INSERTION-SORT
We start with insertion sort, which is an efficient algorithm for sorting a small
number of elements. Insertion sort works the way many people sort a hand of
playing cards. We start with an empty left hand and the cards face down on the
table. We then remove one card at a time from the table and insert it into the
correct position in the left hand. To find the correct position for a card, we compare
it with each of the cards already in the hand, from right to left, as illustrated in
Figure 2.1. At all times, the cards held in the left hand are sorted, and these cards
were originally the top cards of the pile on the table.



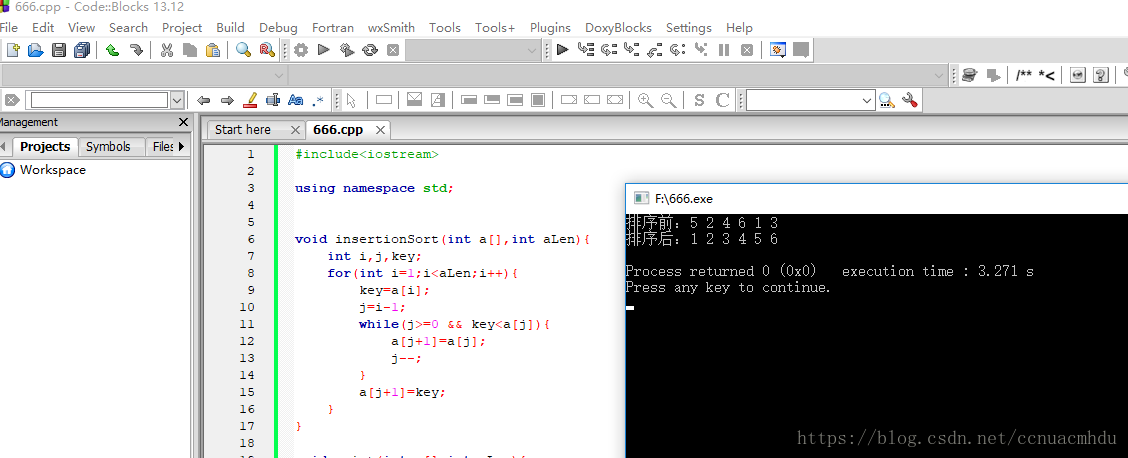
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void insertionSort(int a[],int aLen){
int i,j,key;
for(int i=1;i<aLen;i++){
key=a[i];
j=i-1;
while(j>=0 && key<a[j]){
a[j+1]=a[j];
j--;
}
a[j+1]=key;
}
}
void print(int a[],int aLen){
for(int i=0;i<aLen;i++){
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
int a[6]={5,2,4,6,1,3};
cout<<"排序前:";
print(a,6);
cout<<"排序后:";
insertionSort(a,6);
print(a,6);
return 0;
}
The divide-and-conquer approach—— merge sort
The divide-and-conquer paradigm involves three steps at each level of the recur-
sion:
Divide the problem into a number of subproblems that are smaller instances of the same problem.
Conquer the subproblems by solving them recursively. If the subproblem sizes are small enough, however, just solve the subproblems in a straightforward manner.
Combine the solutions to the subproblems into the solution for the original problem.
merge-sort
The merge sort algorithm closely follows the divide-and-conquer paradigm. In-
tuitively, it operates as follows.
Divide: Divide the n-element sequence to be sorted into two subsequences of n/2 elements each.
Conquer: Sort the two subsequences recursively using merge sort.
Combine: Merge the two sorted subsequences to produce the sorted answer.
The recursion “bottoms out” when the sequence to be sorted has length 1, in which
case there is no work to be done, since every sequence of length 1 is already in
sorted order.
Returning to our card-playing motif, suppose we have two piles of cards face up on a table. Each pile is sorted, with the smallest cards on top. We wish to merge the two piles into a single sorted output pile, which is to be face down on the table. Our basic step consists of choosing the smaller of the two cards on top of the face-up piles, removing it from its pile (which exposes a new top card), and placing this card face down onto the output pile. We repeat this step until one input pile is empty, at which time we just take the remaining input pile and place it face down onto the output pile.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//把数组st到mid部分(包含mid)和mid(不包含mid)到en部分进行合并
void merge(int a[],int st,int mid,int en){
int n1=mid-st+1;
int n2=en-mid;
int *l=new int[n1];
int *r=new int[n2];
for(int i=0;i<n1;i++){
l[i]=a[st+i];
}
for(int i=0;i<n2;i++){
r[i]=a[mid+1+i];
}
int j1=0,j2=0,k=st;
while(j1<n1 && j2<n2 && k<=en){
if(l[j1]<r[j2]){
a[k++]=l[j1++];
}
else{
a[k++]=r[j2++];
}
}
while(j1<n1){
a[k++]=l[j1++];
}
while(j2<n2){
a[k++]=r[j2++];
}
}
void merge_sort(int a[],int st,int en){
if(st<en){
int mid=(st+en)/2;
merge_sort(a,st,mid);
merge_sort(a,mid+1,en);
merge(a,st,mid,en);
}
}
void print(int a[],int aLen){
for(int i=0;i<aLen;i++){
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
int a[6]={5,2,4,6,1,3};
cout<<"Before sorting: ";
print(a,6);
cout<<"After merge-sorting: ";
merge_sort(a,0,6-1);
print(a,6);
return 0;
}





 本文介绍了两种经典的排序算法:插入排序和归并排序。插入排序适用于小规模数据集,通过将每个元素插入到已排序序列中的正确位置来实现排序。归并排序采用分治策略,递归地将序列分为两半,再将两个有序子序列合并为一个有序序列。文章还提供了这两种排序算法的C++实现。
本文介绍了两种经典的排序算法:插入排序和归并排序。插入排序适用于小规模数据集,通过将每个元素插入到已排序序列中的正确位置来实现排序。归并排序采用分治策略,递归地将序列分为两半,再将两个有序子序列合并为一个有序序列。文章还提供了这两种排序算法的C++实现。
















 178
178

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








