常用类
- Object类/Scanner类
- String类/StringBuffer类/StringBuilder类
- 数组高级和Arrays类
- 基本类型包装类(Integer,Character)
- 正则表达式(Pattern,Matcher)
- Math类/Random类/System类
- BigInteger类/BigDecimal类
- Date类/DateFormat类/Calendar类
Object类概述及其构造方法
Object类概述
类层次结构的根类
所有类都直接或者间接的继承自该类构造方法
public Object()
回想面向对象中为什么说:
子类的构造方法默认访问的是父类的无参构造方法
Object类的成员方法
public int hashCode()
public final Class getClass()
public String toString()
public boolean equals(Object obj)
protected void finalize()
protected Object clone()
public int hashCode()
A:返回该对象的哈希码值。默认情况下,该方法会根据对象的地址来计算。
B:不同对象的,hashCode()一般来说不会相同。
但是,同一个对象的hashCode()值肯定相同。
C:不是对象的实际地址值,可以理解为逻辑地址值。
举例:物体和编号。
public final Class getClass()
A:返回此 Object 的运行时类。
B:可以通过Class类中的一个方法,获取对象的真实类的全名称。
public String getName()
public String toString()
A:返回该对象的字符串表示。
底层源码。
public static String valueOf(Object obj) {
return (obj == null) ? "null" : obj.toString();
}
B:它的值等于:
getClass().getName() + '@' + Integer.toHexString(hashCode())
C:由于默认情况下的数据对我们来说没有意义,一般建议重写该方法。
a:手动重写
b:自动生成
public boolean equals(Object obj)
A:指示其他某个对象是否与此对象“相等”。
B:默认情况下比较的是对象的引用是否相同。
C:由于比较对象的引用没有意义,一般建议重写该方法。
a:手动重写
b:自动生成
D:==和equals()的区别。(面试题)
protected void finalize()
A:当垃圾回收器确定不存在对该对象的更多引用时,由对象的垃圾回收器调用此方法。
B:垃圾回收器不会马上回收垃圾,但是我们可以建议它尽快回收垃圾。(System.gc()方法)
C:主要针对堆内存。
protected Object clone()
创建并返回此对象的一个副本,这种克隆机制十分高效,而且二者之间完全隔离。
自定义类实现克隆步骤:
A:自定义类实现Cloneable接口,这是一个标记性接口,实现这个接口的类的对象可以实现自我克隆。
B:自定义类中重写Object类的clone()方法。
C:重写clone()方法时通过super.clone()调用Object类的clone()方法来得到该对象的副本,并返回该副本。
注意:
A:克隆和两个引用指向同一个对象的区别?
B:Object类clone()方法虽然简单,易用,但仅仅是一种”浅克隆”,它只克隆该对象所有的Field值,不会
对引用类型的Field所引用的对象进行克隆。开发中,我们也可以实现对象的”深度克隆”。
Scanner类概述及其构造方法
Scanner类概述
JDK5以后用于获取用户的键盘输入
构造方法
public Scanner(InputStream source)
Scanner类的成员方法
基本格式
hasNextXxx() 判断是否还有下一个输入项,其中Xxx可以是Int,Double等。如果需要判断是否包含下一个字符串,则可以省略Xxx
nextXxx() 获取下一个输入项。Xxx的含义和上个方法中的Xxx相同
默认情况下,Scanner使用空格,回车等作为分隔符常用方法
public int nextInt()
public String nextLine()
String类概述及其构造方法
String类概述
字符串是由多个字符组成的一串数据(字符序列)
字符串可以看成是字符数组构造方法
public String()
public String(byte[] bytes)
public String(byte[] bytes,int offset,int length)
public String(char[] value)
public String(char[] value,int offset,int count)
public String(String original)
在实际开发中,字符串的操作是最常见的操作,没有之一。
而Java没有内置的字符串类型,所以,就在Java类库中提供了一个类String 供我们来使用。
String 类代表字符串。Java 程序中的所有字符串字面值(如 “abc” )都作为此类的实例实现。
注意:
String s = “helloworld”;
s也是一个对象。
String类的特点及面试题
- 字符串是常量,它的值在创建之后不能更改
看程序写结果
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(s1==s2);
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
String s3 = new String("hello");
String s4 = "hello";
System.out.println(s3==s4);
System.out.println(s3.equals(s4));
String s5 = "hello";
String s6 = "hello";
System.out.println(s5==s6);
System.out.println(s5.equals(s6));

String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "world";
String s3 = "helloworld";
System.out.println(s3==s1+s2);
System.out.println(s3.equals(s1+s2));

String类的判断功能
