length)) != -1) {
bufferedOutputStream.write(b, 0, len);
}
bufferedOutputStream.flush();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if (bufferedOutputStream!=null) {
bufferedOutputStream.close();
}
if (bufferedInputStream!=null) {
bufferedInputStream.close();
}
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
针对字符流提供了BufferedReader 和 BufferedWriter ,用法如下:
public class BufferStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferStreamTest test = new BufferStreamTest();
test.testBufferCharStream();
}
public void testBufferCharStream() {
BufferedReader bufferedReader = null;
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = null;
File file = new File("E:\\test\\bufferedreader.txt");
try {
FileReader reader = new FileReader("E:\\czp\\Learning Materials\\ceshi.txt");
//BufferedReader 的数据源是一个字符输入流
bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(reader);
bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));
String s = "";
while( (s = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {//每次读取一行数据
System.out.println(s);
bufferedWriter.write(s);
bufferedWriter.newLine();//换行
bufferedWriter.flush();//刷新缓冲区
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//关闭资源
try {
if (bufferedWriter!=null) {
bufferedWriter.close();
}
if (bufferedReader!=null) {
bufferedReader.close();
}
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
有的时候想用字符流进行数据的读写,但是呢,提供的只有数据的字节流,这时便可使用转换流,代码如下:
public class ConvertStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ConvertStreamTest test = new ConvertStreamTest();
test.testInputStreamReader();
test.testOutputStreamWriter();
}
/**
* 字节输入流转换成字符输入流
*/
public void testInputStreamReader() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;//字节输入流
Reader inputStreamReader = null;//字符输入流
try {
//获取一个字节输入流
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("E:\\czp\\Learning Materials\\ceshi.txt");
//通过转换输入流 InputStreamReader 的构造方法构造一个字符输入流
inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(fileInputStream,"utf-8");
char []ch = new char[2048];
inputStreamReader.read(ch);//正常的在流中读取数据
System.out.println(new String(ch));
} catch (Exception e) {
}finally {
if (inputStreamReader!=null) {
inputStreamReader.close();
}
if (fileInputStream!= null) {
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
}
/**
* 字节输出流转换成字符输出流
*/
public void testOutputStreamWriter() throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
Writer writer = null;
try {
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("E:\\test\\bufferedreader.txt");
writer = new OutputStreamWriter(fileOutputStream, "gbk");
writer.write("测试转换流");
} catch (Exception e) {
}finally {
if (writer != null) {
writer.close();
}
if (fileOutputStream!=null) {
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
}
}
使用java也可实现文件的压缩和解压缩,使用到的两个类是:GZIPInputStream、GZIPOutputStream,他们是util包下的类,不是io包下。代码如下:
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.zip.GZIPInputStream;
import java.util.zip.GZIPOutputStream;
public class GZIPStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
GZIPStreamTest test = new GZIPStreamTest();
test.testZipStream();
test.testUnZipStream();
}
/**
* 压缩操作
* 将E:\\czp\\Learning Materials\\ceshi.txt 压缩到 E:\\test\\a.zip
*/
public void testZipStream() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
GZIPOutputStream gzipOutputStream = null;
File file = new File("E:\\test\\a.zip");
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("E:\\czp\\Learning Materials\\ceshi.txt");
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
gzipOutputStream = new GZIPOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
byte []by = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = fileInputStream.read(by, 0, by.length)) != -1) {
gzipOutputStream.write(by, 0, len);
gzipOutputStream.flush();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}finally {
if (gzipOutputStream != null) {
gzipOutputStream.close();
}
if (fileOutputStream != null) {
fileOutputStream.close();
}
if (fileInputStream != null) {
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
}
/**
* 解压操作
*/
public void testUnZipStream() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
GZIPInputStream gzipInputStream = null;
File file = new File("E:\\test\\b.txt");
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("E:\\test\\a.zip");
gzipInputStream = new GZIPInputStream(fileInputStream);
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
byte []by = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = gzipInputStream.read(by, 0, by.length)) != -1) {
fileOutputStream.write(by, 0, len);
fileOutputStream.flush();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}finally {
if (fileOutputStream != null) {
fileOutputStream.close();
}
if (gzipInputStream != null) {
gzipInputStream.close();
}
if (fileInputStream != null) {
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
}
}
以上只是对java中I/O体系中常用的几个类做了简单的介绍,真正用的时候可以参考API。






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








