目录
声明部分图片来自百战程序员
Spring简介
Spring是一个开源框架,为简化企业级开发而生。
它以IOC(控制反转)和AOP(面向切面)为思想内核,提供了控制层SpringMVC、数据层SpringData、服务层事务管理等众多技术,并可以整合众多第三方框架。
Spring将很多复杂的代码变得优雅简洁,有效的降低代码的耦合度,极大的方便项目的后期维护、升级和扩展。
Spring官网地址: Spring | HomeLevel up your Java code and explore what Spring can do for you.https://spring.io/
Spring结构

Spring框架根据不同的功能被划分成了多个模块,这些模块可以满足一切企业级应用开发的需求,在开发过程中可以根据需求有选择性地使用所需要的模块。
- Core Container:Spring核心模块,任何功能的使用都离不开该模块,是其他模块建立的基础。
- Data Access/Integration:该模块提供了数据持久化的相应功能。
- Web:该模块提供了web开发的相应功能。
- AOP:提供了面向切面编程实现
- Aspects:提供与AspectJ框架的集成,该框架是一个面向切面编程框架。
- Instrumentation:提供了类工具的支持和类加载器的实现,可以在特定的应用服务器中使用。
- Messaging:为Spring框架集成一些基础的报文传送应用
- Test:提供与测试框架的集成
SpringIOC思想
IOC(Inversion of Control) :程序将创建对象的权利交给框架。
之前在开发过程中,对象实例的创建是由调用者管理的
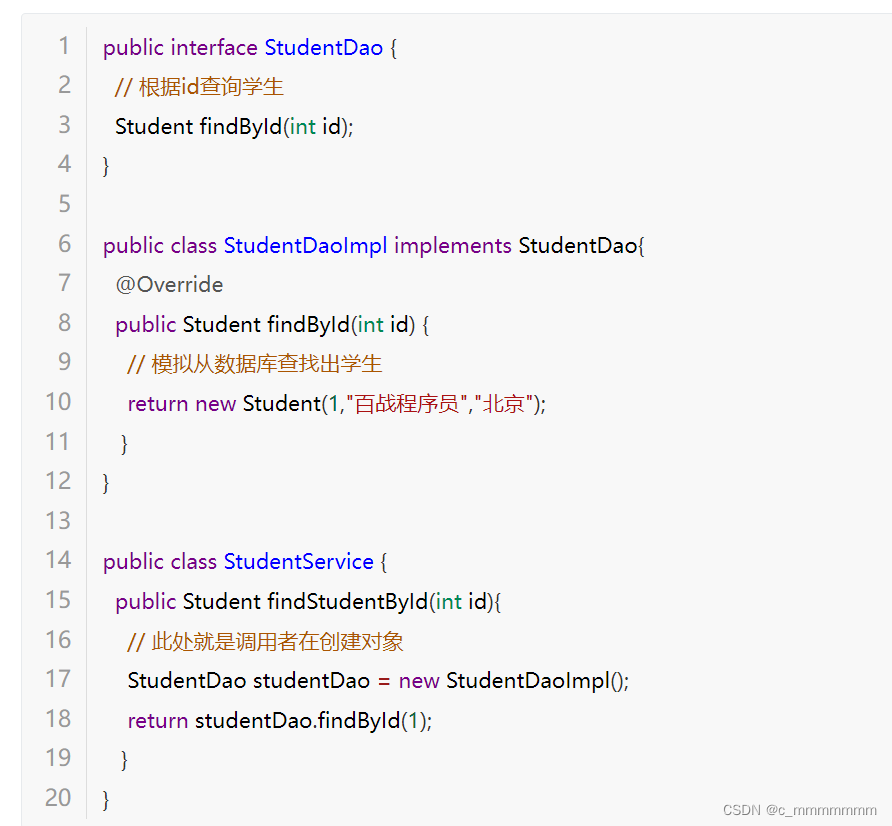
这种写法有两个缺点:
1、浪费资源:
StudentService调用方法时即会创建一个对象,如果不断调用方法则会创建大量StudentDao对象。
2、代码耦合度高:
假设随着开发,我们创建了StudentDao另一个更加完善的实现类StudentDaoImpl2,如果在StudentService中想使用StudentDaoImpl2,则必须修改源码。
而IOC思想是将创建对象的权利交给框架,框架会帮助我们创建对象,分配对象的使用,控制权由程序代码转移到了框架中,控制权发生了反转,这就是Spring的IOC思想。而IOC思想可以完美的解决以上两个问题。
Spring实现IOC
1、创建Maven工程,引入依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.13</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>2、创建POJO类、Dao类和接口
3、编写bean.xml配置文件,配置文件中配置需要Spring帮我们创建的对象。
(id属性就是获取对象的key,class代表获取哪个对象)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl"></bean>
</beans>测试从Spring容器中获取对象。
public class TestContainer{
@Test
public void t1(){
// 创建Spring容器
Application Contextac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
// 从容器获取对象
StudentDaostudent Dao1=(StudentDao) ac.getBean("studentDao");
StudentDaostudent Dao2=(StudentDao) ac.getBean("studentDao");
System.out.println(studentDao1.hashCode());
System.out.println(studentDao2.hashCode());
System.out.println(studentDao1.findById(1));
}
}Spring容器类型