boolean equals(Object obj)
boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str)
boolean contains(String str)
boolean startsWith(String str)
boolean endsWith(String str)
boolean isEmpty()
String类的获取功能
int length()
char charAt(int index)
int indexOf(int ch)
int indexOf(String str)
int indexOf(int ch,int fromIndex)
int indexOf(String str,int fromIndex)
String substring(int start)
String substring(int start,int end)
String类的转换功能
byte[] getBytes()
char[] toCharArray()
static String valueOf(char[] chs)
static String valueOf(int i)
String toLowerCase()
String toUpperCase()
String concat(String str)
String类的其他功能
替换功能
String replace(char old,char new)
String replace(String old,String new)去除字符串两空格
String trim()
按字典顺序比较两个字符串
int compareTo(String str)
int compareToIgnoreCase(String str)
StringBuffer类概述及其构造方法
StringBuffer类概述
我们如果对字符串进行拼接操作,每次拼接,都会构建一个新的String对象,既耗时,又浪费空间。而StringBuffer就可以解决这个问题
线程安全的可变字符序列
StringBuffer和String的区别?
构造方法
public StringBuffer()
public StringBuffer(int capacity)
public StringBuffer(String str)
StringBuffer类的成员方法
添加功能
public StringBuffer append(String str)
public StringBuffer insert(int offset,String str)删除功能
public StringBuffer deleteCharAt(int index)
public StringBuffer delete(int start,int end)替换功能
public StringBuffer replace(int start,int end,String str)
反转功能 public StringBuffer reverse()
截取功能
public String substring(int start)
public String substring(int start,int end)截取功能和前面几个功能的不同
返回值类型是String类型,本身没有发生改变
String,StringBuffer,StringBuilder的区别
1.首先说运行速度,或者说是执行速度,在这方面运行速度快慢为:StringBuilder > StringBuffer > String
String最慢的原因:
String为字符串常量,而StringBuilder和StringBuffer均为字符串变量,即String对象一旦创建之后该对象是不可更改的,但后两者的对象是变量,是可以更改的。
2. 再来说线程安全
在线程安全上,StringBuilder是线程不安全的,而StringBuffer是线程安全的
3. 总结一下
String:适用于少量的字符串操作的情况
StringBuilder:适用于单线程下在字符缓冲区进行大量操作的情况
StringBuffer:适用多线程下在字符缓冲区进行大量操作的情况
Arrays类概述及其常用方法
Arrays类概述
针对数组进行操作的工具类。
提供了排序,查找等功能。成员方法
public static String toString(int[] a)
public static void sort(int[] a)
public static int binarySearch(int[] a,int key)
基本类型包装类概述
将基
- 本数据类型封装成对象的好处在于可以在对象中定义更多的功能方法操作该数据。
- 常用的操作之一:用于基本数据类型与字符串之间的转换。
基本类型和包装类的对应
Byte,Short,Integer,Long,Float,Double
Character,Boolean
Integer类概述及其构造方法
Integer类概述
Integer 类在对象中包装了一个基本类型 int 的值
该类提供了多个方法,能在 int 类型和 String 类型之间互相转换,还提供了处理 int 类型时非常有用的其他一些常量和方法构造方法
public Integer(int value)
public Integer(String s)
Integer类成员方法
int类型和String类型的相互转换
int – String
String – intpublic int intValue()
public static int parseInt(String s)
public static String toString(int i)
public static Integer valueOf(int i)
public static Integer valueOf(String s)
常用的基本进制转换
public static String toBinaryString(int i)
public static String toOctalString(int i)
public static String toHexString(int i)十进制到其他进制
public static String toString(int i,int radix)
其他进制到十进制
public static int parseInt(String s,int radix)
JDK5的新特性
JDK1.5以后,简化了定义方式。
Integer x = new Integer(4);可以直接写成 Integer x = 4;//自动装箱。 x = x + 5;//自动拆箱。通过intValue方法。需要注意:
在使用时,Integer x = null;上面的代码就会出现NullPointerException。

Integer的面试题
Integer i1 = new Integer(127);
Integer i2 = new Integer(127);
System.out.println(i1 == i2);//false
System.out.println(i1.equals(i2));//true
Integer i3 = new Integer(128);
Integer i4 = new Integer(128);
System.out.println(i3 == i4);//false
System.out.println(i3.equals(i4));//true
Integer i5 = 127;
Integer i6 = 127;
System.out.println(i5 == i6);//true
System.out.println(i5.equals(i6));//true
Integer.valueOf(127);
Integer i7 = 128;
Integer i8 = 128;
System.out.println(i7 == i8);//false
System.out.println(i7.equals(i8));//true
使用等号赋值是JDK5的特性,相当于Integer.valueOf(x)。
在java中,Integer具有一个-128至127的缓冲池,在这个区间内赋值,不创建新的对象,而是直接在缓冲池中取值。故(i5==i6)为真。
若是使用new Integer(x),则是在堆内存中创建新的对象,故(i1==i2)为假。
Character类概述及其构造方法
Character类概述
Character 类在对象中包装一个基本类型 char 的值
此外,该类提供了几种方法,以确定字符的类别(小写字母,数字,等等),并将字符从大写转换成小写,反之亦然构造方法
public Character(char value)
Character类成员方法
public static boolean isUpperCase(char ch)
public static boolean isLowerCase(char ch)
public static boolean isDigit(char ch)
public static char toUpperCase(char ch)
public static char toLowerCase(char ch)
正则表达式概述及基本使用
- 正则表达式:是指一个用来描述或者匹配一系列符合某个句法规则的字符串的单个字符串。其实就是一种规则。有自己特殊的应用。
- 举例:校验qq号码.
1:要求必须是5-15位数字
2:0不能开头
正则表达式的组成规则
- 规则字符在java.util.regex Pattern类中
常见组成规则
字符
字符类
预定义字符类
边界匹配器
数量词
正则表达式的应用
判断功能
public boolean matches(String regex)
分割功能
public String[] split(String regex)
替换功能
public String replaceAll(String regex,String replacement)
获取功能
Pattern和Matcher类的使用
Math类概述及其成员方法
Math类概述
Math 类包含用于执行基本数学运算的方法,如初等指数、对数、平方根和三角函数。
成员方法
public static int abs(int a)
public static double ceil(double a)
public static double floor(double a)
public static int max(int a,int b) min自学
public static double pow(double a,double b)
public static double random()
public static int round(float a) 参数为double的自学
public static double sqrt(double a)
Random类概述及其构造方法
Random类概述
此类用于产生随机数
如果用相同的种子创建两个 Random 实例,则对每个实例进行相同的方法调用序列,它们将生成并返回相同的数字序列。构造方法
public Random()
public Random(long seed)
Random类成员方法
public int nextInt()
public int nextInt(int n)
System类概述及其成员方法
System类概述
System 类包含一些有用的类字段和方法。它不能被实例化。
成员方法
public static void gc()
public static void exit(int status)
public static long currentTimeMillis()
public static void arraycopy(Object src,int srcPos,Object dest,int destPos,int length)
System.gc()可用于垃圾回收。当使用System.gc()回收某个对象所占用的内存之前,通过要求程序调用适当的方法来清理资源。在没有明确指定资源清理的情况下,Java提高了默认机制来清理该对象的资源,就是调用Object类的finalize()方法。finalize()方法的作用是释放一个对象占用的内存空间时,会被JVM调用。而子类重写该方法,就可以清理对象占用的资源,该方法有没有链式调用,所以必须手动实现。
从程序的运行结果可以发现,执行System.gc()前,系统会自动调用finalize()方法清除对象占有的资源,通过super.finalize()方式可以实现从下到上的finalize()方法的调用,即先释放自己的资源,再去释放父类的资源。
但是,不要在程序中频繁的调用垃圾回收,因为每一次执行垃圾回收,jvm都会强制启动垃圾回收器运行,这会耗费更多的系统资源,会与正常的Java程序运行争抢资源,只有在执行大量的对象的释放,才调用垃圾回收最好
BigInteger类概述及其构造方法
BigInteger类概述
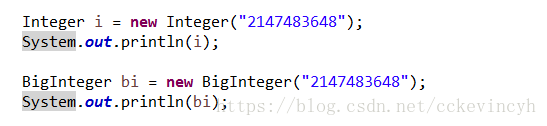
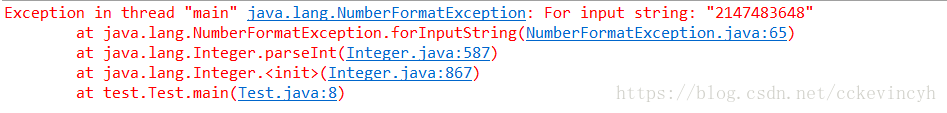
可以让超过Integer范围内的数据进行运算