容器接口
- BeanFactory:BeanFactory是Spring容器中的顶层接口,它可以对Bean对象进行管理。
- ApplicationContext:ApplicationContext是BeanFactory的子接口。它除了继承 BeanFactory的所有功能外,还添加了对国际化、资源访问、事件传播等方面的良好支持。
ApplicationContext有以下三个常用实现类:

容器实现类
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:该类可以从项目中读取配置文件
- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:该类从磁盘中读取配置文件
- AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:使用该类不读取配置文件,而是会读取注解
bean对象的创建方式
1、默认根据POJO类的无参构造方法创建
<!--使用构造方法创建bean-->
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl"></bean>
2、如果POJO类没有无参构造,那么就需要使用工厂类创建(普通方法)
<!--使用工厂类的方法创建bean-->
<bean id="studentDaoFactory" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoFactory"></bean>
<bean id="studentDao" factory-bean="studentDaoFactory" factory-method="getStudentDao"></bean>
3、使用工厂类的静态方法创建
<!--使用工厂的的静态方法创建bean-->
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoFactory2" factory-method="getStudentDao"></bean>
对象的创建策略
Spring通过配置<bean>中的scope属性设置对象的创建策略,共有五种创建策略:
- singleton:单例,默认策略。
整个项目只会创建一个对象,通过<bean>中的lazy-init属性可以设置单例对象的创建时机:
lazy-init="false"(默认):立即创建,在容器启动时会创建配置文件中的所有Bean对象。
lazy-init="true":延迟创建,第一次使用Bean对象时才会创建。
配置单例策略:
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl2" scope="singleton"
lazy-init="false"></bean>prototype:多例,每次从容器中获取时都会创建对象。
<!-- 配置多例策略 -->
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl2" scope="prototype"></bean>
- request:每次请求创建一个对象,只在web环境有效。
- session:每次会话创建一个对象,只在web环境有效。
- gloabal-session:一次集群环境的会话创建一个对象,只在web环境有效。
对象的销毁方式
对象的创建策略不同,销毁时机也不同:
- singleton:对象随着容器的销毁而销毁。
- prototype:使用JAVA垃圾回收机制销毁对象。
- request:当处理请求结束,bean实例将被销毁。
- session:当HTTP Session最终被废弃的时候,bean也会被销毁掉。
- gloabal-session:集群环境下的session销毁,bean实例也将被销毁。
生命周期方法
bean对象的生命周期包含
创建——使用——销毁
,Spring可以配置Bean对象在创建和销毁时自动执行的方法:

配置生命周期方法
<!-- init-method:创建对象时执行的方法 destroy-method:销毁对象时执行的方法 -->
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl2" scope="singleton"
init-method="init" destroy-method="destory"></bean>获取Bean对象的方式
1、通过id/name获取
配置文件
<bean name="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl2"></bean>
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl2"></bean>
获取对象
StudentDao studentDao=(StudentDao) ac.getBean("studentDao");
2、通过类型获取
配置文件
<bean name="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl2"></bean>
获取对象
StudentDao studentDao2=ac.getBean(StudentDao.class);
可以看到使用类型获取不需要强转。
3、通过类型+id/name获取
虽然使用类型获取不需要强转,但如果在容器中有一个接口的多个实现类对象,则获取时会报错,此时需要使用类型+id/name获取
配置文件
<bean name="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl2"></bean>
<beann ame="studentDao1" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl"></bean>
获取对象
StudentDao studentDao2 = ac.getBean("studentDao",StudentDao.class);




















 4万+
4万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