构造方法
public BigInteger(String val)
BigInteger类成员方法
public BigInteger add(BigInteger val)
public BigInteger subtract(BigInteger val)
public BigInteger multiply(BigInteger val)
public BigInteger divide(BigInteger val)
public BigInteger[] divideAndRemainder(BigInteger val)
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigInteger bi1 = new BigInteger("100");
BigInteger bi2 = new BigInteger("50");
System.out.println(bi1.add(bi2));
System.out.println(bi1.subtract(bi2));
System.out.println(bi1.multiply(bi2));
System.out.println(bi1.divide(bi2));
BigInteger[] b = bi1.divideAndRemainder(bi2);
System.out.println(b[0]);
System.out.println(b[1]);
}
BigDecimal类概述及其构造方法
问题的引出:在运算的过程中,float类型和double类型容易引起精度的丢失
System.out.println(0.09 + 0.01);
System.out.println(1.0 - 0.32);
System.out.println(1.015 * 100);
System.out.println(1.301 / 100);
- 由于在运算的时候,float类型和double很容易丢失精度。所以,为了能精确的表示、计算浮点数,Java提供了BigDecimal
BigDecimal类概述
不可变的、任意精度的有符号十进制数。
构造方法
public BigDecimal(String val)
BigDecimal类成员方法
public BigDecimal add(BigDecimal augend)
public BigDecimal subtract(BigDecimal subtrahend)
public BigDecimal multiply(BigDecimal multiplicand)
public BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal divisor)
public BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal divisor,int scale,int roundingMode)
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal bd1 = new BigDecimal("0.09");
BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal("0.01");
System.out.println(bd1.add(bd2));
BigDecimal bd3 = new BigDecimal("1.0");
BigDecimal bd4 = new BigDecimal("0.32");
System.out.println(bd3.subtract(bd4));
BigDecimal bd5 = new BigDecimal("1.015");
BigDecimal bd6 = new BigDecimal("100");
System.out.println(bd5.multiply(bd6));
BigDecimal bd7 = new BigDecimal("1.301");
BigDecimal bd8 = new BigDecimal("100");
System.out.println(bd7.divide(bd8));
System.out.println(bd7.divide(bd8, 2,BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP));
}
Date类概述及其方法
Date类概述
类 Date 表示特定的瞬间,精确到毫秒。
构造方法
public Date()
public Date(long date)成员方法
public long getTime()
public void setTime(long time)
DateFormat类概述及其方法
DateFormat类概述
DateFormat 是日期/时间格式化子类的抽象类,它以与语言无关的方式格式化并解析日期或时间。
是抽象类,所以使用其子类SimpleDateFormatSimpleDateFormat构造方法
public SimpleDateFormat()
public SimpleDateFormat(String pattern)成员方法
public final String format(Date date)
public Date parse(String source)
Calendar类概述及其方法
Calendar类概述
Calendar 类是一个抽象类,它为特定瞬间与一组诸如 YEAR、MONTH、DAY_OF_MONTH、HOUR 等 日历字段之间的转换提供了一些方法,并为操作日历字段(例如获得下星期的日期)提供了一些方法。
成员方法
public static Calendar getInstance()
public int get(int field)
public void add(int field,int amount)
public final void set(int year,int month,int date)





 本文深入讲解Java中的核心类,包括Object、String、Scanner等的基础使用与高级特性,探讨类层次结构、字符串操作、输入处理等内容。
本文深入讲解Java中的核心类,包括Object、String、Scanner等的基础使用与高级特性,探讨类层次结构、字符串操作、输入处理等内容。
















 1228
1228

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








